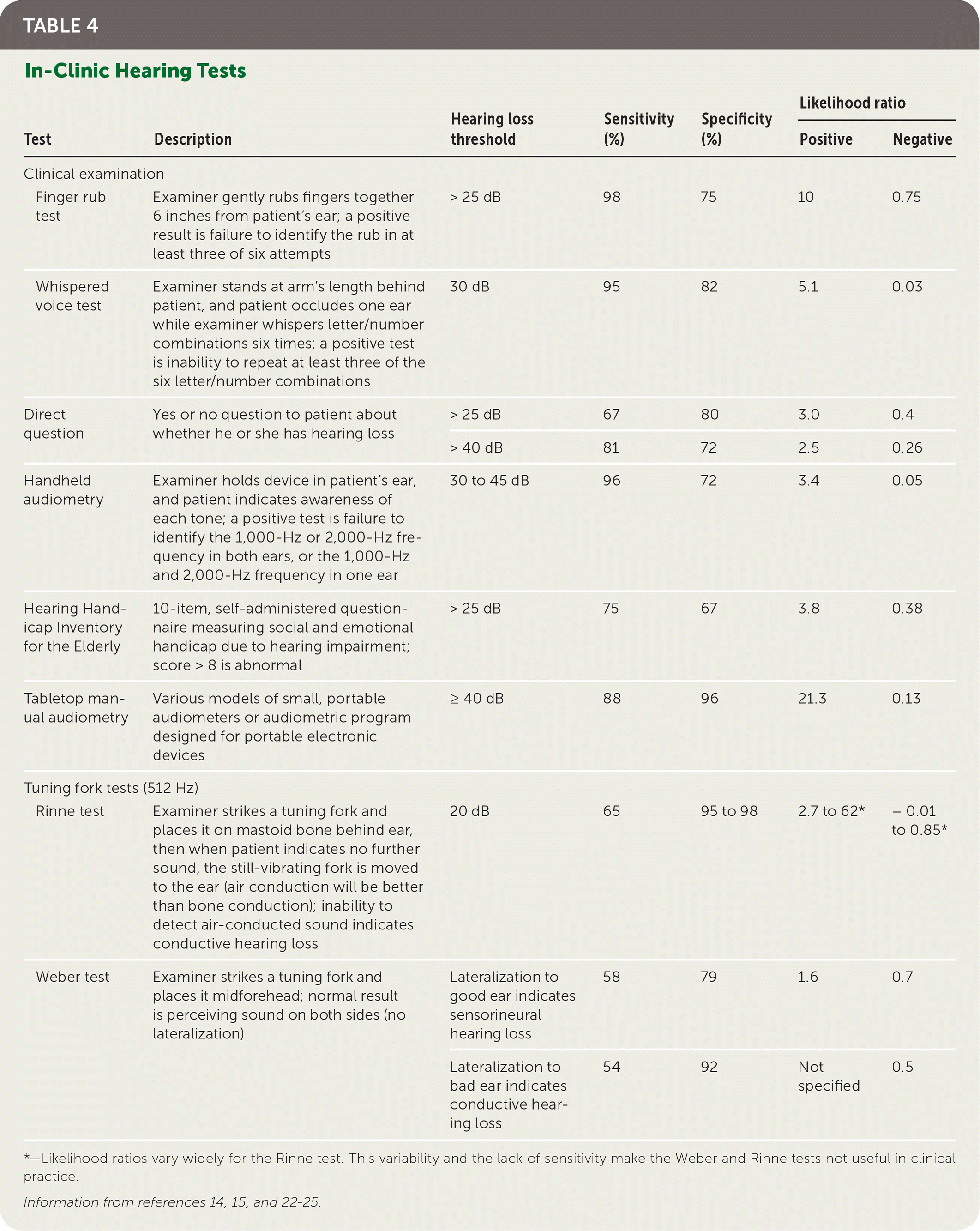
| Clinical examination |
| | Finger rub test | Examiner gently rubs fingers together 6 inches from patient's ear; a positive result is failure to identify the rub in at least three of six attempts | > 25 dB | 98 | 75 | 10 | 0.75 |
| | Whispered voice test | Examiner stands at arm's length behind patient, and patient occludes one ear while examiner whispers letter/number combinations six times; a positive test is inability to repeat at least three of the six letter/number combinations | 30 dB | 95 | 82 | 5.1 | 0.03 |
| Direct question | Yes or no question to patient about whether he or she has hearing loss | > 25 dB | 67 | 80 | 3.0 | 0.4 |
| > 40 dB | 81 | 72 | 2.5 | 0.26 |
| Handheld audiometry | Examiner holds device in patient's ear, and patient indicates awareness of each tone; a positive test is failure to identify the 1,000-Hz or 2,000-Hz frequency in both ears, or the 1,000-Hz and 2,000-Hz frequency in one ear | 30 to 45 dB | 96 | 72 | 3.4 | 0.05 |
| Hearing Handicap Inventory for the Elderly | 10-item, self-administered questionnaire measuring social and emotional handicap due to hearing impairment; score > 8 is abnormal | > 25 dB | 75 | 67 | 3.8 | 0.38 |
| Tabletop manual audiometry | Various models of small, portable audiometers or audiometric program designed for portable electronic devices | ≥ 40 dB | 88 | 96 | 21.3 | 0.13 |
| Tuning fork tests (512 Hz) |
| | Rinne test | Examiner strikes a tuning fork and places it on mastoid bone behind ear, then when patient indicates no further sound, the still-vibrating fork is moved to the ear (air conduction will be better than bone conduction); inability to detect air-conducted sound indicates conductive hearing loss | 20 dB | 65 | 95 to 98 | 2.7 to 62* | – 0.01 to 0.85* |
| Weber test | Examiner strikes a tuning fork and places it midforehead; normal result is perceiving sound on both sides (no lateralization) | Lateralization to good ear indicates sensorineural hearing loss | 58 | 79 | 1.6 | 0.7 |
| Lateralization to bad ear indicates conductive hearing loss | 54 | 92 | Not specified | 0.5 |