Am Fam Physician. 2014;90(5):319-320
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
A 65-year-old woman presented with a three-month history of erythematous skin patches on her trunk and extremities that were slowly increasing in size and number. The patches were pruritic and unresponsive to diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and cetirizine (Zyrtec). The pruritus interfered with her sleep. She did not have recent illness, exposure to animals, travel, weight loss, fever, or bleeding.
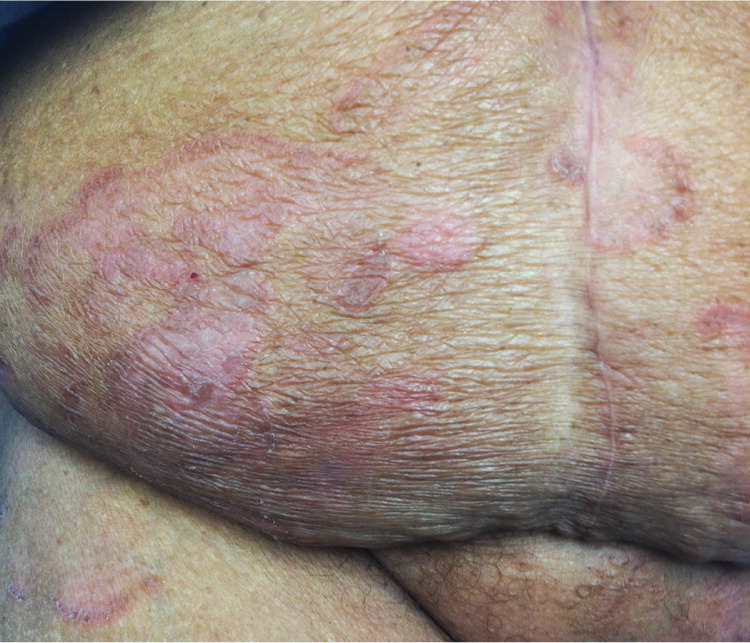
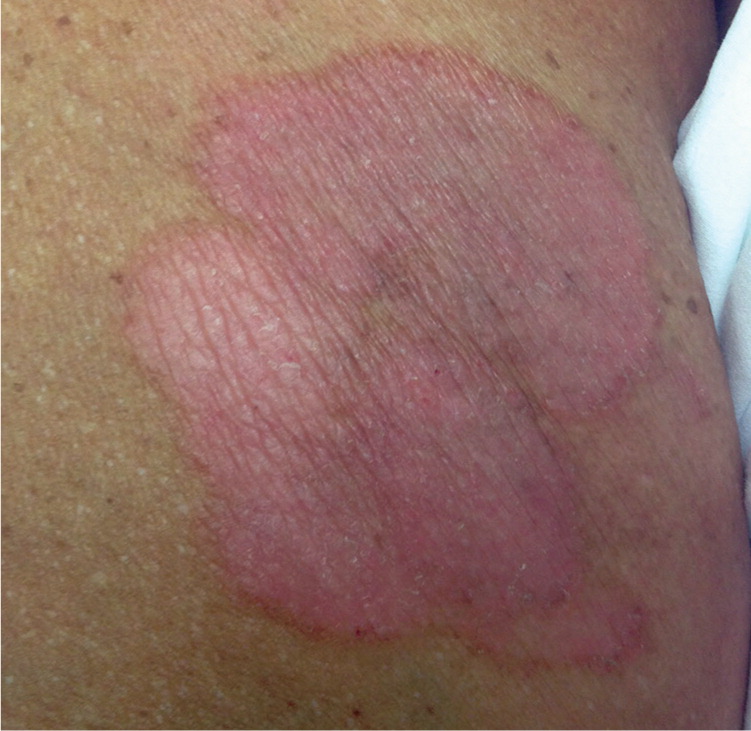
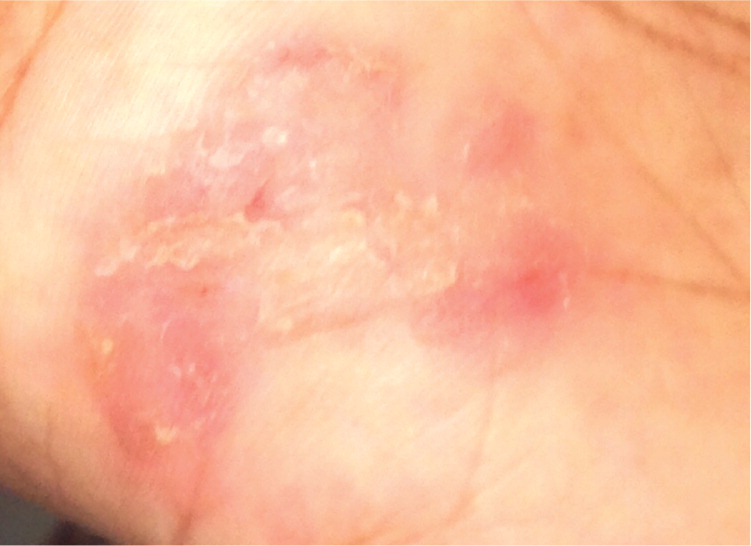
She had a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, allergic rhinitis, and sickle cell trait, and she was taking glyburide, ramipril (Altace), atenolol (Tenormin), hydrochlorothiazide, aspirin, and cetirizine. There was no recent change in her medication use. Physical examination revealed pink, round to oval, confluent patches and plaques on her trunk and extremities (Figures 1 through 3).
