
A more recent article on chronic kidney disease is available.
Am Fam Physician. 2017;96(12):776-783
Patient information: See related handout on chronic kidney disease, written by the authors of this article.
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Chronic kidney disease affects 47 million people in the United States and is associated with significant health care costs, morbidity, and mortality. Because this disease can silently progress to advanced stages, early detection is critical for initiating timely interventions. Multiple guidelines recommend at least annual screening with serum creatinine, urine albumin/creatinine ratio, and urinalysis for patients with risk factors, particularly diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and a history of cardiovascular disease. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found insufficient evidence to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for chronic kidney disease in the general population, and the American College of Physicians recommends against screening asymptomatic adults without risk factors. Persistently elevated serum creatinine and albuminuria are diagnostic and prognostic hallmarks of chronic kidney disease. Lower levels of albuminuria are associated with adverse renal and cardiovascular outcomes. Serum cystatin C is a novel biomarker that is most useful when a false-positive decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate calculated from serum creatinine is suspected. New guidelines incorporate albuminuria into the classification framework for chronic kidney disease and elaborate on identification of the disease, the frequency of follow-up, and recommendations for nephrology referral. Nephrology consultation is indicated for patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2, persistent urine albumin/creatinine ratio greater than 300 mg per g or urine protein/creatinine ratio greater than 500 mg per g, or if there is evidence of a rapid loss of kidney function. A multidisciplinary approach between primary care physicians, nephrologists, and other subspecialists for implementing early interventions, providing education, and planning for advanced renal disease is key for effective management.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major public health concern that affects approximately 47 million persons in the United States, or 14.8% of the U.S. adult population.1 It is associated with significant health care costs, morbidity, and mortality.1,2 The presence of CKD increases the risk of hospitalization, cardiovascular events, and death.3,4 Recent data show that the prevalence of CKD has largely stabilized since 2004, possibly because of better awareness and treatment of obesity, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus.5 A 2014 report showed that Medicare spending for patients with CKD was more than $52 billion, which represents 20% of all Medicare costs.6 The per-person per-year Medicare expense for CKD rises with increasing disease severity, ranging from $1,700 for stage 2 to $12,700 for stage 4, with costs rising exponentially in end-stage renal disease.2,6 Thus, early detection of CKD is critical to slow disease progression, prevent long-term morbidity and mortality, and decrease health care spending. The 2012 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Work Group published updated guidelines on the detection, evaluation, classification, and management of CKD.7 This article reviews current recommendations for the primary care physician.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
| The initial evaluation of GFR should include measurement of serum creatinine and estimation of the GFR using a creatinine-based equation. | C | 7 |
| An early morning spot urine albumin/creatinine ratio is the preferred initial test to measure proteinuria in patients undergoing CKD evaluation. | C | 7, 16, 17 |
| Serum cystatin C should be measured to determine whether decreased GFR represents a false positive in patients who have elevated serum creatinine levels, but no known CKD, no risk factors for CKD, and no albuminuria. | C | 24 |
| CKD should be classified using the estimated GFR and the degree of albuminuria. | C | 7 |
| Patients with CKD should have serum hemoglobin measured at least annually, and more often depending on the severity of CKD. | C | 7, 32 |
| Routine evaluation of bone density should not be performed in patients with an estimated GFR < 45 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 because results may be inaccurate. | C | 7, 33 |
| The evaluation of patients with stage 3a to 5 CKD (estimated GFR < 45 mL per minute per 1.73 m2) should include measurement of serum calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, alkaline phosphatase, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. | C | 7, 33 |
Detection of CKD
CKD is defined as abnormal kidney structure or function lasting more than three months with associated health implications.7 Indicators include albuminuria, urine sediment abnormalities, abnormal renal imaging findings, serum electrolyte or acid-base derangements, and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) less than 60 mL per minute per 1.73 m2.7
SCREENING INDICATIONS
Multiple guidelines recommend that patients with diabetes or hypertension be screened annually for CKD. Furthermore, patients with other risk factors, including cardiovascular disease, older age, history of low birth weight, obesity, and a family history of CKD, warrant consideration for screening.7,10,11 The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded that the evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of routine screening for CKD in asymptomatic adults.12 The American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Family Physicians recommend against screening for CKD in asymptomatic adults without risk factors.13,14
SCREENING TESTS
Screening for CKD includes measurement of serum creatinine, estimation of GFR using a serum creatinine-based equation, measurement of the urine albumin/creatinine ratio, and urinalysis.7 Urinalysis has a high sensitivity for heavy proteinuria (greater than 300 mg per 24 hours, as estimated from the spot urine protein/creatinine ratio) but may not detect clinically significant lower levels (30 to 300 mg).15 Because albumin is the predominantly filtered glomerular protein, initial proteinuria evaluation using the spot urine albumin/creatinine ratio obtained from an early morning sample is recommended.7,16,17 Timed 24-hour urine collections are no longer recommended as an initial diagnostic tool because of the potential for inadequate collection, inconvenience to patients, and the lack of diagnostic advantage over the urine albumin/creatinine ratio.
