
Am Fam Physician. 2001;64(7):1199-1207
See patient information handout on interstitial cystitis, written by the author of this article
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic, severely debilitating disease of the urinary bladder. Excessive urgency and frequency of urination, suprapubic pain, dyspareunia, chronic pelvic pain and negative urine cultures are characteristic of interstitial cystitis. The course of the disease is usually marked by flare-ups and remissions. Other conditions that should be ruled out include bacterial cystitis, urethritis, neoplasia, vaginitis and vulvar vestibulitis. Interstitial cystitis is diagnosed by cystoscopy and hydrodistention of the bladder. Glomerulations or Hunner's ulcers found at cystoscopy are diagnostic. Oral treatments of interstitial cystitis include pentosan polysulfate, tricyclic antidepressants and antihistamines. Intravesicular therapies include hydrodistention, dimethyl sulfoxide and heparin, or a combination of agents. Referral to a support group should be offered to all patients with interstitial cystitis.
Patients with irritative voiding symptoms and negative urine cultures frequently present a diagnostic challenge for primary care physicians. Interstitial cystitis is a severely debilitating disease of the urinary bladder. Symptoms of interstitial cystitis include excessive urgency and frequency of urination, suprapubic pain, dyspareunia and chronic pelvic pain.1 Interstitial cystitis interferes with employment, social relationships and sexual activity. The course of the disease is usually marked by flare-ups and remissions. Interstitial cystitis is a chronic disease that persists throughout the patient's life. On clinical evaluation, patients with interstitial cystitis should have no other definable pathology, such as urinary infections, carcinoma, or radiation-induced or medication-induced cystitis (Parsons CL. Interstitial cystitis, new concepts in pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Presentation at 3rd annual meeting of the American Urological Association, June 4, 1998, San Diego, Calif.).
Epidemiology
The nonulcer type of interstitial cystitis occurs in about 90 percent of patients. The more severe form of the disease (in about 10 percent of patients) involves Hunner's ulcers, which are lesions that involve all of the layers of the bladder wall and appear as brownish-red patches on the bladder mucosa.
Most patients consult at least five physicians, including psychiatrists, over a period of more than four years before interstitial cystitis is diagnosed. Symptomatic patients require considerably more medical care than their age-matched cohorts.7
Etiology
While the exact cause of interstitial cystitis is not known, it is probably related to many factors, including autoimmune, allergic and infectious etiologies.2
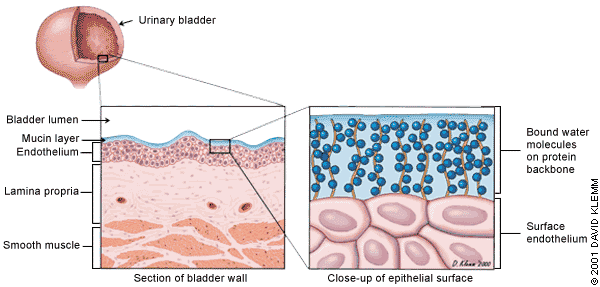
According to one widely held theory, the symptoms of interstitial cystitis originate from a defect in the glycosaminoglycan component of the mucin layer that covers and protects the bladder urothelium8 (Figure 1). A deficiency of this layer is thought to cause interstitial cystitis. Low rates of urinary glycosaminoglycan excretion have been found in patients with interstitial cystitis. The glycosaminoglycan hypothesis is the basis for treating interstitial cystitis with glycosaminoglycan “replacements,” such as sodium pentosan polysulfate (an exogenous, oral glycosaminoglycan) and heparin or hyaluronic acid administered intravesically.8,9 Irritating substances in the urine may leak through the urothelium, causing inflammation, tissue irritation and injury, mast cell degranulation and sensory nerve depolarization, which result in the urinary urgency, frequency and pain of interstitial cystitis.5,6,10 Glycosaminoglycans are highly hydrophilic and protective. They maintain a stable layer of water between the urothelium and the bladder lumen, and prevent adhesion to and invasion of the urothelium by bacteria, microcrystals, ions, proteins and other substances in the urine.
