
Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(2):85-92
Patient information: See related handouts on what you should know about club drugs and what you should know about meth, written by the authors of this article.
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Approximately 10% of the U.S. population 12 years and older reported using illicit substances in 2015. This article reviews the clinical effects and treatment of persons who use cocaine, methamphetamines, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), synthetic cannabinoids, and synthetic cathinones (“bath salts”). Cocaine blocks the reuptake of the monoamine transporters dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Immediate clinical effects include increased energy and euphoria, as well as hypertension and arrhythmias. Acute myocardial infarction, seizures, hallucinations, hyperthermia, and movement disorders are among the possible adverse effects. Like cocaine, methamphetamine blocks reuptake of monoamine transporters, but also stimulates dopamine release and has a longer duration of action. Methamphetamine misuse is associated with severe dental problems. MDMA is a stimulant and psychedelic with a chemical structure similar to serotonin. Adverse effects include serotonin syndrome, hyponatremia, long-term memory impairment, and mood disorders. Synthetic cannabinoids can have a more intense and long-lasting effect than natural cannabis. Acute intoxication may cause severe cardiac and respiratory complications and seizures. Synthetic cathinones are marketed as cheap substitutes for other stimulants. Their effects are similar to those of other stimulants, and they are addictive. Psychosocial intervention is the main form of treatment for addiction to these substances. Promising therapies include disulfiram and substitution therapy for cocaine misuse disorders, and mirtazapine for methamphetamine use disorder.
Illicit drug use is among the top 10 preventable risk factors for years of healthy life lost in developed countries.1 Approximately 10% of the U.S. population 12 years and older reported current use of illicit substances in 2015.2 The risk of lifelong substance use disorder is multifactorial and includes genetics, environment, neurobiology, and earlier age of initiation of substance use. One-third of teenagers younger than 14 years who initiate substance use will develop substance use disorder in their lifetimes.3
WHAT IS NEW ON THIS TOPIC
The American Heart Association recommends that patients with non–ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome and a recent history of cocaine use be treated in the same manner as patients without cocaine-related acute coronary syndrome unless they exhibit signs of acute intoxication, in which case beta blockers should be avoided.
