
Am Fam Physician. 2009;79(7):565-570
Patient information: Seee related handout on baby formula, written by the author of this article.
Author disclosure: Nothing to disclose.
Although the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians recommend breast milk for optimal infant nutrition, many parents still choose formula as an acceptable alternative. The wide variety of available formulas is confusing to parents and physicians, but formulas can be classified according to three basic criteria: caloric density, carbohydrate source, and protein composition. Most infants require a term formula with iron. There is insufficient evidence to recommend supplementation with docosahexaenoic acid or arachidonic acid. Soy formulas are indicated for congenital lactase deficiency and galactosemia, but are not recommended for colic because of insufficient evidence of benefit. Hypoallergenic formulas with extensively hydrolyzed protein are effective for the treatment of milk protein allergy and the prevention of atopic disease in high-risk infants. Antireflux formulas decrease emesis and regurgitation, but have not been shown to affect growth or development. Most infants with reflux require no treatment. Family physicians can use these guidelines to counsel parents about infant formula, countering consumer advertising that is not evidence-based.
Although the American Academy of Family Physicians and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) promote breastfeeding as optimal infant nutrition, many parents still choose infant formula as an acceptable alternative.1,2 The wide variety of available formulas can be confusing and overwhelming for parents and physicians, and formula companies target both audiences with advertising campaigns. Family physicians can advise parents about infant formula choices based on available evidence. Additionally, family physicians should identify the minority of infants who would benefit from a specialized formula.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
| There is insufficient evidence to recommend supplementation of infant formula with docosahexaenoic acid or arachidonic acid. | A | 5, 6 |
| Preterm and enriched formulas may improve short-term growth parameters in premature infants, but have not been shown to improve long-term growth or development. | A | 8 |
| Hypoallergenic formula is effective for the treatment of milk protein allergy and the prevention of atopic disease. | B | 10, 16, 25 |
| Antireflux formulas reduce daily emesis and regurgitation in infants, but have not been shown to improve growth or development. | A | 12, 26 |
| Parental counseling is more effective than changing formula in the treatment of infant colic. | B | 30 |
All formulas are classified based on three parameters: caloric density, carbohydrate source, and protein composition. Commercially available infant formulas are presented by these parameters in Table 1.
| Cost per ounce* | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Brand names | Calories (kcal per oz) | Carbohydrate source | Protein source | Indications | Powdered formula† | Ready-to-feed |
| Breast milk | — | 20 | Lactose | Human milk | Preferred for all infants | — | — |
| Term formula | Carnation Good Start; Enfamil with Iron; Similac with Iron | 20 | Lactose | Cow's milk | Appropriate for most infants | $0.14 | $0.27 |
| Term formula with DHA and AA | Enfamil Lipil; Good Start DHA & ARA; Similac Advance | 20 | Lactose | Cow's milk | Marketed to promote eye and brain development | 0.16 | 0.30 |
| Preterm formula | Enfamil 24 Premature; Preemie SMA 24; Similac 24 Special Care | 24 | Lactose | Cow's milk | Less than 34 weeks' gestation Weight less than 1,800 g (3 lb, 15 oz) | — | 0.80 |
| Enriched formula | Enfacare; Similac Neosure | 22 | Lactose | Cow's milk | 34 to 36 weeks' gestation Weight 1,800 g (3 lb, 15 oz) or greater | 0.19 | 0.32 |
| Soy formula | Enfamil Prosobee; Good Start Soy; Similac Isomil | 20 | Corn-based | Soy | Congenital lactase deficiency, galactosemia | 0.16 | 0.30 |
| Lactose-free formula | Enfamil Lactofree; Similac Sensitive | 20 | Corn-based | Cow's milk | Congenital lactase deficiency, primary lactase deficiency, galactosemia, gastroenteritis in at-risk infants | 0.16 | 0.30 |
| Hypoallergenic formula | Similac Alimentum; Enfamil Nutramigen; Enfamil Pregestimil | 20 | Corn or sucrose | Extensively hydrolyzed | Milk protein allergy | 0.25 | 0.37 |
| Nonallergenic formula | Elecare; Neocate; Nutramigen AA | 20 | Corn or sucrose | Amino acids | Milk protein allergy | 0.35 | — |
| Antireflux formula | Enfamil AR; Similac Sensitive RS | 20 | Lactose, thickened with rice starch | Cow's milk | Gastroesophageal reflux | 0.18 | 0.31 |
| Toddler formula | Enfamil Next Step; Good Start 2; Similac Go and Grow | 20 | Lactose | Milk | Nine to 24 months of age | 0.15 | 0.25 |
Term Formulas
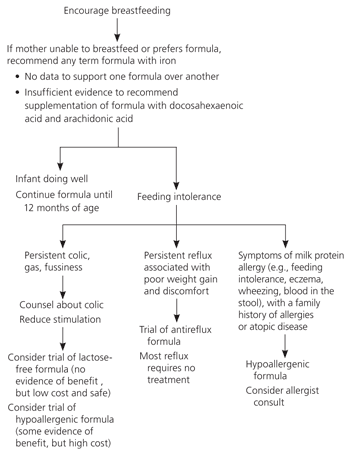
Most infants need a basic formula for term infants. These formulas are modeled after breast milk and contain 20 kcal per ounce. Their carbohydrate source is lactose, and they contain cow's-milk protein. There is no evidence to recommend one brand over another; all formulas are nutritionally interchangeable.
