
Am Fam Physician. 2011;83(1):39-46
Patient information: See related handout on stress fractures, written by the authors of this article.
Author disclosure: Nothing to disclose.
Stress fractures are common injuries in athletes and military recruits. These injuries occur more commonly in lower extremities than in upper extremities. Stress fractures should be considered in patients who present with tenderness or edema after a recent increase in activity or repeated activity with limited rest. The differential diagnosis varies based on location, but commonly includes tendinopathy, compartment syndrome, and nerve or artery entrapment syndrome. Medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints) can be distinguished from tibial stress fractures by diffuse tenderness along the length of the posteromedial tibial shaft and a lack of edema. When stress fracture is suspected, plain radiography should be obtained initially and, if negative, may be repeated after two to three weeks for greater accuracy. If an urgent diagnosis is needed, triple-phase bone scintigraphy or magnetic resonance imaging should be considered. Both modalities have a similar sensitivity, but magnetic resonance imaging has greater specificity. Treatment of stress fractures consists of activity modification, including the use of nonweight-bearing crutches if needed for pain relief. Analgesics are appropriate to relieve pain, and pneumatic bracing can be used to facilitate healing. After the pain is resolved and the examination shows improvement, patients may gradually increase their level of activity. Surgical consultation may be appropriate for patients with stress fractures in high-risk locations, nonunion, or recurrent stress fractures. Prevention of stress fractures has been studied in military personnel, but more research is needed in other populations.
Stress fractures are common injuries that begin with repetitive and excessive stress on the bone. This leads to the acceleration of normal bone remodeling, the production of microfractures (caused by insufficient time for the bone to repair), the creation of a bone stress injury (i.e., stress reaction), and, eventually, a stress fracture.1,2 In contrast, pathological (insufficiency) fractures occur under normal stress in bone weakened by a tumor, infection, or osteoporosis.1,2
| Clinical recommendations | Evidence rating | References | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plain radiography should be the initial imaging modality to diagnose stress fractures. | C | 15 | Consensus opinion |