GFR ESTIMATION
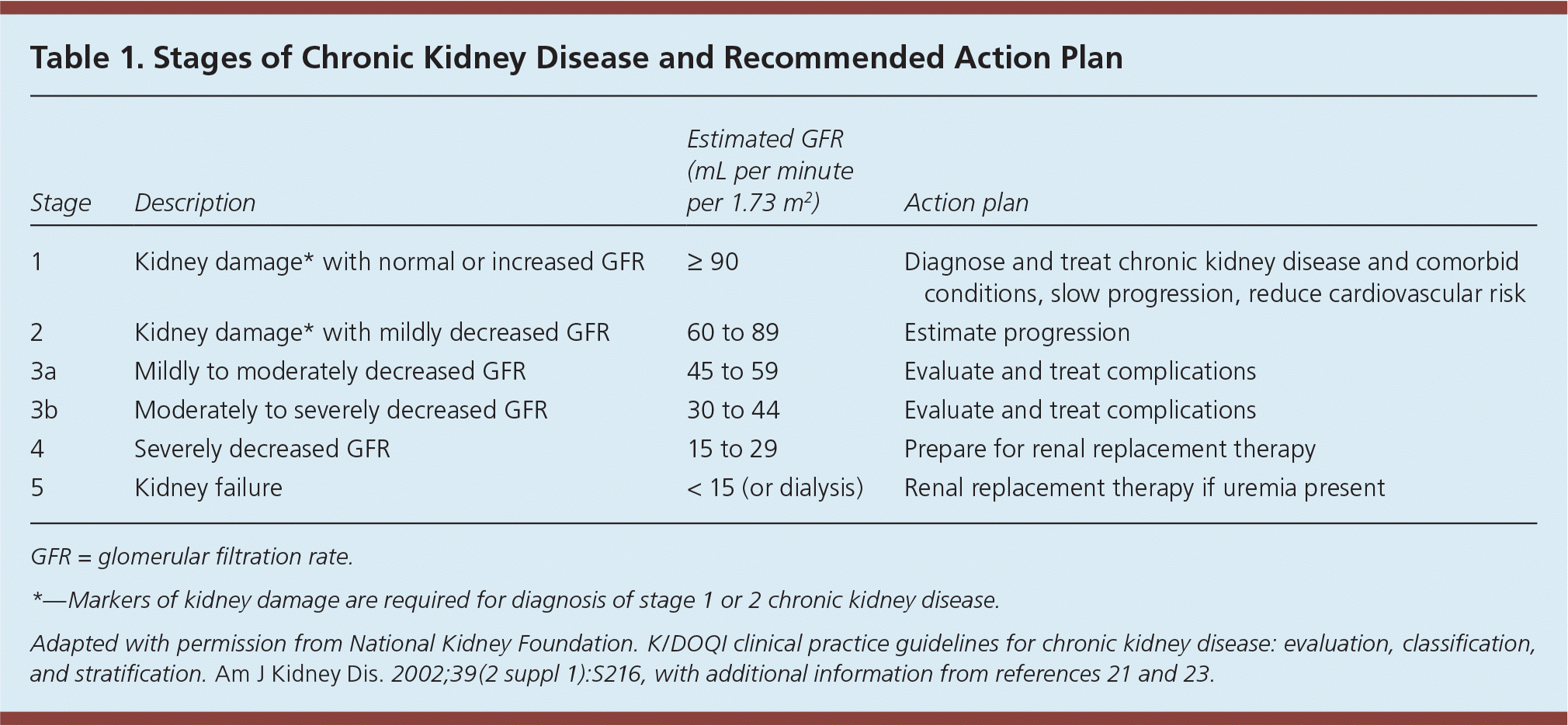
Steady state renal function is best determined by estimation of GFR, which is derived from measurement of serum creatinine. The Cockcroft-Gault equation to estimate GFR is now used only to determine dosing adjustments for medications.18,19 For all other purposes, the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation is the established method of estimating GFR in routine clinical practice because of improved accuracy in persons with near-normal estimated GFR20 (eTable A). Updated GFR categories and terminology are provided in Table 1.21–23
| Equation | Variables | Available at |
|---|---|---|
| Cockcroft-Gault (1976) | Age, sex, weight, and serum creatinine level | Nephron Information Center http://nephron.com/cgi-bin/CGSI.cgi |
| Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (1999) | Age, race, sex, and serum urea, nitrogen, albumin, and creatinine levels | National Kidney Foundation http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/gfr_calculator.cfm |
| Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (2009)* | Age, race, sex, and serum creatinine level | National Kidney Foundation http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/gfr_calculator.cfm |
| Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration cystatin C (2012) | Age, race, sex, and serum cystatin C level | National Kidney Foundation http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/gfr_calculator.cfm |
| Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration creatinine-cystatin C (2012)† | Age, race, sex, and serum cystatin C and serum creatinine levels | National Kidney Foundation http://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/gfr_calculator.cfm |
| Stage | Description | Estimated GFR (mL per minute per 1.73 m2) | Action plan |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kidney damage* with normal or increased GFR | ≥ 90 | Diagnose and treat chronic kidney disease and comorbid conditions, slow progression, reduce cardiovascular risk |
| 2 | Kidney damage* with mildly decreased GFR | 60 to 89 | Estimate progression |
| 3a | Mildly to moderately decreased GFR | 45 to 59 | Evaluate and treat complications |
| 3b | Moderately to severely decreased GFR | 30 to 44 | Evaluate and treat complications |
| 4 | Severely decreased GFR | 15 to 29 | Prepare for renal replacement therapy |
| 5 | Kidney failure | < 15 (or dialysis) | Renal replacement therapy if uremia present |
Serum cystatin C is a filtration marker that has emerged as an alternative to serum creatinine to more accurately estimate GFR and classify CKD. Obtaining the serum cystatin C–based estimated GFR is most beneficial when a false-positive decreased estimated GFR is suspected, such as in a patient without known structural kidney disease, risk factors for CKD, or albuminuria who has a creatinine clearance–calculated estimated GFR of 45 to 59 mL per minute per 1.73 m2.24 In such cases, the serum cystatin C and serum creatinine levels can be obtained concurrently for recalculation of the estimated GFR using the appropriate calculator7,24,25 (eTable A). If the estimated GFR calculated using both serum creatinine and serum cystatin C is greater than 60 mL per minute per 1.73 m2, a diagnosis of CKD is not warranted. A recent community-based longitudinal observational study demonstrated that a reduced serum cystatin C–based estimated GFR was associated with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality.26 It should be noted that serum cystatin C is not reliable in patients with acute kidney injury, inflammatory states, or thyroid dysfunction.7,16,25,27 Furthermore, it is not yet universally available and may add significant cost to the evaluation.
Markers of Kidney Damage
PROTEINURIA
Persistent proteinuria is a defining marker of renal injury regardless of estimated GFR, and it identifies increased cardiovascular disease and mortality risks.17,28 Measurement of proteinuria with the total protein/creatinine ratio is a less sensitive method than the spot albumin/creatinine ratio, and includes filtered albumin, tubular-secreted proteins (Tamm-Horsfall protein), and plasma proteins from other disease processes, such as multiple myeloma and infection. Because the protein/creatinine ratio is less sensitive for low-level proteinuria (less than 150 mg per 24 hours as estimated from the spot urine protein/creatinine ratio), it should not be routinely used for initial screening.
ALBUMINURIA
The spot urine albumin/creatinine ratio is preferred over the protein/creatinine ratio because it detects lower levels of proteinuria. Small amounts of albumin in the urine—between 30 and 300 mg per day—were previously thought to be clinically insignificant. However, modest albuminuria is now recognized to have prognostic significance, and the albumin/creatinine ratio is recommended by current clinical practice guidelines that emphasize albuminuria.7 Menstrual bleeding, urinary tract infection, exercise, and other factors may affect the urinary albumin/creatinine ratio.7
To further risk stratify and optimize early detection of albuminuria in at-risk persons, the terms microal-buminuria and macroalbuminuria have been replaced with normal to mildly increased (albumin/creatinine ratio less than 30 mg per g), moderately increased (30 to 300 mg per g), and severely increased (greater than 300 mg per g).7 Severe albuminuria independently predicts mortality and end-stage renal disease.29 Dipstick urinalysis is not sensitive for detection of small amounts of albumin and is no longer recommended for routine screening or definitive diagnosis.7 Updated proteinuria categories and terminology are provided in the KDIGO 2012 guideline (see Table 7, “Relationship Among Categories for Albuminuria and Proteinuria”).7
OTHER INDICATORS
Urinalysis and urine microscopy still play significant roles in the detection of CKD. Presence of hematuria, cellular casts, chronic pyuria, tubular concentrating defects, and insufficient renal acidification all suggest renal impairment in the correct clinical context. Patients with diabetes and albuminuria have a high risk of progressing to end-stage renal disease as proteinuria worsens.17 Individuals with CKD and diabetes should have a comprehensive evaluation that addresses hypertension and cardiovascular risk to guide future therapeutic interventions.23 Moderate to advanced diabetic kidney disease can potentially be diagnosed without renal biopsy and is based on clinical and laboratory evaluation (eTable B). However, mild diabetic kidney disease may present more subtly.

| Screening initiation |
| At the time of diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| Five years after diagnosis of type 1 diabetes |
| Screening frequency |
| Annually |
| Overt clinical findings consistent with diabetic kidney disease |
| Moderately increased albuminuria (i.e., KDIGO A2) in patients with type 1 diabetes for more than 10 years |
| Moderately increased albuminuria in the presence of diabetic retinopathy |
| Severely increased albuminuria (i.e., KDIGO A3) |
| Clinical findings that should prompt consideration of an alternative diagnosis |
| Absence of albuminuria in patients with stage 3a to 5 chronic kidney disease |
| Absence of diabetic retinopathy |
| Active urinary sediment (cells or casts) |
| Low GFR at the time of diagnosis |
| More than 30% reduction in GFR within two to three months after initiation of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker |
| Rapidly decreasing GFR (more than 4 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 per year) |
| Rapidly increasing proteinuria or nephrotic syndrome |
| Refractory hypertension |
| Signs or symptoms of other systemic disease |
CKD Staging
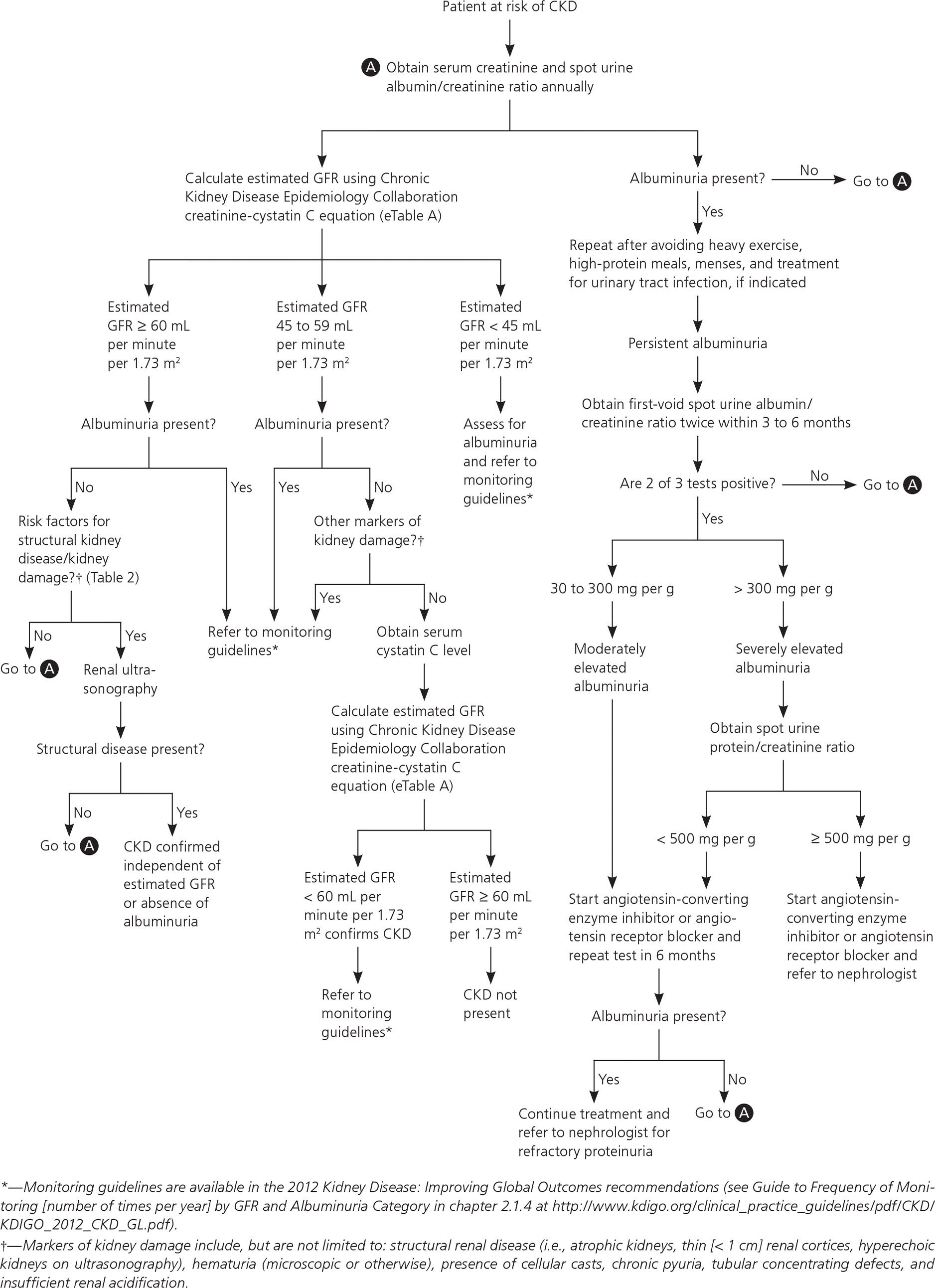
Prognosis, evaluation, and management of CKD are dependent on staging. The 2012 KDIGO guidelines provide an enhanced classification framework for CKD and albuminuria.7 They also elaborate on the identification and prognosis of CKD, frequency of follow-up, and recommendations for nephrology referral. Primary care physicians should classify CKD based on the estimated GFR and degree of albuminuria (see Figure 17, Guide to Frequency of Monitoring [number of times per year] by GFR and Albuminuria Category).7 Renal transplant recipients are considered to have CKD regardless of GFR or absence of albuminuria.
Evaluation of CKD
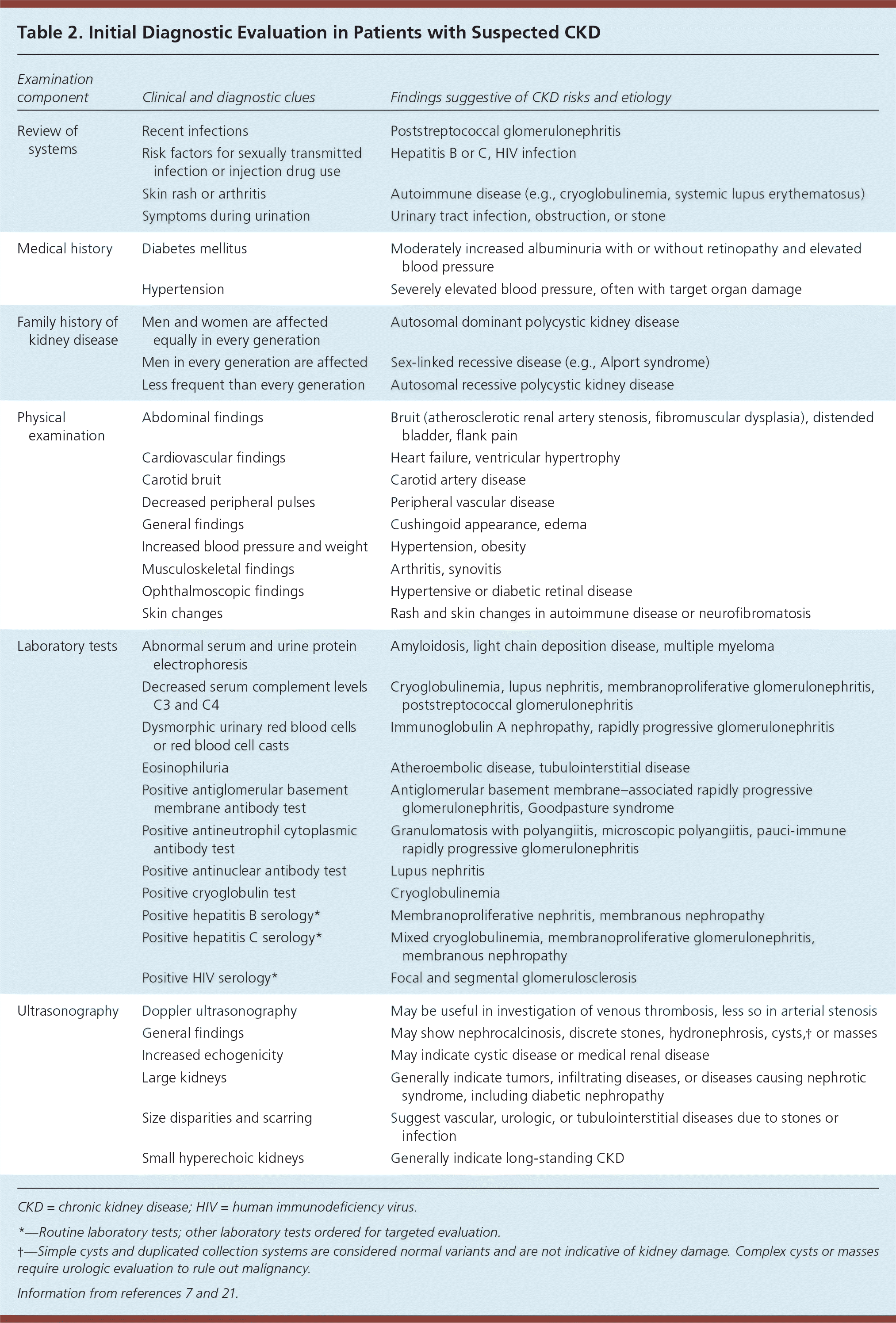
Once reduced GFR and/or presence of proteinuria are determined to be chronic and stable (unchanged for more than three months), a comprehensive initial workup is necessary to determine the etiology of CKD. Etiologies include hypertensive kidney disease, diabetic nephropathy, or primary or secondary glomerulonephritis.7 A full medical history, including exposure to potential nephrotoxins; physical examination; and review of historical and current blood pressure, dietary history, and weight measurements are essential for CKD evaluation7 (Table 27,21). Laboratory assessment should include measurement of serum electrolytes, fasting lipids, A1C, and urine albumin/creatinine ratio.7 Urinalysis with microscopic urine sediment is helpful if intrinsic renal disease is suspected.21 Renal ultrasonography is recommended to evaluate for structural abnormalities.30 Figure 1 outlines a proposed approach to the evaluation of CKD.7
| Examination component | Clinical and diagnostic clues | Findings suggestive of CKD risks and etiology |
|---|---|---|
| Review of systems | Recent infections | Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis |
| Risk factors for sexually transmitted infection or injection drug use | Hepatitis B or C, HIV infection | |
| Skin rash or arthritis | Autoimmune disease (e.g., cryoglobulinemia, systemic lupus erythematosus) | |
| Symptoms during urination | Urinary tract infection, obstruction, or stone | |
| Medical history | Diabetes mellitus | Moderately increased albuminuria with or without retinopathy and elevated blood pressure |
| Hypertension | Severely elevated blood pressure, often with target organ damage | |
| Family history of kidney disease | Men and women are affected equally in every generation | Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease |
| Men in every generation are affected | Sex-linked recessive disease (e.g., Alport syndrome) | |
| Less frequent than every generation | Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease | |
| Physical examination | Abdominal findings | Bruit (atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis, fibromuscular dysplasia), distended bladder, flank pain |
| Cardiovascular findings | Heart failure, ventricular hypertrophy | |
| Carotid bruit | Carotid artery disease | |
| Decreased peripheral pulses | Peripheral vascular disease | |
| General findings | Cushingoid appearance, edema | |
| Increased blood pressure and weight | Hypertension, obesity | |
| Musculoskeletal findings | Arthritis, synovitis | |
| Ophthalmoscopic findings | Hypertensive or diabetic retinal disease | |
| Skin changes | Rash and skin changes in autoimmune disease or neurofibromatosis | |