Methamphetamine misuse is associated with severe dental problems. A study of 571 methamphetamine users showed that 96% had dental caries and 58% had untreated tooth decay.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
| Physicians should consider screening adolescents for illicit drug use because of the high risk of developing substance use disorder in those who initiate use. | C | 13–16 |
| The use of unopposed beta blockers should be avoided in patients with cocaine intoxication and non–ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. | B | 32 |
| Psychosocial treatment may improve short-term adherence to treatment for cocaine and amphetamine (including MDMA) use disorders, and it may improve abstinence rates. | B | 34 |
| Patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection should be asked about MDMA use because of the potential for life-threatening interactions with protease inhibitors. | C | 25 |
This article expands on a practical framework for addressing substance use disorder from a previous American Family Physician article,4 and focuses on several commonly used substances (Table 1),5–10 their clinical effects, and treatment options. Although chronic substance use can lead to significant morbidity and mortality, research has found that primary care physicians fail to diagnose substance use disorder in up to 43% of their patients.11
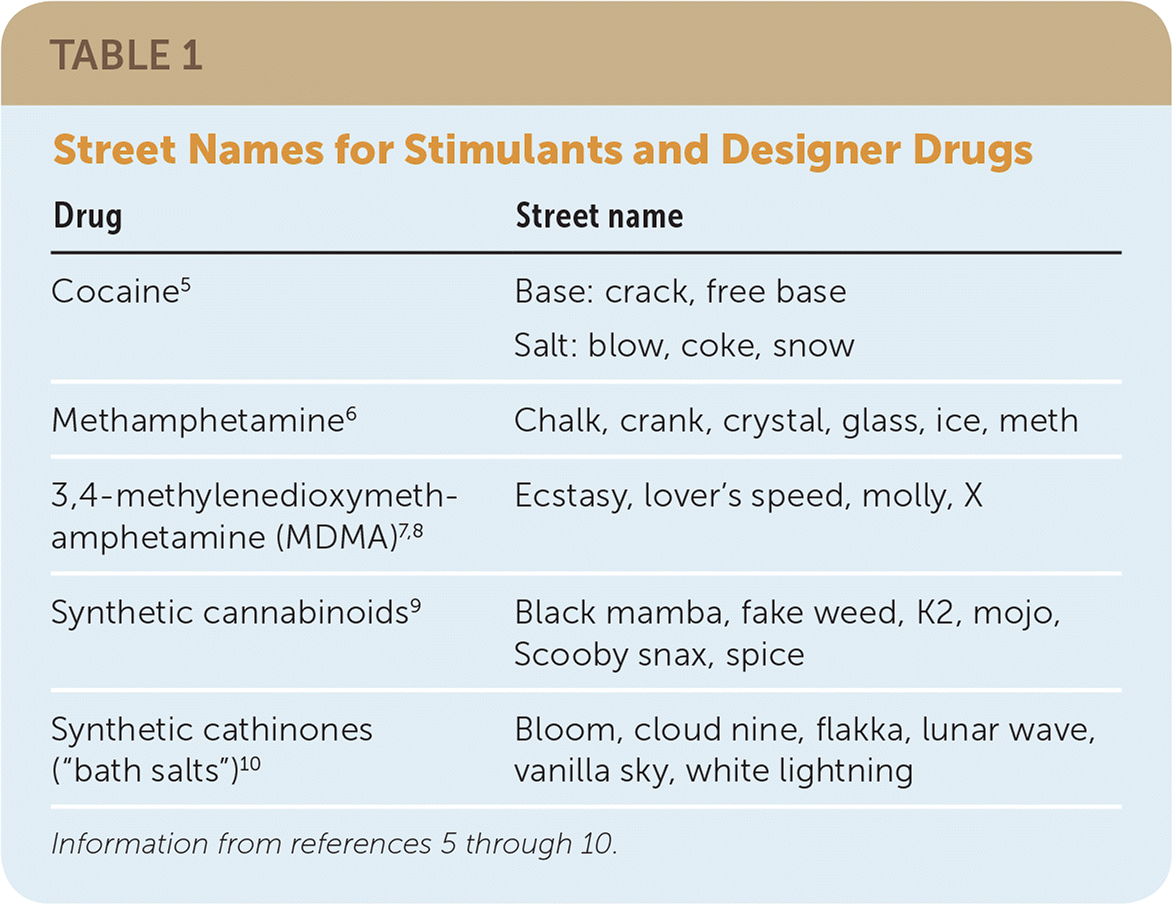
| Drug | Street name |
|---|---|
| Cocaine5 | Base: crack, free base Salt: blow, coke, snow |
| Methamphetamine6 | Chalk, crank, crystal, glass, ice, meth |
| 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA)7,8 | Ecstasy, lover's speed, molly, X |
| Synthetic cannabinoids9 | Black mamba, fake weed, K2, mojo, Scooby snax, spice |
| Synthetic cathinones (“bath salts”)10 | Bloom, cloud nine, flakka, lunar wave, vanilla sky, white lightning |
Screening
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and the American Academy of Family Physicians concluded that current evidence was insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening adolescents, adults, and pregnant women for illicit drug use.1,12 The American Academy of Pediatrics, the American Medical Association's Guidelines for Adolescent Preventive Services, and the Bright Futures initiative endorse screening adolescents for illicit substance use, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends direct questioning of all patients about their use of drugs as part of periodic assessments.13–16
Identification of Patients Using Stimulant and Designer Drugs
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed., uses the term substance use disorder rather than substance abuse and substance misuse.17 These disorders are categorized by the type of substance being used and the level of severity, as determined by the number of diagnostic criteria met (mild = two or three criteria, moderate = four or five, severe = six or more)17,18 (Table 217 ).

