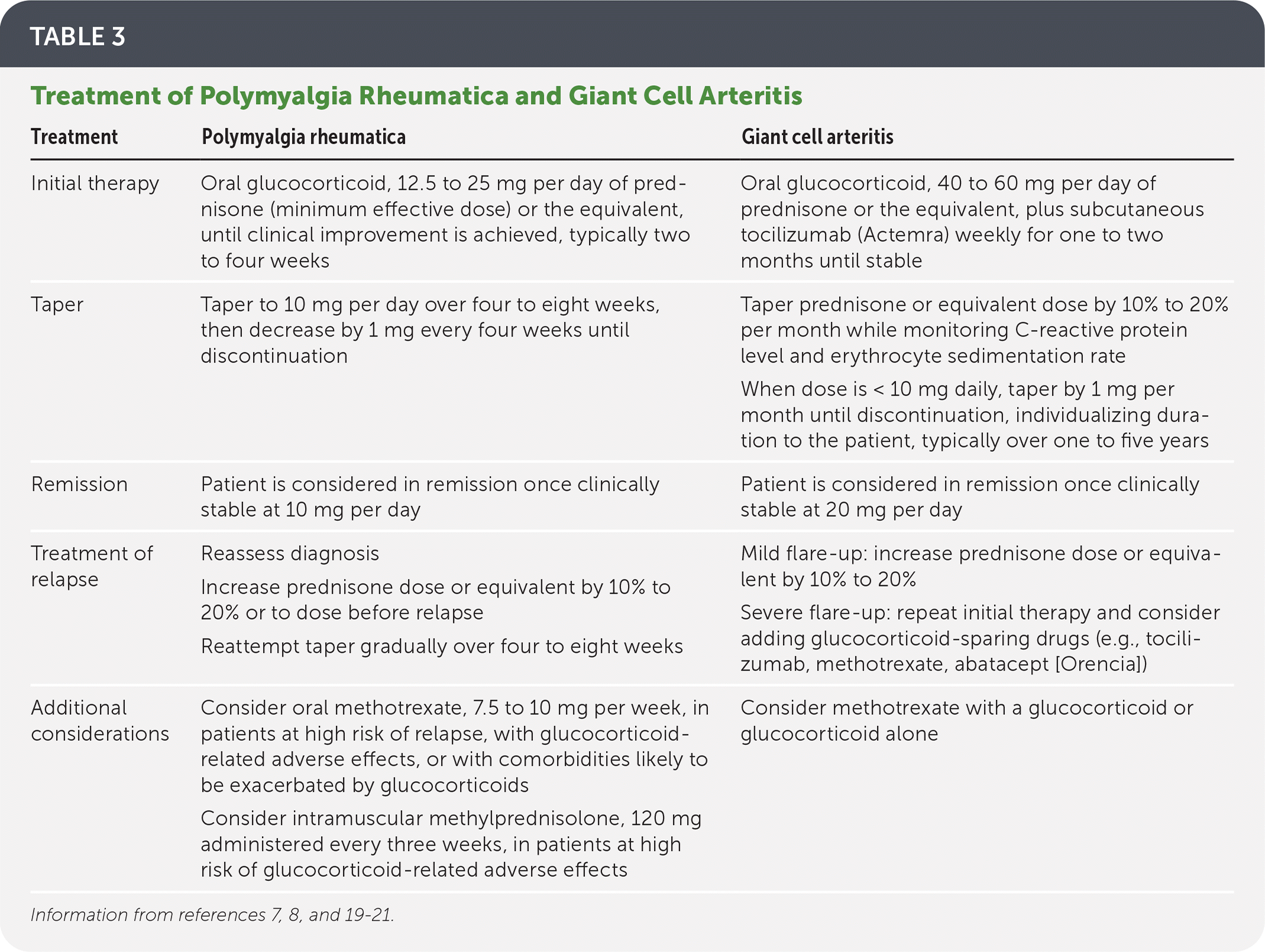
| Treatment | Polymyalgia rheumatica | Giant cell arteritis |
|---|---|---|
| Initial therapy | Oral glucocorticoid, 12.5 to 25 mg per day of prednisone (minimum effective dose) or the equivalent, until clinical improvement is achieved, typically two to four weeks | Oral glucocorticoid, 40 to 60 mg per day of prednisone or the equivalent, plus subcutaneous tocilizumab (Actemra) weekly for one to two months until stable |
| Taper | Taper to 10 mg per day over four to eight weeks, then decrease by 1 mg every four weeks until discontinuation | Taper prednisone or equivalent dose by 10% to 20% per month while monitoring C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate When dose is < 10 mg daily, taper by 1 mg per month until discontinuation, individualizing duration to the patient, typically over one to five years |
| Remission | Patient is considered in remission once clinically stable at 10 mg per day | Patient is considered in remission once clinically stable at 20 mg per day |
| Treatment of relapse | Reassess diagnosis Increase prednisone dose or equivalent by 10% to 20% or to dose before relapse Reattempt taper gradually over four to eight weeks | Mild flare-up: increase prednisone dose or equivalent by 10% to 20% Severe flare-up: repeat initial therapy and consider adding glucocorticoid-sparing drugs (e.g., tocilizumab, methotrexate, abatacept [Orencia]) |
| Additional considerations | Consider oral methotrexate, 7.5 to 10 mg per week, in patients at high risk of relapse, with glucocorticoid-related adverse effects, or with comorbidities likely to be exacerbated by glucocorticoids Consider intramuscular methylprednisolone, 120 mg administered every three weeks, in patients at high risk of glucocorticoid-related adverse effects | Consider methotrexate with a glucocorticoid or glucocorticoid alone |