| Magnetic resonance imaging is preferred over bone scintigraphy for the diagnosis of stress fractures because of greater specificity. | C | 15 | Consensus opinion |
| Patients with tibial stress fracture may use a pneumatic compression device to reduce the time to resumption of full activity. | A | 20 | Cochrane review |
| Bone stimulators should not be used for the treatment of most stress fractures. | B | 24, 25 | Good-quality randomized controlled trial |
| Shock-absorbing orthotics and footwear modification may reduce the occurrence of lower extremity stress injury. | B | 20 | Cochrane review lacking firm recommendation |
The most common locations for stress fractures are the tibia (23.6 percent), tarsal navicular (17.6 percent), metatarsal (16.2 percent), fibula (15.5 percent), femur (6.6 percent), pelvis (1.6 percent), and spine (0.6 percent).3,4 Although less common, upper extremity stress fractures can occur in persons who participate in sports involving throwing or other overhead motions.5
Persons who participate in repetitive, high-intensity training, such as athletes and military recruits, are at increased risk of developing stress fractures.3–6 Recreational runners who average more than 25 miles per week are at increased risk of stress fractures,4,7 as well as athletes who participate in track and field, basketball, soccer, or dance (Table 12–9 ).3,5 Women are at higher risk of stress fracture than men,4 especially women in the military,2 although there are conflicting data among female athletes.3,5

| Consuming more than 10 alcoholic drinks per week |
| Excessive physical activity with limited rest periods |
| Female athlete triad (eating disorders, amenorrhea, osteoporosis) |
| Female sex |
| Low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D |
| Recreational running (more than 25 miles per week) |
| Smoking |
| Sudden increase in physical activity |
| Track (running sports) |
Poor nutrition and lifestyle habits may increase the risk of stress fracture. One study found lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in Finnish male military recruits with stress fractures.8 Women with the female athlete triad (i.e., eating disorders, functional hypothalamic amenorrhea, and osteoporosis) are at higher risk of stress fracture.9 A study of female military recruits demonstrated an increased risk of stress fracture with a history of smoking, exercising less than three times per week, and consuming more than 10 alcoholic drinks per week before the start of basic training.6 Additionally, 16.2 percent of white recruits who smoked and did not exercise developed a stress fracture.6