|
Specify if:
|
Specify if:
|
Laboratory diagnosis is not necessary but is often used in conjunction with the history and physical examination for initial diagnosis and to monitor for abstinence. Urine screening immunoassays are inexpensive and provide rapid results. However, the sample can be easily tampered with by the patient, many of the substances may cross-react with other drugs or medications, and the duration for detection is variable.19
Cocaine is the drug least likely to have a false-positive result by measuring its major metabolite, benzoylecgonine. Cocaine is typically detectable in the urine for two to three days, but this can vary based on usage. Tests for methamphetamines often yield false-positive results because of cross-reactivity with decongestants and appetite suppressants. Urine pH affects the excretion of amphetamines, and ingestion of large quantities of bicarbonate will reduce the ability to detect them. The typical time frame for detection by urine immunoassay is one to three days.19
Newer designer drugs such as synthetic cannabinoids and bath salts are not detected by routine drug screening. Although they can be identified by liquid and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, these tests are not available at most laboratories, and the lengthy turnaround time makes them less useful clinically.19
Cocaine
Cocaine has many street names and comes in two forms: base and salt, each having the same cocaine molecule and pharmacologic action at the brain or target organ, but different routes of administration.19 Cocaine base has been processed to make a rock crystal. It vaporizes when heated, which allows it to be smoked. Cocaine salt is a fine white powder that can be snorted or mixed with water and injected.19 Passive absorption is also possible through inhalation and has been noted in exposed infants and children.19 Cocaine can be detected in blood, urine, hair, saliva, sweat,20 and breast milk,21 and it can cross the placenta.22 It works on the central and peripheral nervous systems by blocking reuptake of monoamine transporters (dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin).19
Cocaine's onset of action varies with the route of administration, with more rapid onset after the drug is smoked or injected. Effects last less than 30 minutes. Intranasal use has a delayed onset with effects lasting approximately 60 minutes. Users frequently readminister to maintain the desired effects.5 Immediate clinical effects include increased energy and alertness, euphoria, sociability, appetite suppression, and decreased need for sleep.19 Unintended adverse effects are more likely with increasing dose and duration of use, and faster onset of action with smoking or injection use.19 Up to 80% of persons with cocaine use disorder have psychotic symptoms, such as hallucinations or paranoia.23
Table 3 lists short- and long-term health effects of cocaine use.5,19,24–29 Coronary vasoconstriction combined with increased cardiac oxygen demand can lead to myocardial ischemia, even without atherosclerosis.30 Cocaine use contributes to 25% of nonfatal myocardial infarctions in patients younger than 45 years.31 When these patients present for urgent treatment of chest pain, avoidance of unopposed beta blockers (drugs without any alpha blockade, such as propranolol) has been recommended based on a