
Am Fam Physician. 2021;103(2):113-114
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
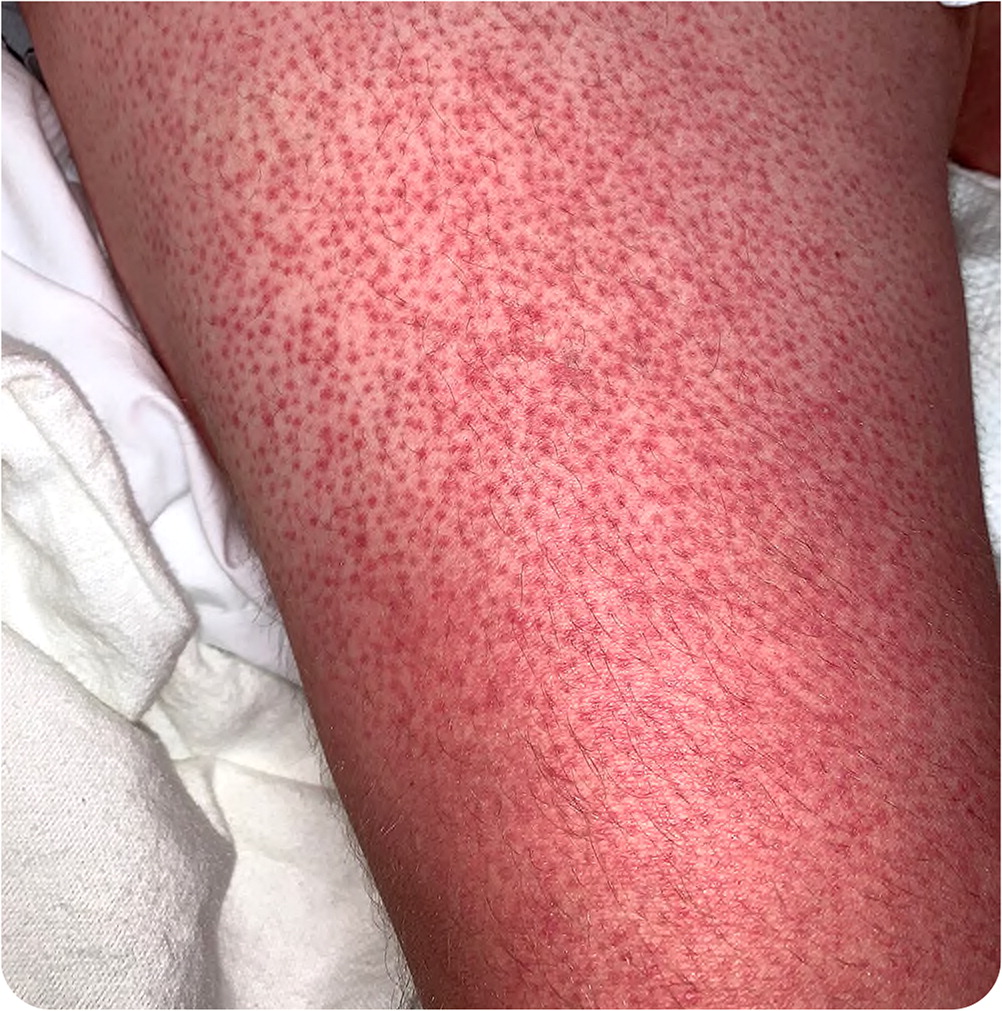
A 33-year-old patient presented with a rash that developed two days earlier and was preceded by fever, headache, nausea, and arthralgias. The rash was worse on the limbs. The medical history was unremarkable, but the patient had recently traveled to the Philippines.

Question
Based on the patient's history and physical examination findings, which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Acute HIV infection
B. Chikungunya virus infection.
C. Dengue.
D. Malaria.
E. Zika virus infection.
Discussion
The answer is C: dengue, a common mosquito-borne disease encountered in more than 100 tropical and subtropical countries in North and South America, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and the Pacific Islands. The incidence is increasing, and outbreaks are becoming more common, including in the Caribbean and the Big Island of Hawaii.1 The disease is caused by one of four dengue viruses transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitos. Most cases in the United States are travel-related, except in Puerto Rico where dengue is endemic.2
Humans are the primary reservoirs for dengue. Patients with the disease may be asymptomatic or have mild to severe or life-threatening symptoms. Common presenting symptoms include high-grade fever, headache, retroorbital pain, myalgias/arthralgias, nausea, vomiting, and rash. The disease progresses to severe dengue in one out of 20 patients.1 Severe dengue follows three phases: febrile, critical, recovery. The critical phase occurs after 72 hours of fever and is distinguished by increased vascular permeability, fever, hemorrhagic manifestations, and marked thrombocytopenia.
Diagnosis of dengue is based on clinical signs and symptoms. The tourniquet test is commonly used.3 To perform this test, a blood pressure cuff is inflated on the arm, then removed. After two minutes, petechiae are counted below the antecubital fossa. The test is positive if there are 10 or more petechiae per 1 square inch (Figure 2). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends testing symptomatic patients with a history of travel to endemic areas.4
Acute HIV infection, also known as primary HIV infection or acute retroviral syndrome, is the period just after initial HIV infection, generally before seroconversion.5 Symptoms are characterized as mononucleosis-like or flulike, with the most prevalent symptoms being fever, fatigue, myalgias/arthralgias, rash, pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, and mucocutaneous ulcerations.5
Chikungunya virus infection and dengue have similar symptoms and are transmitted by the same mosquito vectors.6 Chikungunya virus infection is characterized by fever and intense joint pain but lacks leukopenia and thrombocytopenia. Headache, myalgias, and rash are also possible.7 The laboratory diagnosis of Chikungunya virus infection is based on viral isolation.6

| Condition | Characteristics | Signs and symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Acute HIV infection | Period just after initial HIV infection, generally before seroconversion; also called primary HIV infection or acute retroviral syndrome | Mononucleosis-like or flulike; fever, fatigue, myalgias/arthralgias, rash, pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, and mucocutaneous ulcerations |
| Chikungunya virus infection | Similar to dengue but lacks leukopenia and thrombocytopenia; transmitted by same mosquito vectors as dengue | Fever and intense joint pain; headache, myalgias, and rash are also possible |
| Dengue | Can be diagnosed using the tourniquet test; severe illness has three phases: febrile, critical, and recovery; transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitos | High-grade fever, headache, retroorbital pain, myalgias/arthralgias, nausea, vomiting, and rash |
| Malaria | Parasitic infection | Fever and splenomegaly |
| Zika virus infection | Transmitted by same mosquito vectors as dengue; can cause birth defects, such as microcephaly, if the mother is infected during pregnancy | Often asymptomatic; if present, symptoms are similar to dengue, but conjunctivitis is more common |