Another working theory of interstitial cystitis etiology includes mast cell abnormalities. Mast cells are present in the bladder wall of many patients with interstitial cystitis. Increased numbers of submucosal mast cells are found in these patients.11,12 Antigenic exposure of mast cells causes the release of pharmacologically active mediators (e.g., histamine, prostaglandins, leukotrienes and tryptases) that have a significant effect on smooth muscle, vascular epithelium and inflammation.
OTHER ETIOLOGIC FACTORS
A psychologic etiology of interstitial cystitis has been mentioned, only to be condemned. Research has shown that definite objective abnormalities are present in patients with interstitial cystitis, including findings on bladder biopsy and cystoscopy. The chronic pain, frequency, urgency and sleep deprivation associated with interstitial cystitis may contribute to psychologic stress and secondary depression. Suicidal ideation is three to four times more common in patients with interstitial cystitis than in the general population.15 More than one half of symptomatic patients with interstitial cystitis have depression. Chronic bladder and pelvic pain is usually moderate to severe.1,8,16
An unexplained association has been found between interstitial cystitis and other chronic disease or pain syndromes such as allergies, irritable bowel syndrome, skin sensitivity, vulvodynia, fibromyalgia, migraine, endometriosis and chronic fatigue syndrome.17 Dyspareunia is not uncommon in persons with interstitial cystitis and may be related to the mechanical effects of intercourse on the inflamed bladder.
APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS
Interstitial cystitis is often underdiagnosed or improperly diagnosed. A presumptive diagnosis may be made by looking for appropriate clinical criteria. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) developed inclusion and exclusion criteria for patients who are being considered for interstitial cystitis research (Table 1).18 While the NIDDK criteria are useful for research, they are too restrictive to be used by physicians in diagnosing interstitial cystitis. Inclusion criteria would involve bladder pain, urinary urgency and frequency, bladder capacity of less than 350 mL and cystoscopic evidence of Hunner's ulcers. Strict application of the NIDDK criteria would have misdiagnosed more that 60 percent of patients who were diagnosed by researchers as definitely having or likely to have interstitial cystitis.6
The most typical symptom of interstitial cystitis is pelvic pain. The pain is relieved by voiding small amounts of urine from the bladder, but soon recurs as the bladder fills. Another common symptom is an uncomfortable, constant urge to void that does not go away even after the patient has voided. Incontinence is not typical of interstitial cystitis and, if present, requires that other diagnoses be diligently sought. Dyspareunia (on deep penetration) is not uncommon in patients with interstitial cystitis.
The symptoms of interstitial cystitis typically worsen in the week before menstruation in contrast to the symptoms of endometriosis, which are worse during menses. Sometimes the symptoms of interstitial cystitis are exacerbated after patients consume certain foods, especially coffee, alcohol, carbonated drinks, citrus fruits, tomatoes and chocolate.19 Conditions that must be excluded to diagnose interstitial cystitis include bacteriuria, Chlamydia trachomatis infection, prostatitis, herpes simplex virus infection, neoplasia, neuropathic bladder dysfunction and gynecologic diseases such as vaginitis, urethral diverticulum, vulvar vestibulitis and endometriosis.
| Presence of urgency or frequency, or pelvic/perineal or bladder pain |
| Presence of glomerulations (pinpoint submucosal hemorrhages) or ulcers on cystoscopic examination with hydrodistention under anesthesia |
| Negative urine culture |
| Absence of genitourinary infections or prostatitis |
| Absence of neoplastic diseases or benign bladder tumor |
| Absence of history of radiation, tuberculosis or chemical cystitis (e.g., following cyclophosphamide [Cytoxan] therapy) |
Urinary frequency in patients with interstitial cystitis averages 16 times per day but can be as much as 40 times per day. Nonbacteriuric patients with pyuria should be tested or empirically treated for Chlamydia infection.20
A careful pelvic examination is needed to rule out vaginitis, vulvar lesions and urethral diverticula. Pelvic examination in women often reveals tenderness of the bladder base. Patients should be asked to keep a 24-hour log of voiding activity for frequency of urination and voiding patterns. The patient may be accustomed to an abnormal pattern. Findings on urinalysis may be entirely normal or may show microscopic hematuria or pyuria. Urine culture results are usually sterile. However, patients with interstitial cystitis may also have a concurrent bladder infection. Urine cytology may be helpful in ruling out transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder.21 If indicated, tuberculosis may be ruled out with urine testing for acid-fast bacillus, or bladder biopsy.
