
Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(2):309-312
Necrotizing (malignant) external otitis, an infection involving the temporal and adjacent bones, is a relatively rare complication of external otitis. It occurs primarily in immunocompromised persons, especially older persons with diabetes mellitus, and is often initiated by self-inflicted or iatrogenic trauma to the external auditory canal. The most frequent pathogen is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Patients with necrotizing external otitis complain of severe otalgia that worsens at night, and otorrhea. Clinical findings include granulation tissue in the external auditory canal, especially at the bone-cartilage junction. Facial and other cranial nerve palsies indicate a poor prognosis; intracranial complications are the most frequent cause of death. Diagnosis requires culture of ear secretions and pathologic examination of granulation tissue from the infection site. Imaging studies may include computed tomographic scanning, technetium Tc 99m medronate bone scanning, and gallium citrate Ga 67 scintigraphy. Treatment includes correction of immunosuppression (when possible), local treatment of the auditory canal, long-term systemic antibiotic therapy and, in selected patients, surgery. Family physicians and others who provide medical care for immunocompromised patients should be alert to the possibility of necrotizing external otitis in patients who complain of otalgia, particularly if they have diabetes mellitus and external otitis that has been refractory to standard therapy. Susceptible patients should be educated to avoid manipulation of the ear canal (i.e., they should not use cotton swabs to clean their ears) and to minimize exposure of the ear canal to water with a high chloride concentration. Appropriate patients should be referred to an otolaryngologist.
Osteitis of the temporal and adjacent bones was initially described in 1959.1 Because of the high mortality rate (46 percent) in early series, this condition is often referred to as “malignant otitis externa.”2 It is also called “necrotizing external otitis,” a term that emphasizes the destructive nature of the infection.“Osteitis of the base of the skull,” the most recent but less popular name for this condition, stresses the involvement of bone and the strategic location of the infection.
Necrotizing external otitis is an infection of otologic origin that has potentially life-threatening complications. It is considered a complication of external otitis3 and occurs primarily in older persons who have diabetes mellitus or another condition that compromises the immune system. Family physicians must be able to recognize this infection, initiate treatment, and refer appropriate patients to an otolaryngologist.
Pathogenesis and Clinical Manifestations
Infection of the soft tissue of the external auditory canal (“swimmer's ear”) is common, especially in hot, humid climates. The usual initiating events are trauma (often self-inflicted with cotton swabs) and exposure to swimming-pool water, which has a high concentration of halogens. The most frequently cultured pathogen, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, is not a normal inhabitant of the auditory canal.4 Other possible pathogens include Staphylococcus epidermidis,5 gram-negative bacteria, and fungi.
Patients with external otitis complain of otalgia and sensitivity to auricular movement. Otorrhea may be present, and obliteration of the external auditory canal by edema and secretions may cause hearing loss or a sensation of fullness in the ear.
The infection may extend to the cartilaginous skeleton of the ear canal and through Santorini's fissures to reach the temporal bone, causing osteitis. One of the hallmarks of this extension is granulation tissue in the bone-cartilage junction of the external auditory canal. This otoscopic finding is of extreme importance.
Because of significant differences in natural course and treatment, it is crucial to differentiate severe otitis externa and necrotizing external otitis. Involvement of structures beyond the soft tissues of the auditory canal occurs only in necrotizing external otitis. Osteitis of the base of the skull usually follows external otitis but also may begin with a middle-ear infection.5,6
Although necrotizing external otitis can occur in immunocompetent persons,7 it typically develops in persons with diabetes mellitus or another condition that compromises the immune system, such as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome,8 malignancy, or chemotherapy.9 In diabetes mellitus, poor vascular supply resulting from microvascular disease is aggravated by pseudomonal vasculitis, which further restricts tissue perfusion. Diabetes mellitus is also associated with impaired polymorphonuclear cell function and a higher pH of cerumen in the aural canal. These factors, along with the sensitivity of P. aeruginosa to low pH, further restrict bodily defenses against infection.
Patients with osteitis of the base of the skull sometimes have extra-auricular manifestations, such as cervical lymphadenopathy, trismus (because of temporomandibular joint involvement),10 or irritation of the masseter muscle. As the infection spreads in the temporal bone, it may extend into the cranium and result in cranial nerve palsies. These palsies generally are caused by the secretion of neurotoxins or the compressive effect of the destructive process through the relevant foramina. Because of its anatomic location in the temporal bone, the facial nerve is usually the first nerve to become involved.
Cranial nerve involvement indicates a poor prognosis. Death is usually due to intracranial complications such as sigmoid sinus thrombosis, but it also may occur because of treatment complications, including bone marrow suppression induced by long-term antibiotic therapy. Prognosis is adversely affected by comorbid conditions, which are common in patients who develop malignant otitis externa.
Diagnosis
Family physicians should maintain a high index of suspicion for necrotizing external otitis in immunocompromised patients who have external otitis. Special alertness is required when external otitis is refractory to treatment and patients complain of severe otalgia, especially at night. The diagnosis of necrotizing external otitis is based on the clinical presentation and confirmed by laboratory tests and imaging studies.
LABORATORY TESTS
Mandatory laboratory tests include an erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), white and red blood cell counts, glucose and creatinine levels, and culture of ear secretions. The ESR is typically elevated in necrotizing external otitis; therefore, it is a useful indicator of treatment response. Before topical or systemic antibiotic therapy is started, ear secretions should be cultured, because susceptibility patterns may change after the initiation of treatment (i.e., bacteria might become resistant to an antibiotic during treatment).11 Pathologic examination of granulation tissue removed from the external auditory canal is essential to exclude malignant processes, which may present as nonresponding inflammatory disease.
