
Am Fam Physician. 2004;69(12):2863-2870
Skull deformity in infants continues to be a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Deformational plagiocephaly is a common and somewhat benign cause of skull deformity in infants that must be distinguished from the more serious craniosynostosis, which occurs alone or as a syndrome. Examining an infant’s head from above can help the physician distinguish true lambdoid synostosis from deformational plagiocephaly. In infants with lambdoid synostosis, the posterior bossing is in the parietal area contralateral to the flat part of the head. Deformational plagiocephaly causes frontal bossing ipsilateral to the flat part of the head. In infants with lambdoid synostosis, the ear is displaced posteriorly toward the fused suture. In infants with deformational plagiocephaly, the ear is displaced anteriorly. Isolated sagittal synostosis is the most common type of craniosynostosis. Of the more than 150 craniosynostosis syndromes, Crouzon’s disease and Apert’s syndrome account for the majority of cases. The diagnosis of craniosynostosis relies on physical examination, plain radiography, and computed tomography. Untreated progressive craniosynostosis leads to inhibition of brain growth, and an increase in intracranial and intraorbital pressure. Infants should be evaluated as soon as they are diagnosed.
Cranial skeletogenesis is unique. The cranial skeleton is composed of an assortment of neural crest and mesoderm-derived cartilages and bones that have been highly modified during evolution. Cranial malformations, although uncommon, compromise not only function but also the mental well-being of the person. Recent advances in human genetics have increased our understanding of the ways particular gene perturbations produce cranial skeletal malformations.1 However, an abnormal head shape resulting from cranial malformations in infants continues to be a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.
Development
The bones of the cranium are divided into the skull base and the calvarial vault. The growth of skull bones is driven primarily by the expanding growth of the brain. The brain grows rapidly in utero and during the first three years of life. An infant born at term has nearly 40 percent of his or her adult brain volume, and this increases to 80 percent by three years of age. Correspondingly, the size of the cranium of an infant born at term is 40 percent of adult size; by seven years, this increases to 90 percent.2 Term infants have well-formed skull bones separated by strips of connective tissue, sutures, and fontanelles3 (Figure 1). The sutures and fontanelles close at different times (Table 1).3 Mature suture closure occurs by 12 years of age, but completion continues into the third decade of life and beyond.

Craniosynostosis is the premature fusion of one or more of the cranial sutures and can occur as part of a syndrome or as an isolated defect (nonsyndromic). In the past, the prevalence of craniosynostosis was estimated to be one per 1,800 to 2,200 births and in a recent survey,4 the estimate is even higher. Craniosynostosis is called “simple” when only one suture is involved and “compound” when two or more sutures are involved (Table 2).2,3 The sagittal suture is affected in 40 to 60 percent of cases, the coronal suture in 20 to 30 percent of cases, and the metopic suture in less than 10 percent of cases; true lambdoid synostosis is rare.2 Syndromic craniosynostosis is less common (20 percent), even though more than 150 syndromes with craniosynostosis have been identified.5 In cases of syndromic craniosynostosis, multiple sutures are involved.
Etiology of Craniosynostosis
The etiology of nonsyndromic craniosynostosis is unknown, and the condition is sporadic in most instances. Potential risk factors identified from previous studies include white maternal race,6 advanced maternal age,6 male infant sex,6 maternal smoking,7 maternal residence at high altitude,8 use of nitrosatable drugs (e.g., nitrofurantoin, chlordiazepoxide, chlorpheniramine),9 certain paternal occupations (e.g., agriculture and forestry, mechanics, repairmen),10 and fertility treatments.4 Familial nonsyndromic craniosynostosis, which affects 2 to 6 percent of infants with sagittal synostosis and 8 to 14 percent of infants with coronal synostosis, is transmitted as an autosomal dominant disorder.2
Fibroblast growth factor and fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) regulate fetal osteogenic growth and are expressed in cranial sutures in early fetal life. These factors possibly influence fetal suture patency.2 Mutations in the gene coding for FGFR1 cause Pfeiffer’s disease, and mutations in FGFR2 cause Apert’s syndrome and Crouzon’s disease.11–13
Diagnosis
Commonly, craniosynostosis is present at birth, but it is not always diagnosed when mild. Usually it is diagnosed as a cranial deformity in the first few months of life. The diagnosis relies on physical examination and radiographic studies, including plain radiography and computed tomography (CT). Clinical history should include complications of pregnancy, duration of gestation, and birth weight.14 The history of infant sleeping position is important in differentiating craniosynostosis from plagiocephaly without synostosis.15
| Primary | |
| Simple | |
| Nonsyndromic: sagittal, coronal, metopic, lambdoid | |
| Compound | |
| Nonsyndromic: bicoronal | |
| Syndromic: Crouzon’s disease, Apert’s syndrome, Pfeiffer’s disease, Saethre-Chotzen syndrome | |
| Secondary | |
| Metabolic disorders (e.g., hyperthyroidism) | |
| Malformations (e.g., holoprosencephaly, microcephaly, shunted hydrocephalus, encephalocele) | |
| Exposure of fetus (e.g., valproic acid, phenytoin) | |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis (e.g., Hurler’s syndrome, Morquio’s syndrome) | |
DISTINGUISHING CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS
It is important to differentiate lambdoid synostosis from deformational plagiocephaly (also called occipital plagiocephaly, posterior plagiocephaly, and plagiocephaly without synostosis). The incidence of deformational plagiocephaly is approximately one in 300 live births compared with the incidence of the rarer lambdoid synostosis, which is approximately three in 100,000 live births.16,17 The number of infants with deformational plagiocephaly has increased, partly as a result of the “back to sleep” campaign to prevent sudden infant death syndrome and also because of the increased awareness of deformational plagiocephaly among primary care physicians.18,19
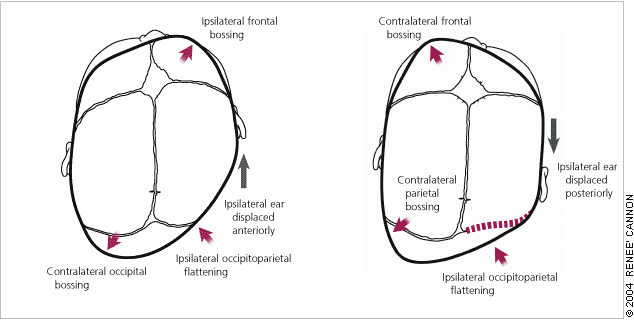
The diagnosis of deformational plagiocephaly can be made clinically by viewing the infant’s head from the top (vertex view).
In true lambdoid synostosis, the posterior bossing is contralateral and parietal; it is absent in deformational plagiocephaly. Ipsilateral frontal bossing, which is prominent in deformational plagiocephaly, is absent or, when present, contralateral in infants with lambdoid synostosis. The ipsilateral ear in lambdoid synostosis is displaced posteriorly toward the fused suture compared with the anterior displacement that occurs in infants with deformational plagiocephaly.
Examination of the infant’s face may show head tilt and contralateral facial flattening in cases of deformational plagiocephaly.20 The diagnosis of deformational plagiocephaly is made when the infant has a typically round head at birth but, a few weeks or months later, the parents notice deformation of head shape. A thorough physical examination by the primary care physician is necessary.
To prevent deformational plagiocephaly, parents should be instructed to alternate their infant’s sleep positions on the right and left occiput, to avoid using the car seat when not in a car, and to limit seating that maintains the supine position. A certain amount of prone positioning (“tummy time”) while the infant is awake and being observed may result in spontaneous correction of deformational plagiocephaly. Exercises to relieve torticollis and positioning the rounded side of the head on the mattress may help correct a flattened head. In some cases of deformational plagiocephaly, the use of skull-molding helmets may be necessary.20–22 If there is a lack of improvement or a progression of the deformity, referral to a pediatric neurosurgeon or a craniofacial center should be considered. Surgical correction rarely is necessary in infants with deformational plagiocephaly.20 However, surgery is almost always indicated for the correction of lambdoid synostosis.
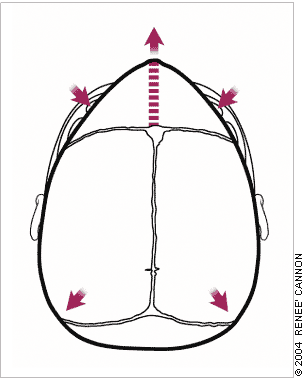
Infants born prematurely have a greater incidence of skull deformity caused by molding after birth. Most of these deformities improve spontaneously in the first few months of life.20
Clinical Evaluation
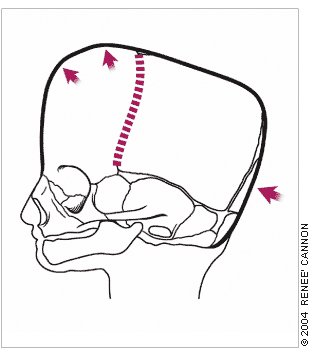
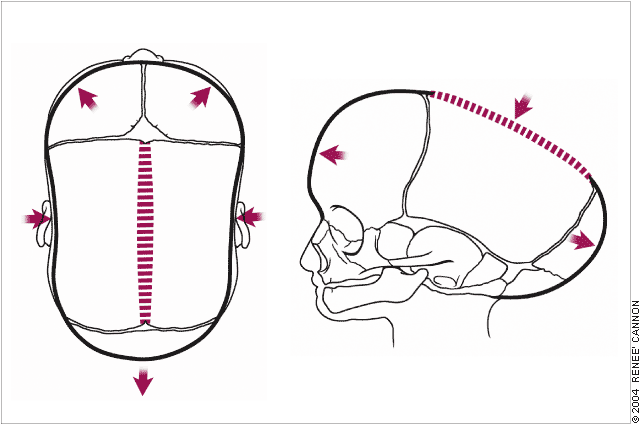
The calvarial shape is characteristic for each type of sutural synostosis (Figures 2 through 5). Measurement of the head circumference is vital to detect associated microcephaly or macrocephaly (caused by hydrocephalus). Overriding of the bones of the calvarial vault is common during the first two to three days of life in an infant born at term and during the first two to three weeks of life in an infant born prematurely. Persistent ridging at the suture lines in an infant with an abnormally shaped head is suggestive of craniosynostosis.
SYNDROMIC CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS
In addition to craniofacial malformations, syndromic craniosynostosis involves multiple systems (i.e., cardiac, genitourinary, musculoskeletal). Many patients have a family history of abnormal head shape. Clinical examination of infants with craniofacial malformations should include careful evaluation of the neck, spine, digits, and toes.14 Crouzon’s disease and Apert’s syndrome will be described below because they occur more frequently than the other syndromes associated with craniosynostosis.
CROUZON’S DISEASE
Crouzon’s disease is inherited through an autosomal-dominant pattern.23 Nearly 60 percent of cases are new mutations, and many are associated with paternal age older than 35 years. Crouzon’s disease occurs in one of every 25,000 live births and accounts for 5 percent of cases of craniosynostosis. Nucleotide alterations causing amino-acid substitutions at the FGFR2 gene on chromosome 10 lead to the Crouzon phenotype. Clinical findings include brachycephalic craniosynostosis, significant hypertelorism, proptosis, maxillary hypoplasia, beaked nose and, possibly, cleft palate. Intracranial anomalies include hydrocephalus, Chiari 1 malformation, and hind-brain herniation (70 percent). Pathology of the ear and cervical spine is common. Infants with Crouzon’s disease do not have anomalies of the hands and feet as do infants with Apert’s syndrome.
APERT’S SYNDROME
Apert’s syndrome (acrocephalosyndactyly) is an autosomal dominant disorder that occurs in one of every 160,000 live births.23 The syndrome is caused by nucleotide alterations resulting in amino-acid substitutions, leading to a mutation in the FGFR2 gene located on chromosome 10. Craniosynostosis and symmetric syndactyly of the extremities are hallmarks of this syndrome. The clinical features include misshapen skull caused by coronal suture synostosis, wide-set eyes, mid-face hypoplasia, choanal stenosis, and shallow orbits. Intracranial anomalies include megalocephaly, hypoplastic white matter, and agenesis of the corpus callosum, leading to cognitive impairment. Cardiac anomalies, including atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect, and renal anomalies such as hydronephrosis occur in 10 percent of these patients.
Radiographic Evaluation
Plain radiography is the first step in the evaluation of suspected craniosynostosis3 and is sufficient for diagnosing single-suture craniosynostosis.24,25 Anteroposterior and lateral views of the skull are usual. It is important to evaluate the entire length of each suture because only a small segment may be involved.3 The signs of craniosynostosis on plain radiography include bony bridging across the suture that produces beaking or heaping up of bone; sclerosis, straightening and narrowing of the suture; and loss of suture clarity.26
The diagnostic value of the CT scan outweighs that of plain radiography because the sutures can be identified more accurately on a CT scan. In addition, CT scanning helps in evaluating the brain for structural abnormalities (e.g., hydrocephalus, agenesis of the corpus callosum) and in excluding other causes of asymmetric vault growth (e.g., brain hemiatrophy, chronic subdural hematoma).3 Three-dimensional surface reconstruction using CT scanning can help the surgeon to accurately delineate the craniofacial deformity and plan surgical reconstruction.27
Complications
The major complications associated with uncorrected craniosynostosis include increased intracranial pressure, asymmetry of the face, and malocclusion. Asymmetry of the orbits leads to strabismus.14
Management
Optimal care of infants with craniofacial anomalies requires a multidisciplinary team approach. Infants should be evaluated within the first few weeks of life. However, referral is appropriate at any age. Once the diagnosis of craniosynostosis is confirmed, the treatment is surgical correction. The best time to intervene is when the infant is between three and nine months of age.14 However, infants with symptoms and signs of increased intracranial pressure require urgent decompression.
SURGICAL INTERVENTION IN NONSYNDROMIC CRAN-IOSYNOSTOSIS
Sagittal Synostosis
Surgical intervention involves either strip craniectomy or cranial vault remodeling with excision of the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones, which are trimmed, reshaped, and affixed with absorbable plates.14 Recently, minimally invasive endoscopic strip craniectomy, which involves significantly less blood loss and a shorter hospital stay, has been successful.28
Coronal Synostosis
The objective of coronal synostosis is to increase the anteroposterior dimensions of the calvaria.
Metopic Synostosis
The main goal of metopic synostosis is to increase the volume of the anterior cranial fossa.14
SURGICAL INTERVENTION IN SYNDROMIC CRANIOSYNOSTOSIS
The management of craniofacial syndromes includes correction of craniosynostosis between three and six months of age, and correction of limb defects between one and two years of age.14 When the patient is a young adult, surgeries to normalize appearance and correct malocclusion are done.
Potential intraoperative complications include massive blood loss and air embolism.2 Mortality rates are low according to recent reports.14 Careful follow-up of the patient is necessary after surgery to ensure that the sutures do not re-fuse. Postoperative monitoring of head circumference and checking for signs and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure are necessary.2