
Am Fam Physician. 2004;69(6):1465-1470
A more recent article on streptococcal pharyngitis is available.
Sore throat is one of the most common reasons for visits to family physicians. While most patients with sore throat have an infectious cause (pharyngitis), fewer than 20 percent have a clear indication for antibiotic therapy (i.e., group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection). Useful, well-validated clinical decision rules are available to help family physicians care for patients who present with pharyngitis. Because of recent improvements in rapid streptococcal antigen tests, throat culture can be reserved for patients whose symptoms do not improve over time or who do not respond to antibiotics.
Pharyngitis is one of the most common conditions encountered by the family physician.1–5 The optimal approach for differentiating among various causes of pharyngitis requires a problem-focused history, a physical examination, and appropriate laboratory testing. Identifying the cause of pharyngitis, especially group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS), is important to prevent potential life-threatening complications.6
Epidemiology and Pathogenesis
The 2000 National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey found that acute pharyngitis accounts for 1.1 percent of visits in the primary care setting and is ranked in the top 20 reported primary diagnoses resulting in office visits.3 Peak seasons for sore throat include late winter and early spring.4 Transmission of typical viral and GABHS pharyngitis occurs mostly by hand contact with nasal discharge, rather than by oral contact.7,8 Symptoms develop after a short incubation period of 24 to 72 hours.
Differential Diagnosis
Sore throat most often is caused by direct infection of the pharynx (pharyngitis), primarily by viruses or bacteria.4 GABHS pharyngitis accounts for 15 to 30 percent of cases in children and 5 to 15 percent of cases in adults.5,6,9,10 Sore throat also may be caused by other conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux, postnasal drip secondary to rhinitis, persistent cough, thyroiditis, allergies, a foreign body, and smoking.1,2,11
This article focuses on infectious causes of sore throat (pharyngitis). If patients do not have any other signs of infection or do not respond as expected to treatment of pharyngitis, physicians should investigate noninfectious causes.
VIRUSES
Viral pharyngitis, the most common cause of sore throat, has a wide differential. Furthermore, different viruses are more prevalent during certain seasons.4 Coryza, conjunctivitis, malaise or fatigue, hoarseness, and low-grade fever suggest the presence of viral pharyngitis.12 Children with viral pharyngitis also can present with atypical symptoms, such as mouth-breathing, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.8,12
INFECTIOUS MONONUCLEOSIS
Infectious mononucleosis is most common in patients 15 to 30 years of age.13 Patients typically present with fever, sore throat, and malaise. On examination, there is pharyngeal injection with exudates. Posterior cervical lymphadenopathy is common in patients with infectious mononucleosis, and its absence makes the diagnosis much less likely. Hepatosplenomegaly also may be present.10–12 If these patients are treated with amoxicillin or ampicillin, 90 percent will develop a classic maculopapular rash.14,15
BACTERIA
Patients with bacterial pharyngitis generally do not have rhinorrhea, cough, or conjunctivitis. The incidence of bacterial pharyngitis is increased in temperate climates during winter and early spring.16 There is often a history of streptococcal throat infection (strep throat) within the past year. GABHS is the most common bacterial cause of pharyngitis.16–18
GABHS Infection
Symptoms of strep throat may include pharyngeal erythema and swelling, tonsillar exudate, edematous uvula, palatine petechiae, and anterior cervical lymphadenopathy. Untreated, GABHS infection lasts seven to 10 days.4,13,19 Patients with untreated streptococcal pharyngitis are infectious during the acute phase of the illness and for one additional week.1 Effective antibiotic therapy shortens the infectious period to 24 hours, reduces the duration of symptoms by about one day, and prevents most complications.
Complications of GABHS Infection
The incidence of complications with GABHS infection, such as rheumatic fever and peritonsillar abscess, is much lower than generally perceived.17 Peritonsillar abscess occurs in fewer than 1 percent of patients treated with antibiotics.1 Patients with peritonsillar abscess typically have a toxic appearance and may present with a “hot potato voice,” fluctuant peritonsillar mass, and asymmetric deviation of the uvula. However, clinical impression is only moderately accurate in diagnosing peritonsillar abscess (78 percent sensitivity and 50 percent specificity in one series of 14 patients).20 Intraoral ultrasound examination is an accurate diagnostic test if abscess is suspected.
Rheumatic fever is exceedingly rare in the United States and other developed countries (annual incidence less than one case per 100,000).21 This illness should be suspected in any patient with joint swelling and pain, subcutaneous nodules, erythema marginatum or heart murmur, and a confirmed streptococcal infection during the preceding month. Patients will have an elevated antistreptolysin-O titer and erthrocyte sedimentation rate.
Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is another rare complication of GABHS pharyngitis, although treatment with antibiotics does not prevent it. Patients present with hematuria and, frequently, edema in the setting of a recent streptococcal infection with an elevated antistreptolysin-O titer.
Scarlet fever is associated with GABHS pharyngitis and usually presents as a punctate, erythematous, blanchable, sandpaper-like exanthem. The rash is found in the neck, groin, and axillae, and is accentuated in body folds and creases (Pastia’s lines).1,4,19 The pharynx and tonsils are erythematous and covered with exudates. The tongue may be bright red with a white coating (strawberry tongue).4
Other Bacterial Causes of Pharyngitis
Gonococcal pharyngitis occurs in sexually active patients18 and presents with fever, severe sore throat, dysuria, and a characteristic greenish exudate.
The role of Chlamydia pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae as causes of acute pharyngitis, particularly in the absence of lower respiratory tract disease, remains somewhat uncertain.18 There is no evidence that testing for atypical bacteria or treatment in the primary care setting improves clinical outcomes in patients with pharyngitis.18
Diphtheria is an acute upper respiratory tract illness that is characterized by sore throat, low-grade fever, and an adherent grayish membrane with surrounding inflammation of the tonsils, pharynx, or nasal passages.16,22 In diphtheria, the throat is moderately sore, with tender cervical adenopathy. Case fatality rates for noncutaneous diphtheria (5 to 10 percent) have remained constant for the past five decades.23 Diphtheria pharyngitis has recently (March 2001) been reported in Delaware County, Pa.24
If examination reveals a serosanguineous nasal discharge and a grayish-white pharyngeal membrane (exudative and extending to the uvula and soft palate) in association with pharyngitis, tonsillitis, and cervical lymphadenopathy, the presumptive diagnosis is diphtheria. The incubation period for Corynebacterium diphtheriae infection is two to four weeks. A confirmatory diagnosis is made by microbacteriologic analysis.
KAWASAKI DISEASE
Kawasaki disease is probably an infectious disease caused by an unknown agent. The disease most often affects children younger than five years and presents with a constellation of symptoms, including sore throat. Characteristic signs and symptoms include fever, bilateral nonpurulent conjunctivitis, anterior cervical node enlargement, erythematous oral mucosa, and an inflamed pharynx with a strawberry tongue. Dermatologic features of the disease become apparent within three days of the onset of fever14,18 and include cracked red lips, a generalized polymorphous erythematous rash with edema and erythema of the hands and feet, and periungual desquamation followed by peeling of the palms. Dermatologic manifestations in concert with characteristic signs and symptoms serve as diagnostic criteria.13
Diagnosis
GENERAL APPROACH
When a patient presents with sore throat, the family physician must consider a wide range of illnesses. Infectious causes range from generally benign viruses to GABHS. Inflammatory presentations may be the result of allergy, reflux disease or, rarely, neoplasm or Kawasaki disease.
In determining the underlying cause and thereby deciding if, when, and how to treat the patient with pharyngitis, the physician must integrate information from the history and physical examination. Environmental and epidemiologic factors also may need to be assessed.
GABHS
Important historical elements include the onset, duration, progression, and severity of the associated symptoms (e.g., fever, cough, respiratory difficulty, swollen lymph nodes); exposure to infections; and presence of comorbid conditions (e.g., diabetes). The pharynx should be examined for erythema, hypertrophy, foreign body, exudates, masses, petechiae, and adenopathy. It also is important to assess the patient for fever, rash, cervical adenopathy, and coryza. When streptococcal pharyngitis is suspected, the physician should listen for the presence of a heart murmur and evaluate the patient for hepatosplenomegaly. Laboratory testing serves as an adjunct to the history and physical examination (Table 1).1,2,4,6,7,11,17,23–27
| Name of test | Type of test | Sensitivity and specificity |
|---|---|---|
| Throat culture | Specimen obtained by throat swab of posterior tonsillopharyngeal area and inoculated onto 5 percent sheep-blood agar plate to which a bacitracin disk is applied; results in 24 to 48 hours | Sensitivity: 97 percent; specificity: 99 percent; results dependent on the technique, medium, and incubation |