small study (n = 30) that found a significant reduction in coronary sinus blood flow in patients using cocaine.25 However, the American Heart Association recommends that patients with non–ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome and a recent history of cocaine use be treated in the same manner as patients without cocaine-related non–ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome unless they exhibit signs of acute intoxication, in which case beta blockers should be avoided because of the risk of potentiating coronary spasm.32 Calcium channel blockers reduce hypertension and coronary vasospasm, but may not decrease tachycardia.33 Left untreated, cocaine-associated vasospasm and hypertension have been associated with acute aortic dissection, in addition to ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.30
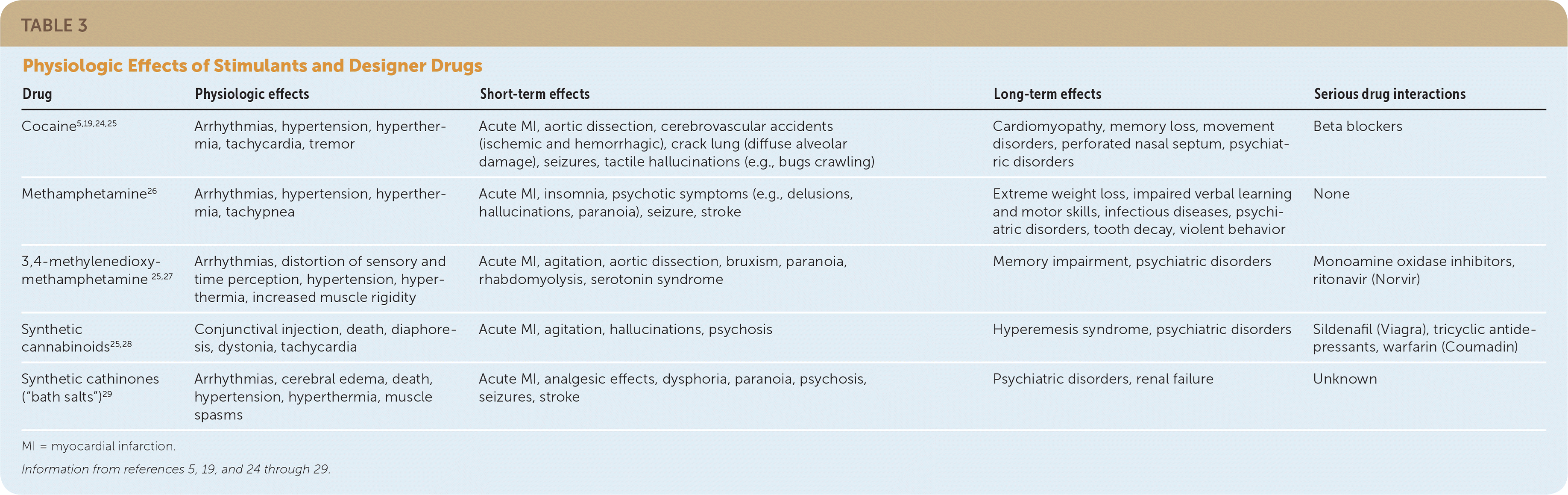
| Drug | Physiologic effects | Short-term effects | Long-term effects | Serious drug interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cocaine5,19,24,25 | Arrhythmias, hypertension, hyperthermia, tachycardia, tremor | Acute MI, aortic dissection, cerebrovascular accidents (ischemic and hemorrhagic), crack lung (diffuse alveolar damage), seizures, tactile hallucinations (e.g., bugs crawling) | Cardiomyopathy, memory loss, movement disorders, perforated nasal septum, psychiatric disorders | Beta blockers |
| Methamphetamine26 | Arrhythmias, hypertension, hyperthermia, tachypnea | Acute MI, insomnia, psychotic symptoms (e.g., delusions, hallucinations, paranoia), seizure, stroke | Extreme weight loss, impaired verbal learning and motor skills, infectious diseases, psychiatric disorders, tooth decay, violent behavior | None |
| 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine 25,27 | Arrhythmias, distortion of sensory and time perception, hypertension, hyperthermia, increased muscle rigidity | Acute MI, agitation, aortic dissection, bruxism, paranoia, rhabdomyolysis, serotonin syndrome | Memory impairment, psychiatric disorders | Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, ritonavir (Norvir) |
| Synthetic cannabinoids25,28 | Conjunctival injection, death, diaphoresis, dystonia, tachycardia | Acute MI, agitation, hallucinations, psychosis | Hyperemesis syndrome, psychiatric disorders | Sildenafil (Viagra), tricyclic antidepressants, warfarin (Coumadin) |
| Synthetic cathinones (“bath salts”)29 | Arrhythmias, cerebral edema, death, hypertension, hyperthermia, muscle spasms | Acute MI, analgesic effects, dysphoria, paranoia, psychosis, seizures, stroke | Psychiatric disorders, renal failure | Unknown |
BEHAVIORAL THERAPY
A 2016 Cochrane review concluded that compared with usual treatment (typically group counseling or case management), psychosocial therapy improved adherence and increased abstinence for adults using cocaine.34 However, this effect may not be maintained in the long term. Psychosocial interventions evaluated included individual or group counseling, intensive outpatient therapy, cognitive behavior therapy, and motivational interviewing.34 Combined group and individual counseling was more effective than either type alone in one randomized controlled trial.34 Table 4 lists behavioral referral resources for clinicians. Resources vary by geographic region, and clinicians should acquaint themselves with local resources.