| Laboratory tests | Abnormal serum and urine protein electrophoresis | Amyloidosis, light chain deposition disease, multiple myeloma |
| Decreased serum complement levels C3 and C4 | Cryoglobulinemia, lupus nephritis, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis | |
| Dysmorphic urinary red blood cells or red blood cell casts | Immunoglobulin A nephropathy, rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis | |
| Eosinophiluria | Atheroembolic disease, tubulointerstitial disease | |
| Positive antiglomerular basement membrane antibody test | Antiglomerular basement membrane–associated rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, Goodpasture syndrome | |
| Positive antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody test | Granulomatosis with polyangiitis, microscopic polyangiitis, pauci-immune rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis | |
| Positive antinuclear antibody test | Lupus nephritis | |
| Positive cryoglobulin test | Cryoglobulinemia | |
| Positive hepatitis B serology* | Membranoproliferative nephritis, membranous nephropathy | |
| Positive hepatitis C serology* | Mixed cryoglobulinemia, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, membranous nephropathy | |
| Positive HIV serology* | Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis | |
| Ultrasonography | Doppler ultrasonography | May be useful in investigation of venous thrombosis, less so in arterial stenosis |
| General findings | May show nephrocalcinosis, discrete stones, hydronephrosis, cysts,† or masses | |
| Increased echogenicity | May indicate cystic disease or medical renal disease | |
| Large kidneys | Generally indicate tumors, infiltrating diseases, or diseases causing nephrotic syndrome, including diabetic nephropathy | |
| Size disparities and scarring | Suggest vascular, urologic, or tubulointerstitial diseases due to stones or infection | |
| Small hyperechoic kidneys | Generally indicate long-standing CKD |
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
Because the presence of albuminuria or a GFR less than 60 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 increases the risk of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality, cardiovascular risk stratification is recommended for all persons with CKD.7,31 Furthermore, the presence of CKD should not preclude antiplatelet agents or therapies for heart failure if indicated.7 GFR and serum electrolyte levels should be monitored as pharmacotherapy for the management of heart failure is escalated, because these parameters may change significantly. Electrocardiography and echocardiography may be useful in identifying end-organ damage from long-standing, poorly controlled hypertension as a potential clue to the etiology of CKD.