Diagnosis
Stress fracture should be suspected in persons with a drastic recent increase in physical activity or repeated excessive activity with limited rest.5–7,10 Pain is a common presenting symptom that can vary by location, such as knee pain with a proximal tibial injury, hip pain with a femoral neck injury, or groin pain with a pelvic fracture.2,7 Specifically, pain with ambulation is common (81 percent).10 On examination, patients usually demonstrate focal tenderness (65.9 to 100 percent) and edema (18 to 44 percent) at the site of injury.4,10,11
Although the hop test (i.e., single leg hopping that produces severe localized pain) is often used and cited in texts as a diagnostic test for lower extremity fractures, no recent literature was found to validate its accuracy. In some studies, a positive hop test was an inclusion criterion4 or a common finding (70 to 100 percent 7,11) in patients with presumed stress fractures, but was also noted in nearly one-half (45.6 percent) of patients with suspected medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints).12 Another diagnostic measure used often, but with little supporting evidence, is the tuning fork test (i.e., applying a tuning fork to the fracture site to produce focal pain). One small study found that the tuning fork test had a sensitivity of 75 percent, a specificity of 67 percent, a positive predictive value of 77 percent, and a negative predictive value of 63 percent for tibial stress fractures.13
Diagnosing stress fractures can be challenging and warrants consideration of the differential diagnosis, based on location (Table 23,6,7,14 ). The differential diagnosis may include tendinopathy, compartment syndrome, and nerve or artery entrapment syndrome. Medial tibial stress syndrome is a common condition that can be distinguished from tibial stress fractures by nonfocal tenderness (diffuse along the mid-distal, posteromedial tibia) and a lack of edema.12 The differential diagnosis may also include a variety of malignancies, such as osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma.1
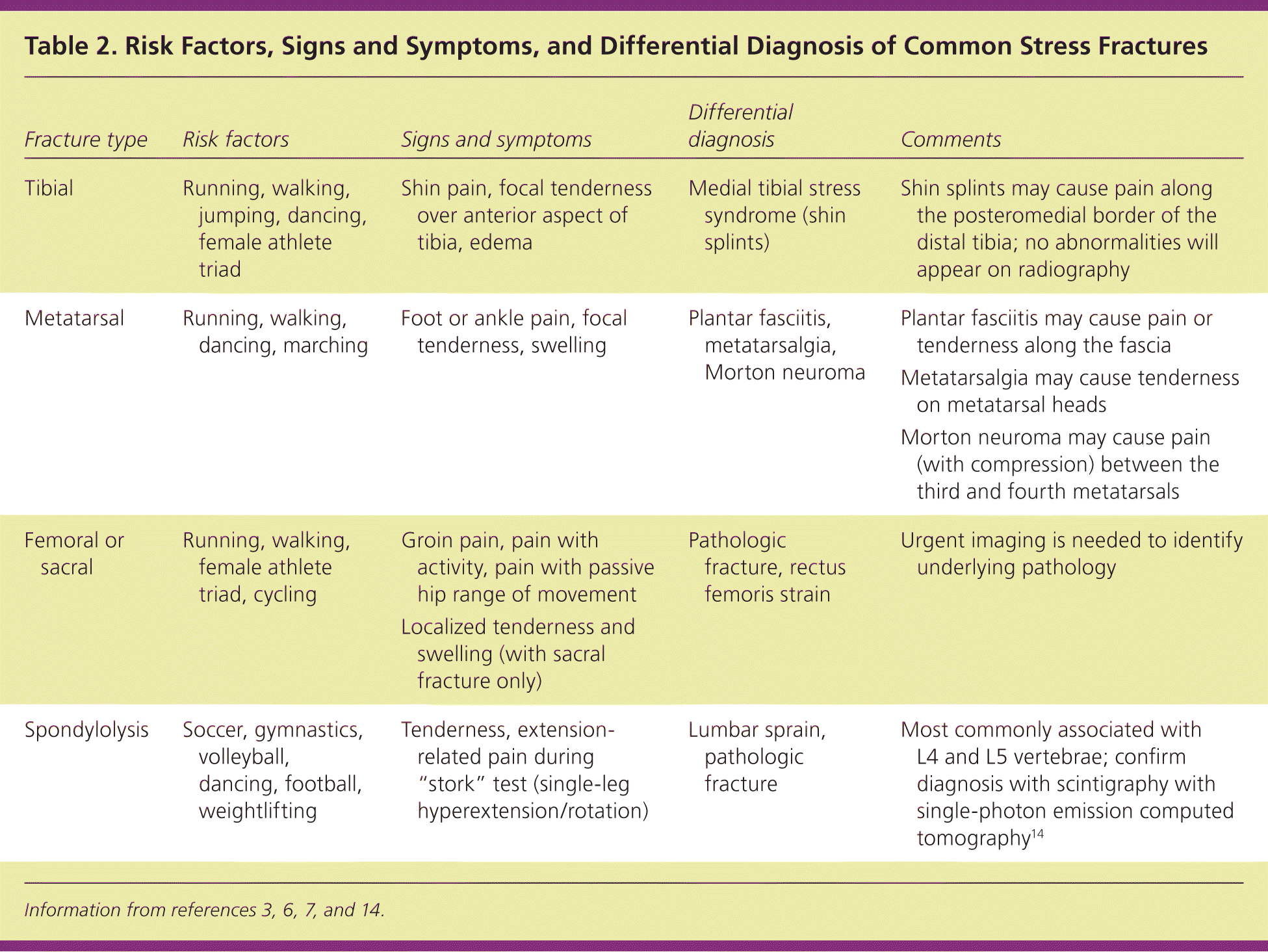
| Fracture type | Risk factors | Signs and symptoms | Differential diagnosis | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibial | Running, walking, jumping, dancing, female athlete triad | Shin pain, focal tenderness over anterior aspect of tibia, edema | Medial tibial stress syndrome (shin splints) | Shin splints may cause pain along the posteromedial border of the distal tibia; no abnormalities will appear on radiography |
| Metatarsal | Running, walking, dancing, marching | Foot or ankle pain, focal tenderness, swelling | Plantar fasciitis, metatarsalgia, Morton neuroma | Plantar fasciitis may cause pain or tenderness along the fascia |
| Metatarsalgia may cause tenderness on metatarsal heads | ||||
| Morton neuroma may cause pain (with compression) between the third and fourth metatarsals | ||||
| Femoral or sacral | Running, walking, female athlete triad, cycling | Groin pain, pain with activity, pain with passive hip range of movement | Pathologic fracture, rectus femoris strain | Urgent imaging is needed to identify underlying pathology |
| Localized tenderness and swelling (with sacral fracture only) | ||||
| Spondylolysis | Soccer, gymnastics, volleyball, dancing, football, weightlifting | Tenderness, extension-related pain during “stork” test (single-leg hyperextension/rotation) | Lumbar sprain, pathologic fracture | Most commonly associated with L4 and L5 vertebrae; confirm diagnosis with scintigraphy with single-photon emission computed tomography14 |
Imaging
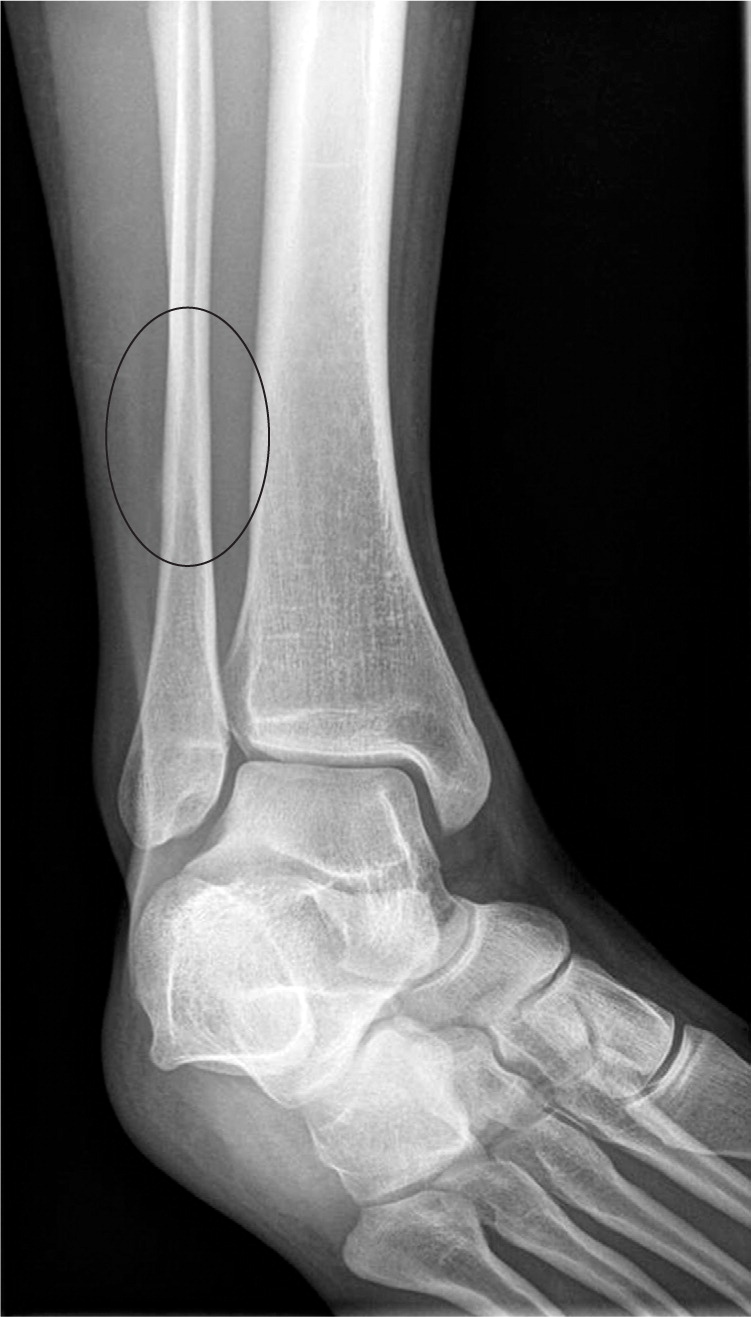
Plain radiography should be the first imaging modality considered because of its availability and low cost (Table 34,10–12,15–17; Figure 1).15 Plain radiography is usually negative initially but is more likely to become positive over time (e.g., initial sensitivity of 10 percent4; sensitivity of 30 to 70 percent after three weeks11). If the initial radiography is negative and an urgent diagnosis is not needed, repeat radiography may be performed after two to three weeks. One algorithm used in the military advocates radiography two weeks after the onset of symptoms (if symptoms persist), with repeat radiography the following week before performing more advanced imaging.6 With plain radiography, a faint lucency may be seen at first, although stress fractures are usually identified by subsequent indirect findings: periosteal thickening or sclerosis, cortical changes with initial decreased density (“gray cortex”), and, more commonly, later callus formation, or endosteal thickening and sclerosis 5,11 (Figure 2).
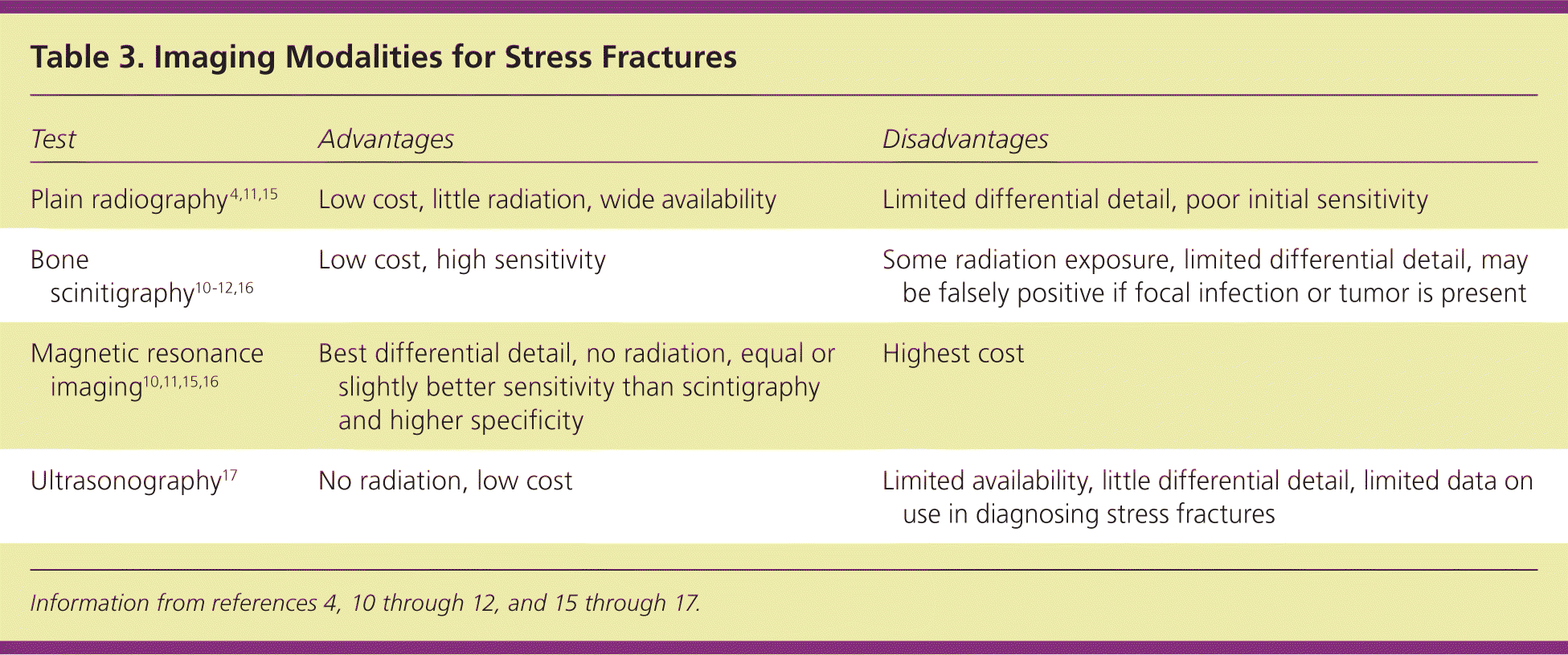
| Test | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Plain radiography 4,11,15 | Low cost, little radiation, wide availability | Limited differential detail, poor initial sensitivity |
| Bone scinitigraphy10–12,16 | Low cost, high sensitivity | Some radiation exposure, limited differential detail, may be falsely positive if focal infection or tumor is present |
| Magnetic resonance imaging10,11,15,16 | Best differential detail, no radiation, equal or slightly better sensitivity than scintigraphy and higher specificity | Highest cost |
| Ultrasonography17 | No radiation, low cost | Limited availability, little differential detail, limited data on use in diagnosing stress fractures |
Although computed tomography (CT) is regularly used for evaluation of bone pathology, its value is limited because of lower sensitivity and higher radiation exposure than other imaging modalities.16 Thin-slice (16-detector) multisection CT has shown promise, but remains inferior to other modalities, such as scintigraphy and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).18
Triple-phase bone scintigraphy (Figure 3) was previously the confirmation test for stress fracture in most studies3–5,7,10 because of its high sensitivity (74 to 100 percent10,16). With scintigraphy, nonfocal radionuclide accumulation is less likely to be caused by stress fracture 11; uptake that is spread diffusely along the tibia is more consistent with medial tibial stress syndrome.10,12 Scintigraphy may be falsely positive in other cases of increased bone activity, such as focal infection and tumors.1 Scintigraphy with single-photon emission CT is preferred over MRI in patients with spondylolysis.14
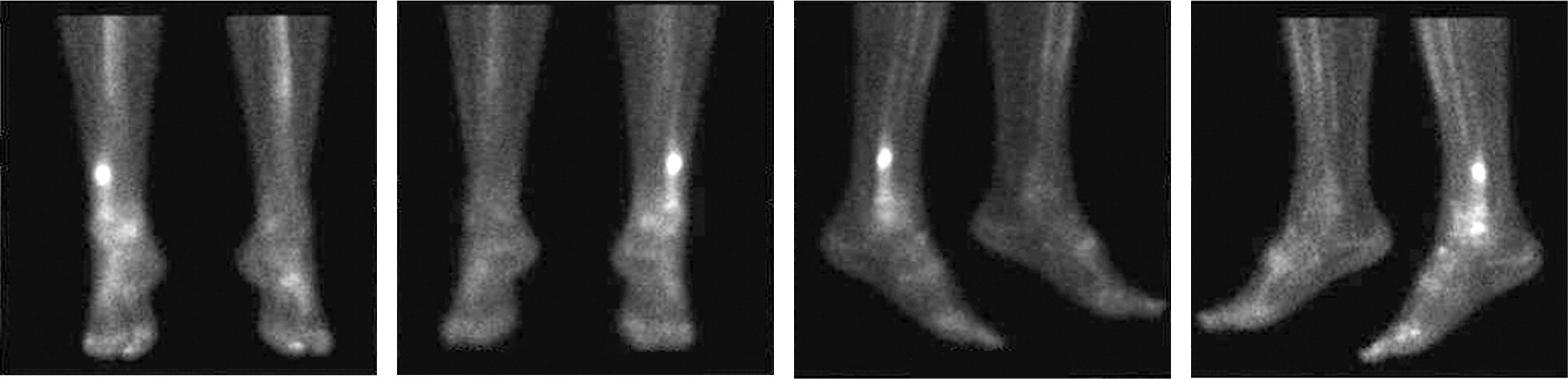
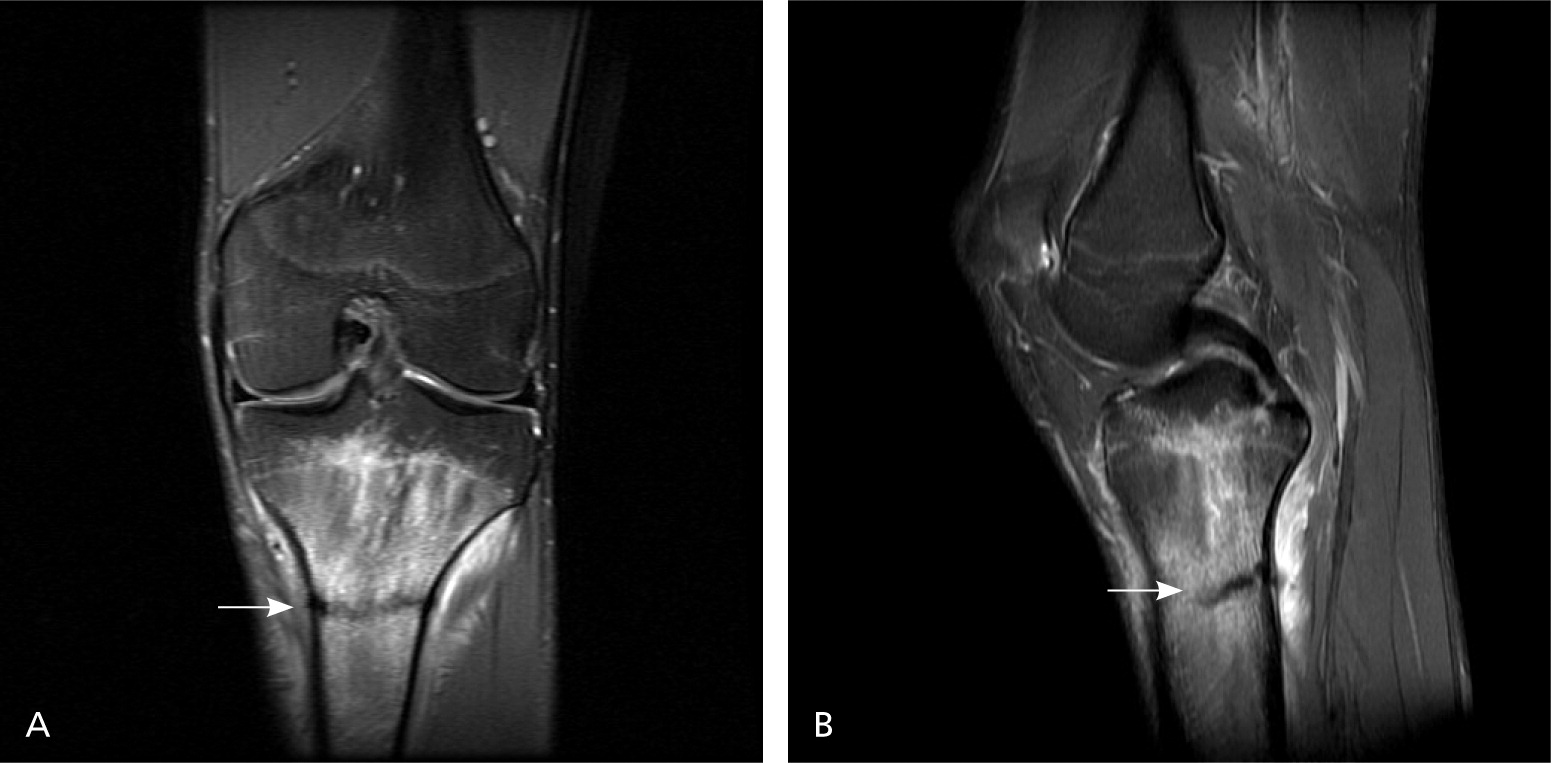
Despite limitations of cost and availability, MRI has replaced scintigraphy as the confirmation test used in most studies.10,11,16 MRI has a sensitivity equal to or slightly better than scintigraphy, but with higher specificity (Table 34,10–12,15–17 ).10,11 For this reason, an expert panel of the American College of Radiology says that MRI may be considered next when plain radiography is negative.15 Because MRI provides greater detail of surrounding tissue (Figure 4), it may be advantageous for evaluating the differential diagnosis.15 One prospective study compared MRI, CT, and bone scintigraphy for evaluation of early tibial bone stress injuries based on the premise that early detection could prevent stress fractures.16 MRI was superior for detection of early stress injury, although both MRI