| Rapid antigen detection test or rapid streptococcal antigen test | Detects presence of group A streptococcal carbohydrate on a throat swab (change in color indicates a positive result); results available within minutes; in-office test | Specificity: > 95 percent; sensitivity: 80 to 97 percent, depending on the test |
| Monospot test | Rapid slide agglutination test for mononucleosis | Overall sensitivity: 86 percent; overall specificity: 99 percent |
| First week sensitivity: 69 percent; specificity: 88 percent | ||
| Second week: sensitivity: 81 percent; specificity: 88 percent |
A systematic review of the clinical diagnosis of pharyngitis1 identified large, blinded, prospective studies using throat cultures as a reference standard. The presence of tonsillar or pharyngeal exudate and a history of exposure to streptococcus in the previous two weeks were the most useful clinical features in predicting current GABHS infection. The absence of tender anterior cervical adenopathy, tonsillar enlargement, and tonsillar or pharyngeal exudate was most useful in ruling out GABHS. However, no single element in the history or physical examination is sensitive or specific enough to exclude or diagnose strep throat.1,4 This dilemma has inspired investigators to develop scoring systems to facilitate the diagnostic process.4,18,24
In one study, investigators identified four findings from the history and physical examination that independently predicted a positive throat culture for GABHS in a population of adults and children.26 [Evidence level B, observational study] The findings were tonsillar exudates, anterior cervical lymphadenopathy, absence of cough, and history of fever higher than 38°C (100.4°F). When combined with the patient’s age, these findings allow the physician to place patients in a low-, moderate-, or high-risk group (Table 2).24 Low-risk patients require no further diagnostic testing, high-risk patients should be considered for empiric therapy, and moderate-risk patients should undergo further evaluation with a rapid antigen test or throat culture to make the diagnosis. This general approach is advocated by a recent evidence-based guideline from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that was written by family physicians, general internists, pediatricians, and other experts.28,29
Laboratory Evaluation
Throat Culture
One method for confirming the diagnosis of GABHS pharyngitis is throat culture. To maximize accuracy, the tonsillar region and posterior pharyngeal wall should be swabbed. The specimen is inoculated onto a 5 percent sheep-blood agar plate, and a bacitracin disk is applied.
| Symptom | Points | |
|---|---|---|
| Fever (subjective or measured in office) | 1 | |
| Absence of cough | 1 | |
| Tender anterior cervical adenopathy | 1 | |
| Tonsillar swelling or exudates | 1 | |
| Age | ||
| Younger than 15 years | +1 | |
| 15 to 45 years | 0 | |
| Older than 45 years | –1 | |
Rapid Antigen Detection Tests
Properly performed, a rapid antigen detection test is almost as sensitive as throat culture.17,26,27 Rapid streptococcal antigen tests are easy to perform, and results are available within minutes. Because of improvements in the sensitivity of these tests, negative results no longer have to be confirmed by throat culture.30 [Evidence level B, nonrandomized trial]
Rapid streptococcal antigen testing is indicated when patients are at moderate risk for GABHS infection based on the clinical score or when the physician is not comfortable with using empiric therapy in a high-risk patient or with further testing in a low-risk patient31 (Figure 1). Patients with a positive test result should be treated with appropriate antibiotics, and those with a negative result should receive supportive treatment and follow-up care. If symptoms do not improve, a throat culture should be considered.31
OTHER INFECTIOUS CAUSES
The presence of at least 10 percent atypical lymphocytes supports the diagnosis (92 percent specificity) of infectious mononucleosis. In a patient with typical symptoms, no further testing is needed.32
When the clinical scenario suggests the presence of infectious mononucleosis, the diagnosis may be obtained by the presence of a positive heterophil antibody test (Monospot test) for Epstein-Barr virus. This test misses about one third of cases in the first week of illness but is more than 80 percent sensitive in the second week. If the diagnosis remains uncertain, the physician should consider a test for IgM antibody to the viral capsid antigen.
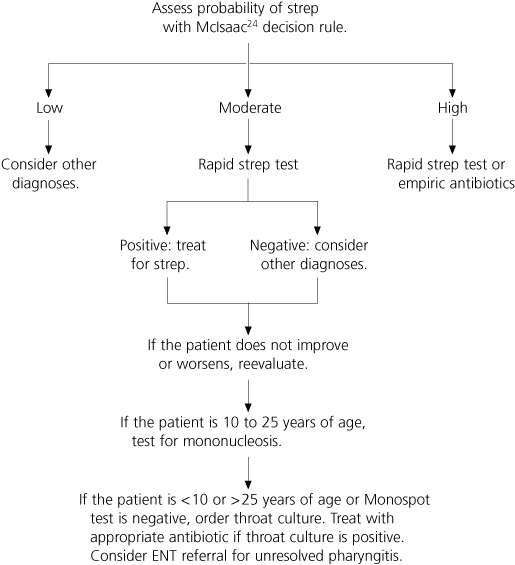
Laryngoscopy is recommended when sore throat is chronic and recurrent, cultures and heterophil antibody tests are negative, and the diagnosis remains uncertain. Additional evaluation is required to investigate for the presence of a foreign body, neoplastic lesions, and other unusual causes of sore throat.