IMAGING STUDIES
Imaging to prove the extension of infection to bony structures is generally necessary to establish the diagnosis of necrotizing external otitis.12 Imaging modalities include computed tomographic (CT) scanning, technetium Tc 99m medronate methylene diphosphonate bone scanning, and gallium citrate Ga 67 scintigraphy.
CT scanning is used to determine the location and extent of diseased tissue (Figure 1). The temporal bone is the first bone to be affected, with imminent involvement of the petrous apex and mastoid. Extratemporal bone extension has become rare since the introduction of powerful antibiotics. In evaluating the CT scan, it is important to remember that at least one third of bone mineral must be lost before radiologic changes become apparent; conversely, bone remineralization continues long after the infection is cured. Thus, as related to the infectious process, pathology is late to appear on the CT scan and late to disappear. These factors limit the usefulness of CT scanning as a follow-up tool.
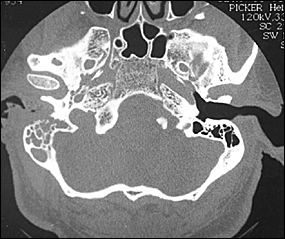
Both osteoclasts and osteoblasts absorb 99mTc. Hence, bone scanning can locate a pathologic process in bone but is not informative about the nature of the process (infectious or other). Because the 99mTc scan remains positive as long as bone repair continues, this imaging modality is not helpful in follow-up.13
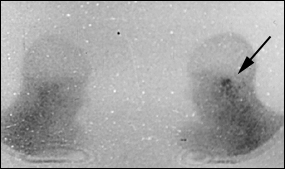
By using imaging modalities in combination, it is possible to prove that the temporal bone is afflicted (CT scanning and 99mTc bone scanning) with an infectious process (67Ga scintigraphy).12
Prevention
In many patients with necrotizing external otitis, the initiating event may be self-inflicted or iatrogenic trauma to the ear canal. Therefore, susceptible patients should be instructed to avoid manipulation of the external auditory canal (i.e., they should not use cotton swabs to remove cerumen). Cleaning of the external auditory canal, including aural irrigation by medical staff, should be carried out with extreme caution to avoid injuring delicate skin in the canal.15 Eczematous conditions involving the meatus of the canal should be treated topically, because these conditions may result in pruritus that leads to scratching of the irritated skin.3
Treatment
Treatment of necrotizing external otitis includes correction of immunosuppression (when possible), local treatment of the auditory canal, long-term systemic antibiotic therapy and, in selected patients, surgery.
Strict control of diabetes mellitus is mandatory, although it can be difficult to achieve during the acute illness. Other immunosuppressive states and comorbid conditions also must be aggressively managed.
Local treatment of the auditory canal includes meticulous cleaning and debridement plus topical application of antimicrobial agents (antibiotics and others). Sequestra and other necrotic tissue should be removed. Initially, treatment may include the application of antimicrobial-impregnated dressings to the canal. An antipseudomonal agent should be used first; if necessary, the agent can be changed on the basis of the culture results.
As in other infections involving bone, long-term administration of systemic antibiotics is the mainstay of treatment. Antibiotics that are effective against P. aeruginosa include aminoglycosides, penicillins (especially piperacillin–tazobactam [Zosyn]), ceftazidime (Fortaz), cefepime (Maxipime) and, occasionally, imipenem (with cilastatin [Primaxin]). Depending on bacterial sensitivity, a combination of agents may be needed. One common combination is an antipseudomonal penicillin and an amino-glycoside (Table 1).
| Drug | Dosage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) | 750 mg orally every 12 hours | Fluoroquinolone for oral therapy |
| 400 mg IV every 12 hours | ||
| Ticarcillin-clavulanate potassium (Timentin) | 3 g IV every 4 hours | Antipseudomonal penicillin |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam (Zosyn) | 4 to 6 g IV every 4 to 6 hours | Antipseudomonal penicillin; at this dosage, combine piperacillin-tazobactam with an aminoglycoside. |
| Ceftazidime (Fortaz) | 2 g IV every 8 hours | Third-generation cephalosporin |
| Cefepime (Maxipime) | 2 g IV every 12 hours | Fourth-generation cephalosporin |
| Tobramycin (Nebcin) | According to patient weight: 1 to 1.66 mg per kg IV or IM every 8 hours | Aminoglycoside; combine tobramycin with a penicillin. |
| Gentamicin (Garamycin) | According to patient weight: 1 to 1.66 mg per kg IV or IM every 8 hours | Aminoglycoside; combine gentamicin with a penicillin. |
The introduction of orally administered antipseudomonal agents in the 1980s simplified the ambulatory treatment of osteitis of the base of the skull.16,17 Fluoroquinolones, primarily ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and ofloxacin (Floxin), are DNA-gyrase inhibitors that are effective against P. aeruginosa and well tolerated by patients. Poor vascularization of the target area is one of the reasons that high-dose antibiotic therapy is needed to treat ma lignant otitis externa. For example, the appropriate dosage of ciprofloxacin is 750 mg twice daily.17 Because of the reported emergence of ciprofloxacin-resistant pseudomonal strains,11,18 culture should be performed before topical or systemic antimicrobial therapy is initiated.
Verifying the response to treatment can be difficult. Thus, determining the proper timing for its cessation can be problematic. Treatment should be continued for at least four weeks, but the duration of therapy must be individualized on the basis of the clinical presentation (night pain, physical findings), ESR, and imaging studies.
Hyperbaric oxygen, an adjunct to antibiotic therapy, is believed to increase the ability of polymorphonuclear cells to fend off pathogenic bacteria.19 [Evidence level B, uncontrolled study] However, complexity of administration often limits the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy.