Am Fam Physician. 2014;90(10):690-694
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
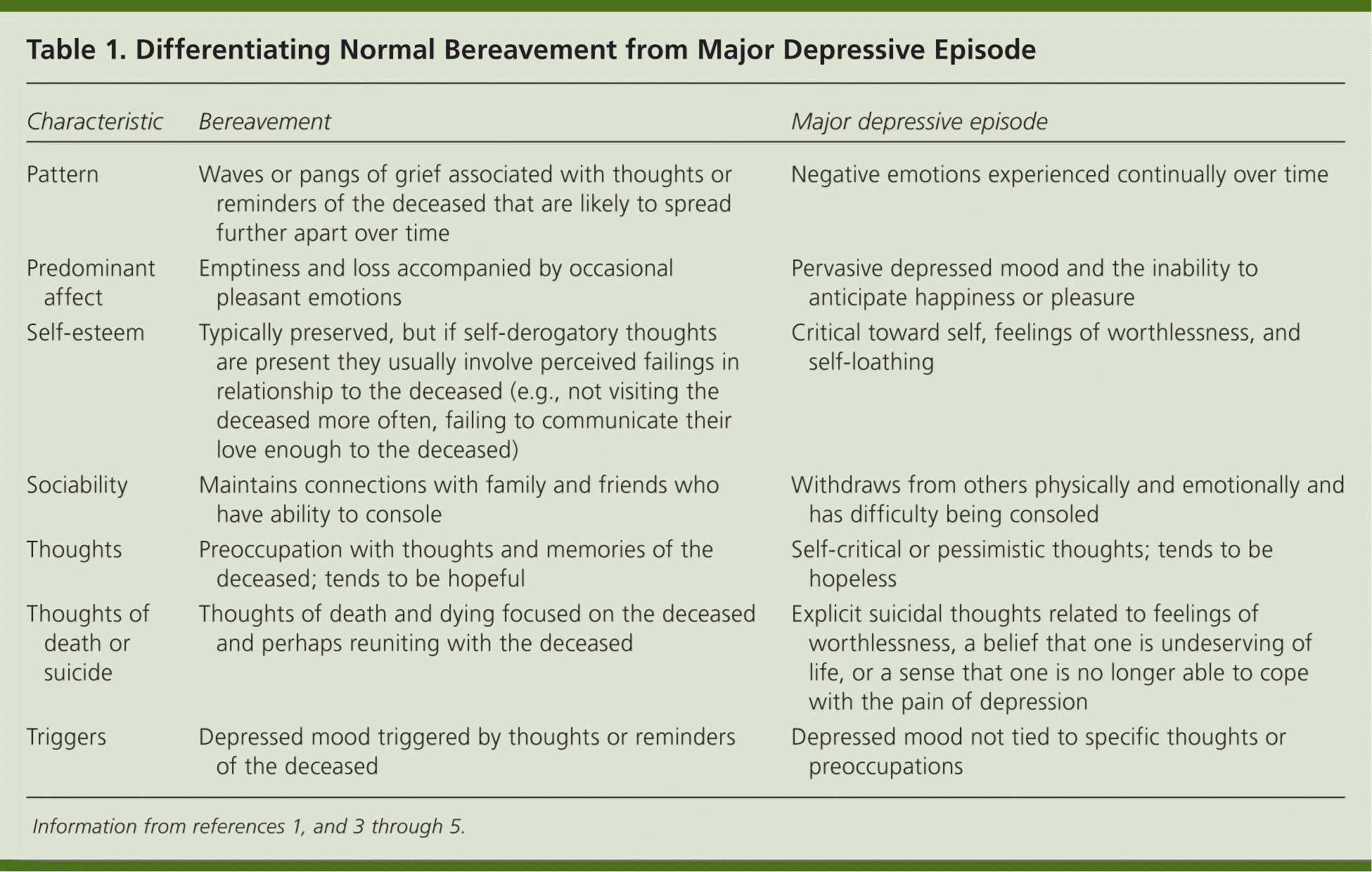
In May 2013, the American Psychiatric Association released the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).1 One of the more controversial revisions in the DSM-5 is the elimination of the bereavement exclusion criterion for major depressive disorder (MDD), suggesting to some that grief is not a normal process. Within the DSM-IV, text revision,2 persons who experienced the death of a loved one and who had a depressed mood would not be diagnosed with MDD unless symptoms persisted beyond two months or were characterized by marked functional impairment, morbid preoccupation with worthlessness, suicidal ideation, psychotic symptoms, or psychomotor retardation. In the DSM-5, a note replaces what has traditionally been referred to as the bereavement exclusion criterion, or criterion E, for MDD in the DSM-IV, text revision. The note suggests that responses to any significant loss may include symptoms resembling a depressive episode, and although they may be understandable or appropriate to the loss, the presence of a major depressive episode should be considered carefully. In a footnote, the DSM-5 provides additional guidance on how to differentiate grief from MDD. To allow for diagnostic flexibility, the DSM-5 provides another option for noting normal reactions to the death of a loved one by including uncomplicated bereavement in the chapter titled “Other Conditions That May Be a Focus of Clinical Attention” (V62.82). Table 1 provides information on differentiating normal bereavement from a major depressive episode.1,3–5
| Characteristic | Bereavement | Major depressive episode |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern | Waves or pangs of grief associated with thoughts or reminders of the deceased that are likely to spread further apart over time | Negative emotions experienced continually over time |
| Predominant affect | Emptiness and loss accompanied by occasional pleasant emotions | Pervasive depressed mood and the inability to anticipate happiness or pleasure |
| Self-esteem | Typically preserved, but if self-derogatory thoughts are present they usually involve perceived failings in relationship to the deceased (e.g., not visiting the deceased more often, failing to communicate their love enough to the deceased) | Critical toward self, feelings of worthlessness, and self-loathing |
| Sociability | Maintains connections with family and friends who have ability to console | Withdraws from others physically and emotionally and has difficulty being consoled |
| Thoughts | Preoccupation with thoughts and memories of the deceased; tends to be hopeful | Self-critical or pessimistic thoughts; tends to be hopeless |
| Thoughts of death or suicide | Thoughts of death and dying focused on the deceased and perhaps reuniting with the deceased | Explicit suicidal thoughts related to feelings of worthlessness, a belief that one is undeserving of life, or a sense that one is no longer able to cope with the pain of depression |
| Triggers | Depressed mood triggered by thoughts or reminders of the deceased | Depressed mood not tied to specific thoughts or preoccupations |
