Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(1):121-128
Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, commonly known as “morning sickness,” affects approximately 80 percent of pregnant women. Although several theories have been proposed, the exact cause remains unclear. Recent research has implicated Helicobacter pylori as one possible cause. Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy is generally a mild, self-limited condition that may be controlled with conservative measures. A small percentage of pregnant women have a more profound course, with the most severe form being hyperemesis gravidarum. Unlike morning sickness, hyperemesis gravidarum may have negative implications for maternal and fetal health. Physicians should carefully evaluate patients with nonresolving or worsening symptoms to rule out the most common pregnancy-related and nonpregnancy-related causes of severe vomiting. Once pathologic causes have been ruled out, treatment is individualized. Initial treatment should be conservative and should involve dietary changes, emotional support, and perhaps alternative therapy such as ginger or acupressure. Women with more complicated nausea and vomiting of pregnancy also may need pharmacologic therapy. Several medications, including pyridoxine and doxylamine, have been shown to be safe and effective treatments. Pregnant women who have severe vomiting may require hospitalization, orally or intravenously administered corticosteroid therapy, and total parenteral nutrition.
Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy begins between the fourth and seventh week after the last menstrual period in 80 percent of pregnant women and resolves by the 20th week of gestation in all but 10 percent of these women.1 The condition has been shown to be more common in urban women than in rural women.2 One study3 identified increased risk in housewives and decreased risk in “white collar” or professional white women who consumed alcohol before conception, and in women over 35 years of age with a history of infertility.
Hyperemesis gravidarum, a severe form of nausea and vomiting, affects one in 200 pregnant women.4 Although the definition of this condition has not been standardized, accepted clinical features include persistent vomiting, dehydration, ketosis, electrolyte disturbances, and weight loss (more than 5 percent of body weight). Multiple gestation, gestational trophoblastic disease, triploidy, trisomy 21 syndrome (Down syndrome), and hydrops fetalis have been associated with an increased incidence of hyperemesis gravidarum.5
Etiology and Pathophysiology
The etiology of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy remains unknown, but a number of possible causes have been investigated.
Although many physicians were taught that psychologic factors are responsible for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy and hyperemesis gravidarum, few data support this theory. In one well-known study,4 the Cornell Medical Index was administered to 44 pregnant women with hyperemesis and 49 pregnant women without hyperemesis; the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) was administered only to the pregnant women with hyperemesis. The MMPI data suggested that women with hyperemesis have hysteria, excessive dependence on their mothers, and infantile personalities. However, the study findings were not conclusive because comparative testing was not performed.
Gastrointestinal tract dysfunction also has been suggested as a cause of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. In one study6 in which progesterone was prescribed to nonpregnant women, resultant nausea and vomiting suggested that delayed gastric motility caused by progesterone may be responsible for the condition. Another study7 reviewed many potential gastrointestinal causes of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, including abnormalities of gastric electrical rhythm (gastric dysrhythmias).
Many reports have suggested that hormones may cause nausea and vomiting of pregnancy and hyperemesis gravidarum. In one comparative study,8 women with nausea and vomiting of pregnancy were found to have elevated levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG); however, another study9 did not support this finding. Some studies have shown elevated estrogen levels in women with this condition; others have not.7 Hence, the roles of hCG and estrogen remain controversial. Many pregnant women with hyperemesis have suppressed thyrotropin-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. Work is ongoing to elucidate the interaction of hCG and TSH in pregnant women with hyperemesis.5
A recent study10 suggested that chronic infection with Helicobacter pylori may play a role in hyperemesis gravidarum. In this study, 61.8 percent of pregnant women with hyper-emesis were found to be positive for the H. pylori genome, compared with 27.6 percent of pregnant women without hyperemesis.
Differential Diagnosis and Evaluation
A thorough history and a complete physical examination are important in the evaluation of pregnant women who present with persistent vomiting. Nausea and vomiting in early pregnancy is usually a self-limited condition. When the condition is more severe, potentially serious causes need to be ruled out (Table 1).5 If nausea and vomiting begin after nine weeks of gestation, other causes should be investigated.
If the findings of the history and physical examination suggest a specific cause, testing is directed toward confirming that cause. For example, the findings may suggest pyelonephritis, a common condition in pregnancy. Ultrasonography may be helpful in ruling out gallbladder, liver, and kidney disorders. In addition to hyperemesis gravidarum, pregnancy-related causes of persistent vomiting include acute fatty liver and preeclampsia. Nonpregnancy-related causes include gastrointestinal, genitourinary, metabolic, and neurologic disorders.
Maternal and Fetal Outcomes
Women with uncomplicated nausea and vomiting of pregnancy (“morning sickness”) have been noted to have improved pregnancy outcomes, including fewer miscarriages, pre-term deliveries, and stillbirths, as well as fewer instances of fetal low birth weight, growth retardation, and mortality.11,12 In contrast, hyperemesis gravidarum has been associated with increases in maternal adverse effects, including splenic avulsion, esophageal rupture, Mallory-Weiss tears, pneumothorax, peripheral neuropathy, and preeclampsia, as well as increases in fetal growth restriction and mortality.13–15
Treatment
The management of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy depends on the severity of the symptoms. Treatment measures range from dietary changes to more aggressive approaches involving antiemetic medications, hospitalization, or even total parenteral nutrition (TPN). We prefer to start with dietary changes and then add medications as necessary. A Cochrane review of various nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatments for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy and hyperemesis gravidarum was recently published.16 [Evidence level B, systematic review of variable-quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs)]
NONPHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY
Dietary Measures
Initial treatment of women with mild nausea and vomiting of pregnancy (i.e., morning sickness) should include dietary changes. Affected pregnant women should be instructed to eat frequent, small meals and to avoid smells and food textures that cause nausea. Solid foods should be bland tasting, high in carbohydrates, and low in fat. Salty foods (e.g., salted crackers, potato chips) usually can be tolerated early in the morning, and sour and tart liquids (e.g., lemonade) often are tolerated better than water. Family members should be informed that pregnant women with nausea and vomiting of pregnancy may need to alter mealtimes and other home routines.
Emotional Support
Although nausea and vomiting of pregnancy and hyperemesis gravidarum are not strongly associated with psychologic illness, some women may become depressed or exhibit other affective changes. It is important that these women receive appropriate support from family members and medical and nursing staff. Consultation is indicated if a pregnant woman is depressed, domestic violence is suspected, or evidence of substance abuse or psychiatric illness exists.
Accupressure
Several studies17,18 have suggested acupressure as a treatment for nausea. The most common location for acupressure is the pericardium 6 or Neiguan point, which is located three fingerbreadths above the wrist on the volar surface. Various commercial products for relieving motion sickness (e.g., Sea-Band, ReliefBand) apply pressure to this area. One review19 of data from seven trials involving Neiguan point acupressure indicated that these products are helpful for controlling morning sickness in early pregnancy; however, a recent study20 demonstrated no benefit for acupressure in pregnant women.
Further data are necessary to determine whether acupressure is a viable treatment for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. However, acupressure is a nonpharmacologic intervention without known adverse side effects. Some physicians may wish to offer it to their patients.
Ginger
A popular alternative treatment for morning sickness, ginger has been used in teas, preserves, ginger ale, and capsule form. One European study21 demonstrated that ginger powder (1 g per day) was more effective than placebo in reducing the symptoms of hyperemesis gravidarum.
There have been no published reports of fetal anomalies associated with the use of ginger. However, one investigator22 warned that ginger root contains thromboxane synthetase inhibitor, which may interfere with testosterone receptor binding in the fetus. Other investigators23 noted that although safety data are lacking, people in many cultures use ginger as a spice; the amounts used are similar to those commonly prescribed for the treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.
PHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY
Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) and Doxylamine
Pyridoxine can be used as a single agent or in conjunction with doxylamine. One small study demonstrated that vitamin B6 in a dosage of 25 mg taken orally every eight hours (75 mg per day) was more effective than placebo for controlling nausea and vomiting in pregnant women.24 [Evidence level A, RCT] In pharmacologic doses, vitamin B6 has not been found to be teratogenic. A single 25-mg doxylamine (Unisom) tablet taken at night can be used alone or in combination with pyridoxine (25 mg three times daily).
In the 1970s, a medication combining pyridoxine and doxylamine (Bendectin) commonly was used to treat women with nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Although multiple studies showed no increased risk of birth defects, the manufacturer voluntarily withdrew Bendectin from the market in 1983 because of litigation. Pyridoxine-doxylamine is still the only medication that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has specifically labeled for the treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.
Pyridoxine-doxylamine is available in Canada under the trade name Diclectin (10 mg of pyridoxine and 10 mg of doxylamine in a delayed-release tablet). Diclectin typically is prescribed in a dosage of two tablets at night for mild symptoms and in a dosage of up to four tablets per day for more severe symptoms.
Antiemetics
If the previously discussed therapies are unsuccessful, a trial of antiemetics is warranted. The phenothiazines prochlorperazine (Compazine) and chlorpromazine (Thorazine) have been shown to reduce nausea and vomiting of pregnancy compared with placebo.25 A reasonable regimen is prochlorperazine administered rectally in a dosage of 25 mg every 12 hours (50 mg per day) or promethazine (Phenergan) given orally or rectally in a dosage of 25 mg every four hours (150 mg per day).
If treatment with prochlorperazine or promethazine is unsuccessful, some physicians try other antiemetics, such as trimethobenzamide (Tigan) or ondansetron (Zofran). In a small study26 of intravenous therapy in women with hyperemesis gravidarum, no increased benefit was demonstrated for ondansetron over promethazine. Although one study27 of 315 pregnant women demonstrated a slightly increased risk of birth defects when phenothiazines were given during the first trimester, a larger study28 showed no association with fetal malformations.
Women with severe nausea and vomiting of pregnancy or hyperemesis gravidarum may benefit from droperidol (Inapsine) and diphenhydramine (Benadryl). One study29 found that continuous intravenous administration of both droperidol and diphen-hydramine resulted in significantly shorter hospitalizations and fewer readmissions compared with a variety of other inpatient antiemetic therapies.
Antihistamines and Anticholinergics
Meclizine (Antivert), dimenhydrinate (Dramamine), and diphenhydramine have been used to control nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. All have been shown to be more effective than placebo.25 Although meclizine was previously thought to be teratogenic, studies have demonstrated its safety during pregnancy.28 One study30 found an association between diphen-hydramine and cleft lip and palate, but a subsequent study31 did not support this finding.
Motility Drugs
Metoclopramide (Reglan) acts by increasing pressure at the lower esophageal sphincter, as well as speeding transit through the stomach. This drug has been shown to be more effective than placebo in the treatment of hyperemesis gravidarum.32 Metoclopramide has not been associated with an increased incidence of congenital malformations.
Corticosteroids
A randomized, double-blind, controlled study33 found no hospital readmissions for recurrent vomiting in women with hyperemesis gravidarum who were treated with orally administered methylprednisolone (Medrol), compared with five readmissions in those who received oral promethazine therapy. The authors of the study suggested that methylprednisolone, in a dosage of 16 mg three times daily (48 mg per day) followed by tapering over two weeks, is a worthwhile treatment for women with refractory hyperemesis gravidarum.
Of note, these and other authors have found that almost all women with hyperemesis gravidarum can tolerate oral corticosteroid therapy. We have used the two-week tapering regimen in pregnant women who have been refractory to standard antiemetic therapy and have noted a subjective decrease in hospitalization rates and readmissions.