Recently, formulas with long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids have been heavily marketed to promote eye and brain development. Arachidonic acid (AA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are the most common additives. These fatty acids are found in breast milk, but not conventional formula, and are thought to be important in the development of membrane constituents in the central nervous system. Clinical trials of the effects of AA and DHA on cognitive, social, and motor development have been inconsistent. Although no harm has been demonstrated, most well-conducted randomized trials show no benefit. Thus, recent Cochrane reviews conclude that supplementation of formula with DHA and AA cannot be recommended based on current evidence.5,6 Additionally, these formulas cost more than formulas without the above additives.
Preterm and Enriched Formulas
Preterm infants have higher protein and calorie requirements. In addition, they need more calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus (minerals transferred in utero during the third trimester). These special requirements led to the development of enriched and preterm formulas designed to facilitate “catch-up” growth. Preterm formulas contain 24 kcal per ounce, whereas enriched formulas contain 22 kcal per ounce. Enriched formulas are available in stores as liquid or powder. Preterm formulas must be ordered in ready-to-feed bottles and are more expensive.
It is currently the standard of care to prescribe these formulas for preterm infants. Cut-offs for weight and gestational age are based on expert opinion, with variation between institutions. Infants are usually transitioned from 24 to 22 kcal per ounce when they achieve a weight of 1,800 g (3 lb, 15 oz) or 34 weeks' gestational age.7 Hospital discharge is rare before 34 weeks, so infants presenting for outpatient care are typically on 22-kcal formula. There are no studies to guide timing for the discontinuation of enriched formula. Although preterm and enriched formulas may improve short-term growth parameters, they do not appear to affect longer-term growth or development at 18 months of age.8
Specialized Term Formulas
| Mechanism | Condition | Onset | Symptoms | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme deficiency (inability to digest carbohydrate) | Congenital lactase deficiency | Birth | Intractable diarrhea as soon as formula is given; life-threatening | Case reports only |
| Primary lactase deficiency | Infancy, childhood | Gas, fussiness, emesis, diarrhea; may be difficult to distinguish from colic | 20 percent of Hispanic, Asian, and black children; less common in white children; overdiagnosed in infancy | |
| Secondary lactase deficiency | Following gastroenteritis, chemotherapy, etc. | Gas, fussiness, emesis, diarrhea; occurs after small bowel injury; temporary | Common | |
| Immunoglobulin E-mediated allergy (antibodies against cow's-milk protein) | Milk protein allergy | Infancy | Eczema (most common presentation), wheezing, or gastrointestinal symptoms | 2 to 3 percent of infants |
SOY FORMULAS
Despite limited indications for its use, soy formula accounts for almost 25 percent of formula sales in the United States.11 These formulas are made with corn-based carbohydrate and soy protein, making them free of lactose and cow's-milk protein. Many parents believe that this improves digestibility.
According to a recent guideline from the AAP, the use of soy formula should be limited to infants with galactosemia or congenital lactase deficiency.11 Soy formula may also be used by strict vegan families who wish to avoid animal protein. The AAP guideline cites a lack of proven benefit for other conditions including milk protein allergy, generalized colic, and acute gastroenteritis.
One cohort study identified soy formula as a risk factor for the development of peanut allergy (odds ratio = 2.6; 95% confidence interval, 1.3 to 5.2).14 A subsequent randomized controlled trial failed to demonstrate any such association.15 Thus, the evidence regarding soy formula and peanut allergy is mixed; additional studies are needed. Soy formulas are not effective for the prevention of atopic disease.16
Soy protein contains phytoestrogens and isoflavones, which have been shown to have estrogenic effects in animals. Early concerns were raised that these compounds might have deleterious hormonal effects on growing infants. A retrospective cohort study demonstrated increased menstrual bleeding in women exposed to soy during infancy, but found no statistical difference in more than 30 other variables studied.18 Feminization has not been seen in male infants fed soy protein.19
Multiple studies have confirmed normal growth in term infants fed soy formula. In contrast, preterm infants have significantly less weight gain when they are fed soy formula instead of standard formula with similar caloric density.20 Osteopenia of prematurity is also increased.21 Thus, soy formula should never be used for preterm infants.11
Despite widespread use of soy formula, evidence-based indications are limited. Family physicians should direct parents toward breastfeeding and cow's-milk–based formulas in most cases.