Several reasons have been proffered for eliminating the bereavement exclusion criterion. These include: (1) removing the implication that bereavement typically lasts only two months; (2) recognizing bereavement as a severe psychological stressor that can precipitate MDD in vulnerable persons; (3) understanding that bereavement-related major depression is genetically influenced and is associated with similar personality characteristics, patterns of comorbidity, course, and risks of chronicity and recurrence as non–bereavement-related MDD; and (4) seeing that bereavement-related depression responds similarly to psychosocial and pharmacologic treatments as non–bereavement-related depression.6,7 Those favoring the elimination of the bereavement exclusion criterion also note that MDD can occur in someone who is grieving, just as it may occur in persons experiencing other types of stressors or losses (e.g., job loss); yet, the presence of those stressors does not preclude a diagnosis of depression.7 Proponents of eliminating the bereavement exclusion criterion accept the risk of stigmatizing grieving patients with a mental health diagnosis because this risk is outweighed by the potential for proper clinical attention and treatment of depression5 and the prevention of suicide.8,9
Many reasons exist to maintain the bereavement exclusion criterion. First, despite claims that MDD and bereavement-related depression are similar,3,10,11 evidence suggests otherwise.12,13 One study found that single, brief, bereavement-related depressive episodes have distinct demographic and symptom profiles compared with other types of depression, and that these bereavement-related depressive symptoms were not associated with increased risk of future depression.12 A literature review found no support for arguments contesting the bereavement exclusion criterion.13 This review also found no increased risk of suicide among persons with excluded bereavement-related depression. Eliminating the bereavement exclusion criterion will also result in an increasing number of persons with normal grief to be inappropriately diagnosed with MDD after only two weeks of depressive symptoms. Not only is the grieving patient now stigmatized with a mental health disorder, but clinicians may unnecessarily prescribe antidepressant medications, exposing patients to the associated adverse effects.4 With nearly 2.5 million deaths each year in the United States,14 the harm associated with the inappropriate diagnosis and treatment of grieving patients is apparent and disturbing. For grieving patients with more serious depression, the DSM-IV, text revision, allows a diagnosis of MDD if certain conditions exist.
Rather than arguing for the presence or removal of the bereavement exclusion criterion for depression, we suggest the following steps. First, future studies should continue to focus on differentiating bereavement-related depression from non–bereavement-related depression to enhance a clinician's ability to properly assess and manage each. Second, efforts at proper education and training of students, residents, and clinicians on recognizing and responding to depression in grieving patients should be enhanced, with most of the education geared toward primary care physicians who care for the majority of grieving patients. Finally, clinicians should take the time necessary to monitor their patients, and to provide counseling and possibly referral, knowing that some grieving patients may develop more severe symptoms of depression and, thus, may need more than time alone to heal.