| Alcoholics Anonymous (https://www.aa.org) |
| American Society of Addiction Medicine physician finder (https://asam.ps.membersuite.com/directory/SearchDirectory_Criteria.aspx) |
| Narcotics Anonymous (https://na.org) |
| SMART Recovery (https://www.smartrecovery.org) |
| Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration treatment locator (https://findtreatment.samhsa.gov or 800-662-4357) |
MEDICAL THERAPY
No medications have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of cocaine use disorder. A Cochrane review of seven randomized controlled trials (N = 492) concluded that there is low-level evidence to support the use of disulfiram (Antabuse) in addition to psychosocial therapy for treatment of cocaine use disorder.35 Other Cochrane reviews found no evidence for the use of anticonvulsants,36 dopamine agonists,37 anti-psychotics,38 auricular acupuncture,39 or antidepressants (including desipramine, fluoxetine [Prozac], and bupropion [Wellbutrin])40 in the treatment of cocaine use disorder.
Substitution therapy (replacing an illegal drug with a legal, oral, longer-acting drug that has lower addiction potential, such as methylphenidate [Ritalin] or amphetamine salts) seems promising for cocaine use disorder. However, a 2016 Cochrane review concluded that evidence does not clearly demonstrate effectiveness, and that more high-quality studies are needed.41
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine can be prescribed as a schedule II drug for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Most illicit methamphetamine used in the United States is at much higher doses than for medicinal use and is manufactured in illegal laboratories. It can also be made in small clandestine laboratories with ingredients such as pseudoephedrine.6
Methamphetamine can be taken orally, smoked, snorted, or dissolved in water or alcohol and injected. Smoking or injecting delivers methamphetamine to the brain quickly, causing a euphoric rush or “flash.” Because the effects are transient, repeated doses are often used to sustain the effect, leading to the binge-and-crash pattern common with stimulant misuse. Like cocaine, methamphetamine blocks the reuptake of monoamine neurotransmitters. However, methamphetamine also stimulates the release of dopamine into synapses and has a much longer duration of action than cocaine.6
Methamphetamine causes many of the same clinical effects as other stimulants (Table 3).5,19,24–29 Imaging studies have shown structural and functional changes in areas of the brain associated with emotion and memory, which may persist long after methamphetamine use is stopped.6 Long-term use of methamphetamine can produce changes in appearance, such as weight loss and dental problems (“meth mouth”).6 A study of 571 methamphetamine users revealed that 96% had dental caries and 58% had untreated tooth decay.42
TREATMENT
Although no medications are approved for treatment of methamphetamine use disorder, a few have shown promise. A randomized controlled trial enrolled 60 men who have sex with men; participants had methamphetamine use disorder and were actively using the drug.43 All of the men received weekly counseling plus mirtazapine (Remeron), 30 mg per day, or placebo. Men in the mirtazapine group had decreased methamphetamine use and sexual risk, despite low adherence. Another randomized controlled trial found no overall improvement with bupropion.44
MDMA
3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, also known as “ecstasy”) is a sympathomimetic amphetamine with a chemical structure similar to serotonin. It acts as both a stimulant and a psychedelic, inducing feelings of increased energy and pleasure, especially from tactile stimulation. It is generally taken in pill form, but is sometimes snorted or ingested as a liquid. The effects of MDMA last about three to six hours, and doses are often repeated to maintain effects.8
