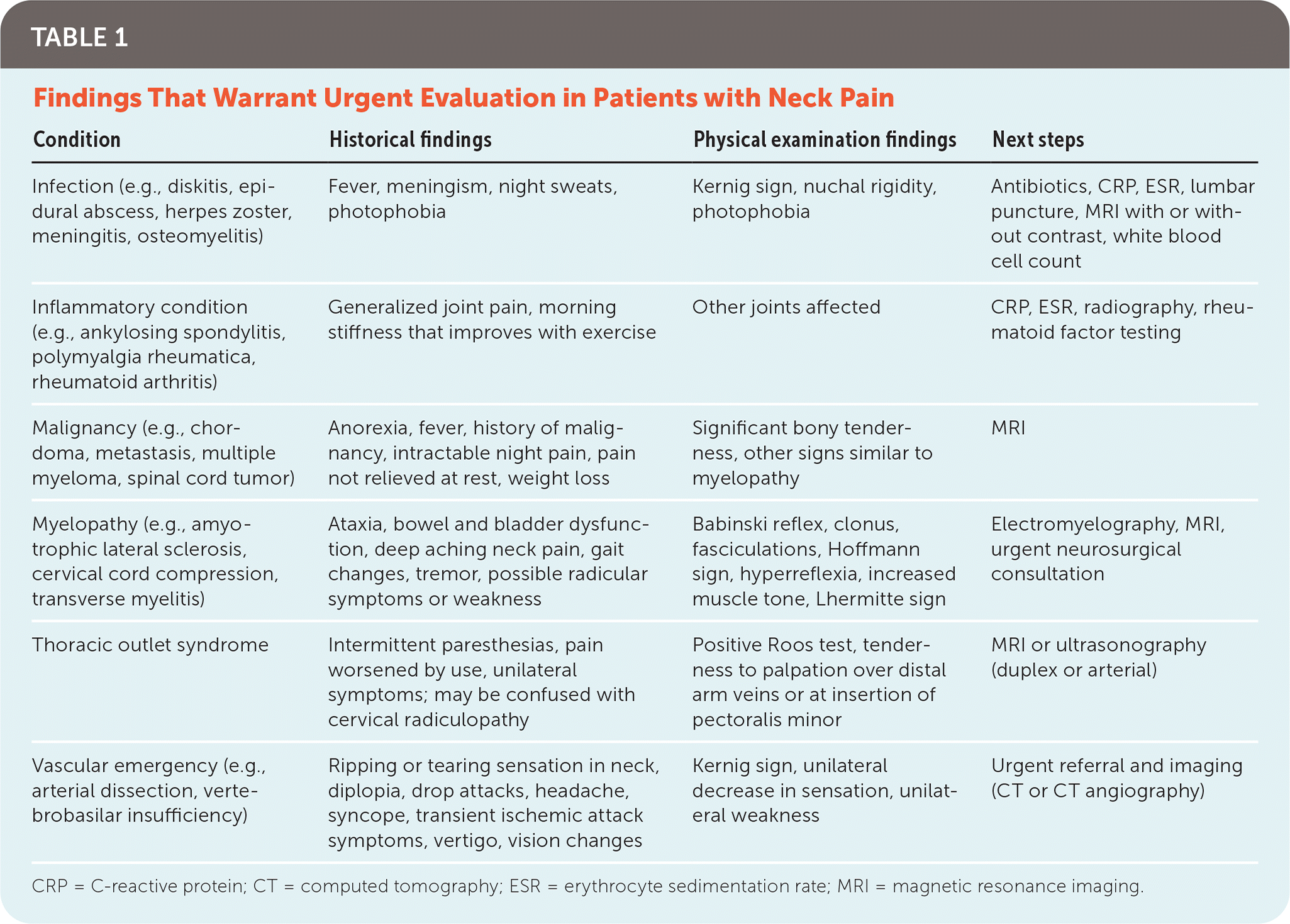
| Infection (e.g., diskitis, epidural abscess, herpes zoster, meningitis, osteomyelitis) | Fever, meningism, night sweats, photophobia | Kernig sign, nuchal rigidity, photophobia | Antibiotics, CRP, ESR, lumbar puncture, MRI with or without contrast, white blood cell count |
| Inflammatory condition (e.g., ankylosing spondylitis, polymyalgia rheumatica, rheumatoid arthritis) | Generalized joint pain, morning stiffness that improves with exercise | Other joints affected | CRP, ESR, radiography, rheumatoid factor testing |
| Malignancy (e.g., chordoma, metastasis, multiple myeloma, spinal cord tumor) | Anorexia, fever, history of malignancy, intractable night pain, pain not relieved at rest, weight loss | Significant bony tenderness, other signs similar to myelopathy | MRI |
| Myelopathy (e.g., amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, cervical cord compression, transverse myelitis) | Ataxia, bowel and bladder dysfunction, deep aching neck pain, gait changes, tremor, possible radicular symptoms or weakness | Babinski reflex, clonus, fasciculations, Hoffmann sign, hyperreflexia, increased muscle tone, Lhermitte sign | Electromyelography, MRI, urgent neurosurgical consultation |
| Thoracic outlet syndrome | Intermittent paresthesias, pain worsened by use, unilateral symptoms; may be confused with cervical radiculopathy | Positive Roos test, tenderness to palpation over distal arm veins or at insertion of pectoralis minor | MRI or ultrasonography (duplex or arterial) |
| Vascular emergency (e.g., arterial dissection, vertebrobasilar insufficiency) | Ripping or tearing sensation in neck, diplopia, drop attacks, headache, syncope, transient ischemic attack symptoms, vertigo, vision changes | Kernig sign, unilateral decrease in sensation, unilateral weakness | Urgent referral and imaging (CT or CT angiography) |