Corticosteroid therapy generally is considered safe during pregnancy. However, a recent meta-analysis34 demonstrated a marginally increased risk of major malformation and a 3.4-fold increased risk of oral cleft in infants exposed to corticosteroids in the first trimester.
| Medication | Dosage* | Pregnancy category | |
| Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)† | 25 mg orally three times daily | A‡ | |
| Doxylamine (Unisom)† | 25 mg orally once daily | § | |
| Antiemetics | |||
| Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) | 10 to 25 mg orally two to four times daily | C | |
| Prochlorperazine (Compazine) | 5 to 10 mg orally three or four times daily | C | |
| Promethazine (Phenergan) | 12.5 to 25 mg orally every four to six hours | C | |
| Trimethobenzamide (Tigan) | 250 mg orally three or four times daily | C | |
| Ondansetron (Zofran) | 8 mg orally two or three times daily | B | |
| Droperidol (Inapsine) | 0.5 to 2 mg IV or IM every three or four hours | C | |
| Antihistamines and anticholinergics | |||
| Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) | 25 to 50 mg orally every four to eight hours | B | |
| Meclizine (Antivert) | 25 mg orally every four to six hours | B | |
| Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) | 50 to 100 mg orally every four to six hours | B | |
| Motility drug | |||
| Metoclopramide (Reglan) | 5 to 10 mg orally three times daily | B | |
| Corticosteroid | |||
| Methylprednisolone (Medrol) | 16 mg orally three times daily; then taper | C | |
OTHER TREATMENTS
Intravenous Fluids
Pregnant women who, despite the previously discussed treatments, are unable to keep down liquids will probably require intravenous fluids. Normal saline or lactated Ringer's solution is the mainstay of intravenous fluid therapy. Many physicians use solutions that contain dextrose; however, it may be advisable to give thiamine (vitamin B1) first,5 because of the theoretic risk of Wernicke's encephalopathy.
Intravenous fluid may provide relief from nausea and vomiting, but many pregnant women also require an antiemetic administered orally, rectally, or by infusion with the fluid. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, intravenous fluid therapy may be given in the hospital or at home by a visiting nurse.
Enteral or Parenteral Nutrition
Enteral tube feeding and TPN are last-resort treatments for pregnant women who continue to vomit and lose weight despite aggressive treatment with any or all of the previously discussed modalities. Few studies have evaluated enteral nutrition, although all seven women in one small study38 tolerated feedings using an 8-French Dobbhoff nasogastric tube and infusion rates of up to 100 mL per hour.
TPN is administered through a central venous catheter. Its content is determined by the pregnant woman's daily caloric requirements and any existing electrolyte abnormalities. Consultation with a perinatologist experienced in parenteral nutrition, as well as a gastroenterologist or inpatient parenteral nutrition service, may be prudent. Both TPN and central venous access can result in significant complications, including sepsis.
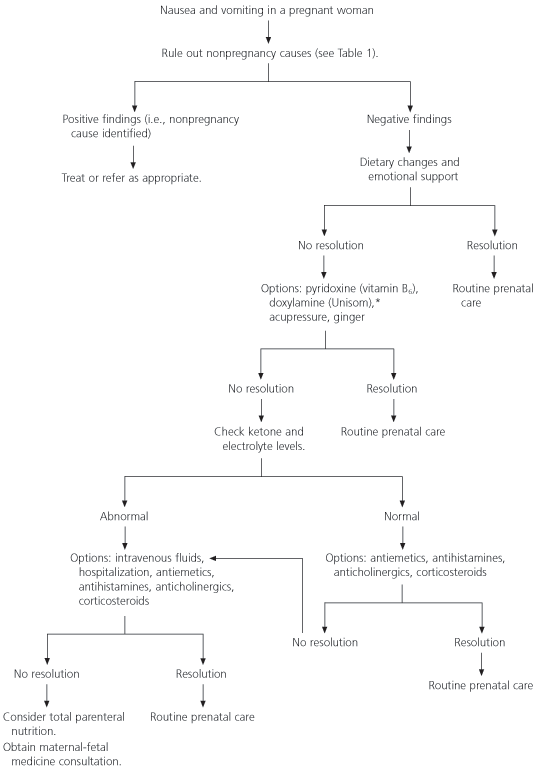
An algorithm for the suggested evaluation and management of women with nausea and vomiting of pregnancy is provided in Figure 1.