MDMA stimulates the release of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, as well as cortisol, oxytocin, and antidiuretic hormone. MDMA causes a 10-fold greater serotonin release than methamphetamine, which induces intense mood effects.27 Depletion of the brain's serotonin contributes to MDMA's negative aftereffects on behavior and mood. Serotonin syndrome and hyponatremia are possible consequences of MDMA toxicity. Hyponatremia can result from dilutional effects of water overconsumption from thirst and overheating, in addition to increased free water absorption at the kidneys due to increased levels of antidiuretic hormone.27 The protease inhibitor ritonavir (Norvir) has been found to potentiate MDMA, leading to cardiac arrest and death.25 Animal studies have shown that MDMA can cause long-lasting damage to serotonin-containing neurons. The addiction potential of MDMA has not been well studied.8
TREATMENT
Synthetic Cannabinoids
Synthetic cannabinoids are compounds with cannabinoid-like action, but a different chemical structure than marijuana-derived cannabinoids. These compounds are sprayed onto dried, shredded plant material to be smoked or available as liquids to be vaporized and inhaled in electronic delivery devices. They have been sold in convenience stores or online as incense; the chemical formulation frequently changes to avoid detection by standard drug tests and regulatory efforts.45
Synthetic cannabinoids are direct agonists with a high affinity for the cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor, as opposed to tetrahydrocannabinol, which is a partial agonist of the CB1 and CB2 receptors. This difference can lead to more intense and long-lasting effects. Acute intoxication and withdrawal syndromes from synthetic cannabinoids may require hospitalization because of severe cardiac, respiratory, and seizure complications.46 More than two dozen deaths were attributed to synthetic cannabinoids during a two-month outbreak in Mississippi in 2015.9
Because chemical composition of synthetic cannabinoids varies from batch to batch, and because they may be mixed with other substances, clinical and mind-altering effects vary considerably. Synthetic cannabinoids are thought to be addictive, and withdrawal symptoms may include headaches, anxiety, depression, and irritability.45
TREATMENT
Although there are no studies of treatments for synthetic cannabinoid use, studies are available for cannabis use disorder. Compared with minimal or inactive treatment controls, psychosocial interventions reduce the frequency of use and severity of dependence in frequent users of cannabis.47 Intensive intervention using a combination of cognitive behavior therapy and motivational enhancement therapy with abstinence-based incentives was most consistently supported. It is not known if these findings are generalizable to synthetic cannabinoid use disorder.
A Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to recommend selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, bupropion, buspirone (Buspar), or norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of cannabis use disorder.48 Limited data suggest a role for preparations containing tetrahydrocannabinol, gabapentin (Neurontin), and N-acetylcysteine. However, it is not known if these findings would be applicable for synthetic cannabinoid use disorder.48
Bath Salts
Synthetic cathinones, or “bath salts,” are synthetic drugs chemically related to cathinone, a stimulant found in the khat plant of eastern Africa and South Asia. They are marketed as cheap substitutes for other stimulants. Synthetic cathinones are usually sold as a white or brown crystal-like powder, and may be labeled as bath salts, plant food, or jewelry cleaner. They may be swallowed, snorted, smoked, or injected to produce desired stimulant effects, including increased sociability and libido.10
TREATMENT
Behavioral therapy, including cognitive behavior therapy and motivational incentives, can be used to treat patients with synthetic cathinone use disorder.10 There are currently no pharmacologic treatments for dependence on synthetic cathinones.
This article updates previous articles on this topic by Winslow, et al.26 , and by Gahlinger7 .
Data Sources: A PubMed search was performed using the key terms cocaine, methamphetamines, MDMA, synthetic cannabinoids, bath salts, and synthetic cathinones. The search included meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, and review articles. Also searched were the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Essential Evidence Plus, evidence-based guidelines from the National Guideline Clearinghouse, and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Search dates: December 2016 to April 2018.
