
Am Fam Physician. 2000;61(10):3025-3026
See related article on prostatitis.
What is prostatitis?
Prostatitis is common and affects many men at some time. Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland. When part of your body is inflamed, it is red, hot and sore. Prostatitis can cause many symptoms. It can make it difficult or painful to urinate. It can make you have to urinate more often. It can also give you a fever, low-back pain or pain in your groin (the area where the legs meet your body). It may make you less interested in having sex or unable to get an erection or keep it. Prostatitis is easy to confuse with other infections in the urinary tract.
What is the prostate gland?
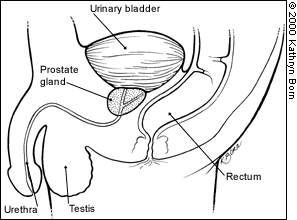
The prostate is a gland that lies just below a man's urinary bladder. It surrounds the urethra like a donut and is in front of the rectum. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the bladder, through the penis and out of the body. Your doctor may check your prostate by putting a finger into your rectum to feel the back of your prostate gland.
The prostate gland makes a fluid that provides nutrients for sperm. This fluid makes up most of the ejaculate fluid. We do not yet know all of the ways the prostate gland works.
What causes prostatitis?
Prostatitis is divided into categories based on cause. Two kinds of prostatitis, acute prostatitis and chronic bacterial prostatitis, are caused by infection of the prostate. Some kinds of prostatitis might be caused when the muscles of the pelvis or the bladder don't work right.
How is prostatitis treated?
The treatment is based on the cause. Your doctor may do a rectal exam and test urine samples to find out the cause.
An antibiotic is used to treat prostatitis that is caused by an infection. Some antibiotics that might be used are trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxin. You might have to take antibiotics for several weeks or even a few months. If prostatitis is severe, you might have to go to a hospital for treatment with fluids and antibiotics.
What if my prostatitis is not caused by infection?
Because we do not understand what causes prostatitis without infection, it can be hard to treat. Your doctor might try an antibiotic to treat a hidden infection. Other treatments are aimed at making you feel better. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, and hot soaking baths may help you feel better. Some men get better by taking medicines that help the way the bladder or prostate gland work. These medicines include oxybutynin, doxazosin, prazosin, tamsulosin and terazosin.
Can prostatitis be passed on during sex?
Sometimes prostatitis is caused by a sexually transmitted organism, such as chlamydia. However, most cases are caused by infections that are not sexually transmitted. These infections can't be passed on to sexual partners.
Can prostatitis come back?
Men who have had prostatitis once are more likely to get it again. Antibiotics may not get into the prostate gland well. Small amounts of bacteria might “hide” in the prostate and not be killed by the antibiotic. Once you stop taking the antibiotic, the infection can get bad again. If this happens, you might have to take antibiotics for a long time to prevent another infection. Prostatitis that is not caused by infection is often chronic. If you have this kind of prostatitis, you might have to take medicine for a long time.
Should I have my prostate gland taken out if I have prostatitis?
Prostatitis can usually be treated with medicine. Most of the time, surgery is not needed.
Does prostatitis cause cancer?
Although prostatitis can cause you trouble, it does not cause cancer. There is a blood test some doctors use for prostate cancer called the prostate-specific antigen test (called the PSA, for short). If you have prostatitis, your PSA level might go up. This does not mean you have cancer. Your doctor will treat your prostatitis and may check your PSA level again.