Question
Discussion
The answer is C: mycosis fungoides. This disease is a relatively rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and is also known as Sézary syndrome in its advanced stages. It initially presents as asymmetric, pink or reddish skin patches that are gradually replaced with plaques. In the latter phase of the disease, tumors and nodules develop from preexisting plaques. Early on, the lesions are often misdiagnosed as more common skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis. New mycosis fungoides plaques develop on any area of the skin, and older ones fade over days to weeks.1
With mycosis fungoides, the T cells within the skin become cancerous. The disease primarily affects adults older than 50 years and is more common in men than in women. It occurs in persons of color and of African descent more often than in white persons of European descent. Mycosis fungoides is considered the most benign cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, with 40% to 100% of patients surviving for at least 10 years after diagnosis.1
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by pruritic, erythematous, and scaly lesions often located on the flexor surfaces. It is associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis as an allergic triad. Atopic dermatitis can present in three clinical phases: acute (vesicular, weeping, crusting eruption); subacute (dry, scaly, erythematous papules and plaques); and chronic (lichenification from repeated scratching).2
A fixed drug eruption is the result of a drug allergy and manifests as a single or multiple round, sharply demarcated, dusky red plaques or blisters that recur at the same site each time the drug is taken. Lesions can occur on any part of the skin or mucous membranes, but the glans penis is the most common site.3
Nummular eczema is characterized by circular or oval lesions. Initially, this eruption consists of small edematous papules that become crusted and scaly. The lesions remain in the same area and do not increase in size. The common locations are the trunk or the extensor surfaces of the extremities, particularly the pretibial areas and the dorsum of the hands (most common).4
Psoriasis is a T cell–mediated autoimmune disorder that begins with an environmental factor that induces cytokine production. With plaque psoriasis, lesions begin as papules and eventually coalesce to form plaques. Plaques are typically symmetric and bilateral, well demarcated, and covered by a silvery scale. Plaques associated with psoriasis exhibit the Auspitz sign (bleeding with the removal of the scale) and the Koebner phenomenon (lesions are induced by trauma). Common locations include the extensor surfaces, lower back, scalp, and nails.5

| Condition | Characteristics | Common location |
|---|---|---|
| Atopic dermatitis | Pruritic, erythematous, scaly lesions; associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis | Often localized to the flexor surfaces |
| Fixed drug eruption | Single or multiple, round, sharply demarcated, dusky red plaques or blisters that appear soon after drug exposure and reappear in the same site each time the drug is taken | Glans penis is most common |
| Mycosis fungoides | Asymmetric, reddish patches and plaques; often misdiagnosed early on as other benign skin conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis | Any area |
| Nummular eczema | Circular or oval lesions that remain in the same area and do not increase in size | Trunk and extensor surfaces of the extremities, particularly the pretibial areas and the dorsum of the hands (most common) |
| Plaque psoriasis | Symmetric and bilateral plaques that are well demarcated and covered by a silvery scale; Auspitz sign and Koebner phenomenon | Extensor surfaces, lower back, scalp, and nails |