Urodynamic studies are not specifically diagnostic of interstitial cystitis. Radiographic studies, such as intravenous pyelography or voiding cystourethrography, are seldom indicated in the evaluation of patients with suspected interstitial cystitis.6





After the above evaluations are completed, confirmation of the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis depends on cystoscopic findings. Hydrodistention of the bladder is often performed during cystoscopy under general anesthesia. Hydrodistention consists of filling the bladder with saline solution or sterile water beyond its normal capacity. On distention, pinpoint hemorrhages or fissures with bleeding, called glomerulations, may appear6,21(Figure 2). Glomerulations may be seen in various types of bladder conditions and may also be seen in asymptomatic women.22
Hunner's ulcers (Figure 3) and severe reductions in bladder capacity are found infrequently because most patients have the nonulcer variety of interstitial cystitis. Reductions in bladder capacity are manifested by scarring of the bladder wall (Figures 4a and 4b). Following bladder hydrodistention, terminal blood tinge of the draining distention fluids occurs in about 90 percent of patients. Biopsies are indicated in patients with suspected interstitial cystitis to exclude specific bladder pathology such as carcinoma, dysplasia or tuberculosis; to confirm bladder wall inflammation; and to identify subgroups of patients, such as those with excessive mast cells or eosinophils.11 Generally, cystoscopy and bladder biopsy are performed in ambulatory surgery settings.6 The hydrodistention performed at the time of cystoscopy may be therapeutic.6 This relief may last from several weeks to months. Figure 5 depicts the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis.
MEDICAL THERAPY
Although treatment is usually nonspecific and empiric, relief of the symptoms of interstitial cystitis should be the goal6 (Table 220 ). Support, understanding and reassurance should be provided by caregivers and family. The patient should be told that interstitial cystitis is not a malignancy or a harbinger of systemic disease.23 Treatment, especially in young patients with nonulcer interstitial cystitis, should involve the least invasive therapy that provides reasonable symptomatic improvement. Patients should be counseled that treatment is meant to alleviate symptoms, that there is not yet a specific cure and that the disease is chronic in nature. The rationale for each treatment option and the possible necessity of changing medications and using combination treatments should be emphasized.
Acidic foods, caffeine, alcohol, artificial sweeteners and chocolate may aggravate the symptoms of interstitial cystitis in some patients and should be avoided.16
ORAL TREATMENTS
First-line oral treatments for interstitial cystitis include tricyclic antidepressants, antihistamines and pentosan polysulfate (Elmiron). No placebo-controlled studies with tricyclic antidepressants have been performed, but these medications have been found to be beneficial in several open-label studies.24 Tricyclic antidepressants block pain arousal and are widely used in pain clinics for their pain blocking effects. Other medications that may reduce the symptoms of interstitial cystitis include sedatives (for improved sleep) and medications that inhibit nociception. Some of the most commonly used tricyclics are amitriptyline (Elavil), doxepin (Sinequan) and imipramine (Tofranil), administered in dosages of 25 to 75 mg at bedtime. These agents may be started at very low dosages and gradually titrated up until symptom relief is obtained or until side effects become bothersome. Use of hydroxyzine (Atarax), an antihistamine, is based on the hypothesis that histamine released by mast cell degranulation may be responsible for symptoms of interstitial cystitis. Hydroxyzine (in a dosage of 25 to 75 mg at bedtime) and the H2-receptor antagonist cimetidine (Tagamet), in a dosage of 300 mg twice daily, were both effective in open-label studies.25,26
| General measures |
| Support and reassurance |
| Elimination of foods that increase |
| Symptoms |
| Oral therapy |
| Pentosan polysulfate (Elmiron)* |
| Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline [Elavil], doxepin [Sinequan], imipramine [Tofranil])† |
| Antihistamines (H1- and H2-receptor antagonists, hydroxyzine [Atarax], cimetidine [Tagamet])† |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs‡ |
| Bladder analgesics‡ |
| Intravesical therapy |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide (Rimso-50)* |
| Heparin† |
| Silver nitrate‡ |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide plus heparin or hydrocortisone† |
| Oxychlorosene, 0.4 percent‡ |
| Bacillus Calmette-Guérin* |
| Other |
| Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation* |
| Physical therapy‡ |
Pentosan polysulfate is the only oral therapy for the treatment of interstitial cystitis symptoms that has been studied in placebo-controlled trials.9,25,27,28 Pentosan polysulfate is a highly sulfated, semisynthetic glucosaminoglycan with chemical and structural similarities to naturally occurring glucosaminoglycans. The medication is well tolerated and has a favorable side effect profile. In one study, bladder pain was relieved by at least 50 percent in 38 percent of patients taking pentosan polysulfate compared with 18 percent improvement in patients treated with placebo.29
It may take three to six months for patients to respond to pentosan polysulfate.29 The usual dosage is 100 mg orally three times per day. Adverse reactions to pentosan polysulfate include diarrhea, dyspepsia, reversible alopecia, headache, rash, dizziness, abdominal pain and uncommon liver function abnormalities (1 to 4 percent).