and bone scintigraphy identified the actual stress fractures. However, MRI may also identify reactive bone remodeling (interpreted as early stress injuries) and, therefore, should be clinically correlated for stress fracture.12,19 In a study of asymptomatic collegiate runners, 43 percent were found to have stress injury on MRI.19 None of the stress injuries progressed to stress fractures, and all were resolved at the one-year followup.19 Another study of shin splints demonstrated similar bone stress changes on MRI, including 80 percent of asymptomatic control patients.12
Although musculoskeletal ultrasonography is becoming more widely available, limited data exist for its use in diagnosing stress fractures. One small prospective pilot study found that ultrasonography had a sensitivity of 83.3 percent, a specificity of 75.0 percent, a positive predictive value of 58.8 percent, and a negative predictive value of 91.7 percent for metatarsal stress fractures.17 The potential advantages of ultrasonography include low cost and no radiation exposure, but additional studies are needed.
Treatment
Depending on the injury, healing time for stress fractures can vary from four to 12 weeks or longer from the time activity is restricted.4,5 Initial treatment should include reducing activity to the level of pain-free functioning. Treatment should begin as soon as the injury is suspected, because delayed treatment has been correlated with prolonged return to activity.5 Table 4 summarizes general preventive measures and treatment options for stress fractures.4,20–23

| Prevention |
| Address modifiable risk factors (Table 1) |
| Modify activity level or training patterns, and ensure adequate rest20 |
| Consider daily supplementation of calcium (2,000 mg) and vitamin D (800 IU)21 |
| Address abnormal biomechanics if needed, and consider shock-absorbing shoe inserts20 |
| Treatment |
| Reduce activity to the level of pain-free functioning22 |
| Consider acetaminophen, which may be favored over nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs23 |
| Stretch and strengthen supporting structures in rehabilitative program4 |
| Increase activity in graduated fashion after several weeks of rest and improved symptoms |
| Use pneumatic compression device (e.g., a stirrup leg brace, compression walking boots) or other biomechanical stress-relieving measures (e.g., crutches) for lower-extremity stress fractures20 |
| Encourage cross training to maintain cardiovascular fitness4 |
| Consider surgery for patients with recalcitrant or high-risk stress fractures22 |