ANEMIA
Patients with CKD are at increased risk of anemia and mineral and bone disorders. Hemoglobin should be measured at least annually in patients with stage 3 CKD, and more frequently as renal function declines.7,32 A complete blood count, absolute reticulocyte count, ferritin level, transferrin saturation, and vitamin B12 and folate levels should be obtained in patients with anemia.32 There is no role for measurement of serum erythropoietin level in the primary care setting.
MINERAL AND BONE DISORDERS
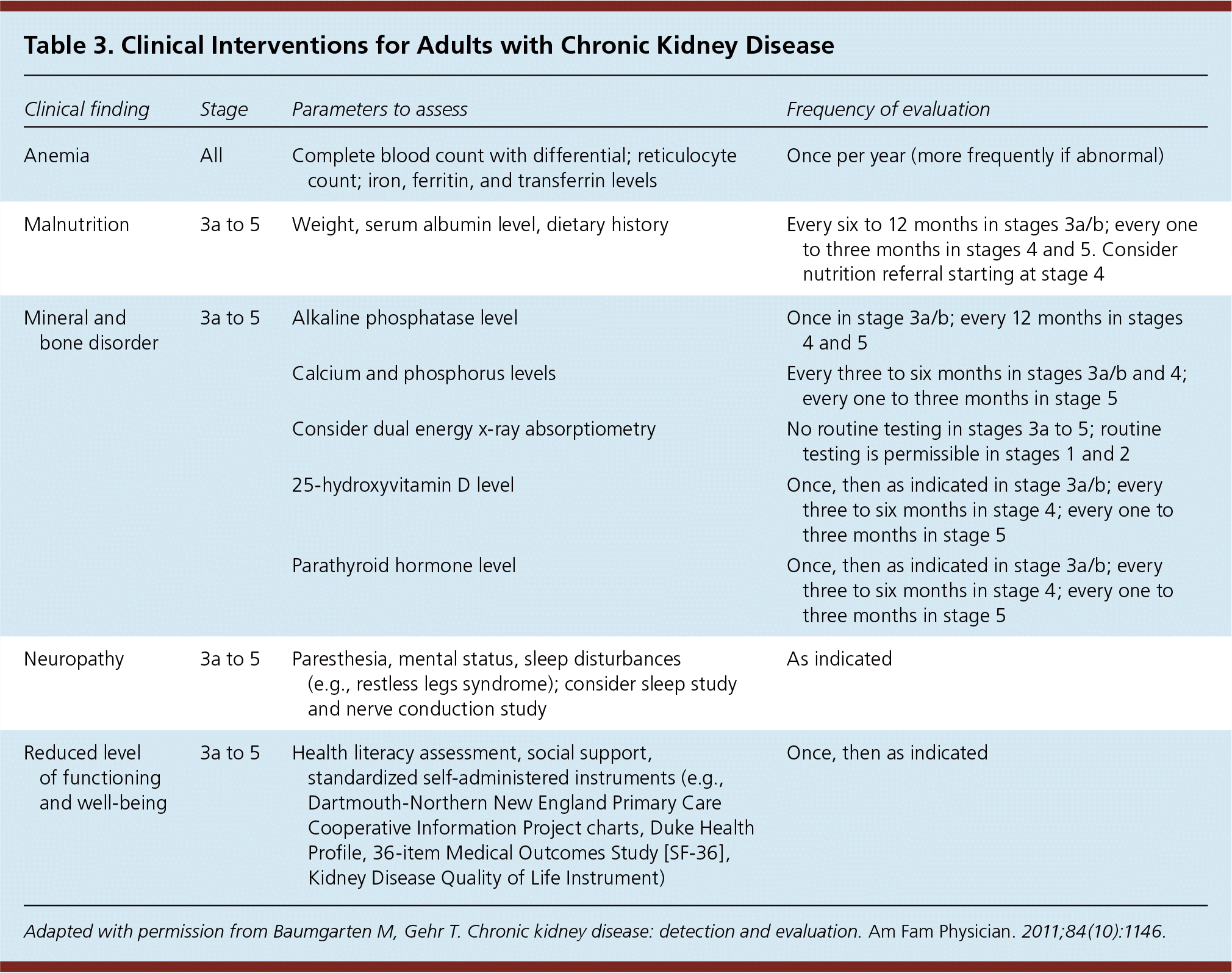
Patients with stage 1 to 3a CKD can be screened for osteoporosis using the same strategy as the general population. For those with more advanced CKD, densitometry is not recommended because fracture risk prediction is less accurate.7,33 Additionally, certain subsets of metabolic bone disease (e.g., adynamic bone disease) are not detected by densitometry.7,33 Bone biopsy is the diagnostic procedure of choice to evaluate for possible adynamic bone disease in patients with advanced CKD. Patients with stage 3a to 5 CKD should have serum calcium, phosphorus, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, parathyroid hormone, and alkaline phosphatase levels checked regularly; abnormal levels may indicate the presence of renal mineral and bone disorders.7,33 Consultation with a nephrologist and/or endocrinologist is recommended for patients with advanced kidney disease in whom renal mineral and bone disorder is suspected. Details of these and other interventions for patients with CKD are outlined in Table 3.21
| Clinical finding | Stage | Parameters to assess | Frequency of evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anemia | All | Complete blood count with differential; reticulocyte count; iron, ferritin, and transferrin levels | Once per year (more frequently if abnormal) |
| Malnutrition | 3a to 5 | Weight, serum albumin level, dietary history | Every six to 12 months in stages 3a/b; every one to three months in stages 4 and 5. Consider nutrition referral starting at stage 4 |
| Mineral and bone disorder | 3a to 5 | Alkaline phosphatase level | Once in stage 3a/b; every 12 months in stages 4 and 5 |
| Calcium and phosphorus levels | Every three to six months in stages 3a/b and 4; every one to three months in stage 5 | ||
| Consider dual energy x-ray absorptiometry | No routine testing in stages 3a to 5; routine testing is permissible in stages 1 and 2 | ||
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D level | Once, then as indicated in stage 3a/b; every three to six months in stage 4; every one to three months in stage 5 | ||
| Parathyroid hormone level | Once, then as indicated in stage 3a/b; every three to six months in stage 4; every one to three months in stage 5 | ||
| Neuropathy | 3a to 5 | Paresthesia, mental status, sleep disturbances (e.g., restless legs syndrome); consider sleep study and nerve conduction study | As indicated |