Although no research has been done, some experts in the treatment of interstitial cystitis combine two of the above oral medications for an enhanced treatment response. Some patients feel better after taking aspirin or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, probably because mast cell degranulation releases prostaglandins and leukotrienes.11 Other drugs that may be used to treat interstitial cystitis are anticholinergics, bladder analgesics such as phenazopyridine (Pyridium) or oxy-butynin chloride (Ditropan), calcium channel blockers such as nifedipine (Procardia), or gabapentin (Neurontin). No studies have been done to show the efficacy of these medications.
INTRAVESICULAR TREATMENTS
Intravesicular pharmacotherapy provides high local drug concentrations in the bladder, avoids systemic side effects and eliminates the problem of low levels of urinary excretion with orally administered agents.11 The most commonly used and only intravesical agent labeled by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of interstitial cystitis is dimethyl sulfoxide (Rimso-50). A controlled study of patients with interstitial cystitis showed that dimethyl sulfoxide was superior to placebo, with 53 percent of patients in the treatment group having significant improvement of symptoms.30 Although dimethyl sulfoxide is an anti-inflammatory agent, it seems to have some analgesic and muscle relaxant properties as well.
Instillations of dimethyl sulfoxide are usually given every one to two weeks for a total of four to eight treatments. Following the initial course of treatment, some patients achieve long-term remission, but most relapse eventually. Additional treatment schedules for those who relapse vary but usually consist of instillation every four to six weeks.6 The technique does not require anesthesia, hospitalization or the use of an operating room. Patients who are suitably motivated and trained can be taught the technique of intermittent self-catheterization and instillation of dimethyl sulfoxide, allowing for self-treatment when symptoms occur. Sometimes dimethyl sulfoxide is combined with heparin, steroids, bicarbonate and a local anesthetic for intravesical administration.6
In an open-label study, 56 percent of patients with interstitial cystitis experienced relief from symptoms using heparin intravesically, in a dosage of 10,000 U three times a week.31 In another study, monthly heparin instillation prolonged the response to dimethyl sulfoxide.32 Instillation of hyaluronic acid, in a dosage of 40 mg weekly, provided complete symptom relief in 25 percent of patients and partial relief in 46 percent.33
In a controlled study using six weekly instillations of bacillus Calmette-Guérin, 60 percent of patients with interstitial cystitis had symptom reduction compared with 27 percent of patients receiving placebo.34
ADJUVANT TREATMENTS
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation resulted in improvement or remission in 54 percent of patients with classic interstitial cystitis (i.e., Hunner's ulcers) and in 26 percent of patients with nonulcer interstitial cystitis.35 Many patients with interstitial cystitis have spasms of the pelvic floor muscles that contribute to symptoms of pelvic pain, urgency and frequency. Physical therapy with biofeedback for pelvic floor relaxation may be helpful in such patients.
Support groups of persons who have the same disorder may be especially helpful. Physician support and attention to associated psychosocial problems can greatly improve the patient's response to treatment.