The patient can be examined every two to three weeks to ensure pain-free functioning, monitor changes in symptoms, and evaluate improvement in provocative testing. When patients are pain free, they may increase activity in a slow, graduated manner.4
Analgesics, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, may be considered for pain control. However, antiinflammatories should be used with caution, because some animal studies have shown that they may inhibit healing in subjects with traumatic fractures.23
Patients may require limited or full nonweight-bearing crutches to reduce pain. A Cochrane review pooling data from three small studies suggested that patients with tibial stress fracture who used a pneumatic brace (e.g., a stirrup leg brace) showed a significant reduction in time to recommencing full activity; however, more evidence is needed for confirmation.20 Pneumatic compression walking boots may be used to reduce pain from lower extremity stress fractures. Physical therapy and cross training with non-aggravating activities may help maintain flexibility and strength, and cardiovascular fitness, respectively, during the rest period.4
Bone stimulation via electrical or ultrasonic impulses has been an area of growing interest, but evidence is currently lacking. A single randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 26 patients demonstrated no effect from low-intensity ultrasonic impulses in reducing healing time.24 Similarly, a single RCT of 50 patients found no benefit from electrical field stimulation in tibial stress fracture clinical healing.25 However, there is some evidence for the use of stimulation in nonhealing traumatic fractures, and it may also be considered for recalcitrant stress fractures.26
Certain stress fractures may lead to complications, including progression to complete fractures, development of avascular necrosis, or delays in healing or nonunion. Examples of these high-risk stress fractures include the superolateral femoral neck, patella, anterior tibia, medial malleolus, talus, tarsal navicular, and the fifth metatarsal.22 High-risk stress fractures may warrant consultation with an orthopedist or sports medicine subspecialist.
In special circumstances, such as in competitive athletes during their sport's season, patients may choose to modify their activity to a decreased level of intensity (tolerable without exacerbation), and delay complete rest until the season is finished.22 In these situations, athletes should be aware of the potential for prolonged recovery or the need for additional interventions, including surgery.
Prevention