LACTOSE-FREE FORMULAS
Lactose-free formulas are an alternative to soy formula for parents wishing to avoid lactose. Lactose-free formulas are indicated for galactosemia and congenital lactase deficiency, as well as primary lactase deficiency. Infants with perceived gastrointestinal symptoms require a hydrogen breath test or intestinal biopsy to formally diagnose lactase deficiency. In reality, most physicians instead suggest a trial of lactose-free formula to see if symptoms improve. Lactose intolerance is over-diagnosed in infancy; most proven cases develop after 12 months of age.9
Temporary lactase deficiency can also occur following acute gastroenteritis. Soy and lactose-free formulas shorten the course of diarrhea, but do not change overall recovery or weight two weeks after the illness.17 Most infants can safely continue breast milk or standard formula during diarrheal illnesses.22 At-risk infants (those younger than three months or those who are malnourished) might benefit from a switch to lactose-free formula following acute gastroenteritis.9
HYPOALLERGENIC AND NONALLERGENIC FORMULAS
Only a small minority of infants have true immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated milk protein allergy. In these cases, infants form antibodies against large protein molecules in cow's milk. Milk protein allergy can present with any combination of cutaneous, respiratory, and gastrointestinal complaints; blood in the stool is a classic symptom. Milk protein allergy is usually diagnosed in the setting of a strong family history of allergies or atopic disease. Referral to an allergist may be helpful because skin prick tests and IgE levels for cow's-milk protein are available. Non-IgE-mediated cow's-milk protein intolerance can manifest as enteropathy and enterocolitis. Because most infants with milk-induced enteropathy will be equally sensitive to soy protein, hypoallergenic and nonallergenic formulas are the preferred alternatives.11
Hypoallergenic formulas contain extensively hydrolyzed proteins that are less likely to stimulate antibody production. Infants with milk protein allergy fed hypoallergenic formula have slightly greater weight gain during the first year than infants fed standard formula.23 In addition, many infants show improvement in atopic symptoms. A few infants continue to have symptoms despite switching to hypoallergenic formula; nonallergenic amino acid–based formulas are effective for these rare cases.24
The increasing incidence of asthma, eczema, and food allergy has led to substantial interest in the prevention of atopic disease. There is strong evidence that exclusive breastfeeding until at least four months of age decreases the incidence of eczema and protects against wheezing.25 It appears that formulas with extensively hydrolyzed proteins may also have protective benefits,16 but the higher expense of hypoallergenic formulas must be considered when deciding whether to recommend them for prevention in asymptomatic infants. Amino acid–based formulas have not been studied for prevention of atopic disease.
ANTIREFLUX FORMULAS
Gastroesophageal reflux is common in infants partly because of a decreased resting tone of the lower esophageal sphincter. Reflux may be considered physiologic and does not require treatment unless it is accompanied by poor weight gain or significant infant discomfort. Nevertheless, reflux is a common source of parental concern, creating demand for antireflux formulas thickened with added rice starch. Before commercial development of these formulas, parents had to add rice cereal or another carbohydrate to standard infant formula. Prethickened formulas are more convenient and do not require enlargement of nipple holes (as required when rice cereal is added to standard formula).
Antireflux formulas have been shown to decrease daily episodes of regurgitation and emesis.12,26 It is not clear whether they improve long-term outcomes, such as growth or development. Although most parents should be reassured that gastroesophageal reflux is normal and will resolve with time, antireflux formulas appear safe and nutritionally adequate for severe or persistent cases.
Infant Formula and Colic
Parents often change formulas in response to infant colic. Soy and lactose-free formulas are heavily marketed for colic without a formal diagnosis of lactose intolerance. Most colic improves spontaneously between four and six months of age; new formulas tried during this time may be credited with the improvement, perpetuating the popular belief that colic is exacerbated by certain formulas.
Because evidence for soy formula in the treatment of colic is limited and based on poor-quality trials, the AAP concluded that there is no proven role for soy in the management or prevention of colic.11,27,28 There is no evidence to support lactose-free formula either, but a short trial may be reasonable in infants with colic who also have gastrointestinal symptoms. Two systematic reviews have found some benefit with hypoallergenic formula13,29; this potential benefit must be weighed against substantially greater cost. Physicians may recommend a one- to two-week trial of hypoallergenic formula for refractory cases. Counseling parents about infant crying appears to reduce symptoms of colic more than any change in formula.30
Toddler Formulas
Recently, toddler or “next step” formulas have been developed for children nine to 24 months of age. These milk-based formulas contain added iron, vitamin C, vitamin E, and zinc. They also contain DHA and AA and more calcium than standard infant formulas (but not significantly more than whole milk).
Manufacturers' information describes toddler formula as “insurance” or “extra nutrition” for picky toddlers who may not eat a well-balanced diet of solids. There is no evidence of advantage over whole milk in terms of growth or development; head-to-head trials are needed. Because toddler formulas are significantly more expensive than whole milk, family physicians can counsel parents against routine use. Parents who remain concerned about picky eaters could be directed toward a multivitamin instead.