| Reduced level of functioning and well-being | 3a to 5 | Health literacy assessment, social support, standardized self-administered instruments (e.g., Dartmouth-Northern New England Primary Care Cooperative Information Project charts, Duke Health Profile, 36-item Medical Outcomes Study [SF-36], Kidney Disease Quality of Life Instrument) | Once, then as indicated |
Indications for Nephrology Referral
Nephrology consultation is indicated when the estimated GFR is less than 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2, or earlier if necessary (Table 4).7,34 For patients with progressive CKD, referral to a nephrologist for renal replacement therapy is essential when the risk of renal failure within one year is 10% to 20%. Validated risk calculators for progression to end-stage renal disease are available.27 A multidisciplinary approach between primary care physicians and nephrologists for implementing early interventions, providing education, and planning for advanced renal disease is key for effective management of CKD.

| Diagnosis of CKD cause |
| Acute kidney injury (unresponsive to initial management)* |
| Anemia of CKD |
| Family history of kidney disease |
| Presence of red blood cell casts in the urine |
| Progression of CKD† |
| Management of CKD complications |
| Anemia of chronic kidney disease when hemoglobin < 10 g per dL (100 g per L) |
| CKD and refractory hypertension |
| Mineral and bone disorder of CKD |
| Persistent abnormalities in serum potassium |
| Persistent elevated albuminuria (albumin/creatinine ratio > 300 mg per g [> 30 mg per mmol]) or refractory proteinuria (urinary protein/creatinine ratio > 500 to 1,000 mg per g [> 50 to 100 mg per mmol]) |
| Recurrent nephrolithiasis or concern for nephrocalcinosis |
| Preparation for renal replacement therapy |
| GFR < 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 (KDIGO GFR categories G4 and G5) |
This article updates previous articles on this topic by Baumgarten and Gehr,21 and by Snyder and Pendergraph.35
Data sources: We searched the websites of the National Kidney Foundation, Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, American Diabetes Association, American Medical Association, United States Renal Data System, PubMed, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, UpToDate, and the World Health Organization. The following search terms were entered: Medicare, chronic kidney disease, dialysis, proteinuria, albuminuria, diabetic kidney disease, hypertension, renal ultrasound, urinalysis, anemia, lipid, cardiovascular disease, mortality, bone densitometry, and bone and mineral disease. Search dates: October 15, 2016, through November 20, 2017.
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy of the Department of Defense, Department of Army, U.S. Army Medical Department, or the U.S. government.