Although various methods have been proposed to prevent stress fractures (Table 44,20–23 ), few have been validated in studies of appropriate magnitude to justify definitive recommendations. Many preventive studies are conducted in military basic training, and their usefulness in other populations is unknown.
Orthotics, such as shock-absorbing shoe inserts, were shown to be effective in reducing the occurrence of lower extremity stress injury in military recruits.20
Calcium and vitamin D metabolism and supplementation may play a role in the prevention of stress fracture, but the data are controversial. The intention-to-treat analysis of a double-blind RCT found a 20 percent lower incidence of stress fractures compared with placebo (5.3 versus 6.6 percent; P = .0026) in female recruits who took a daily calcium supplement (2,000 mg) and vitamin D supplement (800 IU).21 However, after further analysis, the study lacked statistical significance in participants who completed the study per protocol (adjusted odds ratio = 0.789; 95% confidence interval, 0.616 to 1.01; P = .0589).21,27
Bisphosphonates have been proposed for the prevention of stress fractures. However, an RCT in military recruits showed that prophylactic treatment with risedronate (Actonel; 30 mg daily for 10 days, followed by 30 mg weekly for the next 12 weeks) was not effective in reducing total stress fracture incidence, delaying the time to onset, or decreasing the severity of stress fractures incurred.28 Additionally, concerns with bisphosphonates include the potential for abnormal long-term bone deposition (especially in young persons), potential teratogenic effects (U.S. Food and Drug Administration pregnancy category C or D), and lack of approval for this indication from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.29
Data Sources: A PubMed search was completed in Clinical Queries using the following key terms: stress fracture, MRI sensitivity of stress fracture, medial tibial stress, x-ray sensitivity stress fracture, hop test stress fracture, tuning fork test, fulcrum test, spondylolysis, dreaded black line, and stress fracture treatment. The search included meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, and reviews. Also searched were the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality evidence reports, Bandolier, Clinical Evidence, the Cochrane database, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, the Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement, the National Guideline Clearinghouse database, and the Trip database. Search date: March 1, 2010, with repeat searches in July 2010.
