
This is a corrected version of the article that appeared in print.
Am Fam Physician. 2023;107(3):319-322
Published online February 13, 2023.
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Key Points for Practice
• The COVID-19 primary vaccination series is recommended for everyone six months and older.
• Bivalent COVID-19 vaccine boosters are recommended for everyone six months to four years of age who completed the Moderna primary series and everyone five years and older to improve protection from the Omicron variant.
• The pneumococcal vaccines PCV15 and PCV20 are recommended for adults 65 years and older; those who received older vaccines should be given an updated version.
• For pre- and postexposure prophylaxis against mpox, Jynneos is recommended as a standard 0.5-mL subcutaneous injection or a 0.1-mL intradermal injection.
From the AFP Editors
The 2023 child/adolescent and adult immunization schedules have been approved by the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and are accessible at https://www.aafp.org/family-physician/patient-care/prevention-wellness/immunizations-vaccines.html. These schedules include links to COVID-19 vaccination information, vaccination information statements, adverse event reporting, and a QR code for online schedules. Notable changes include updates to COVID-19 recommendations and mpox (formerly monkeypox) vaccination.
Changes to Both the Child/Adolescent and Adult Immunization Schedules
COVID-19 VACCINATION
Everyone six months and older should receive a COVID-19 vaccination, which may be administered on the same day as other vaccines.
The four COVID-19 vaccines approved or authorized for emergency use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, and recommended for primary series vaccination by ACIP include the following:
Two- or three-dose monovalent mRNA BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech, Comirnaty)
Two- or three-dose monovalent mRNA mRNA-1273 (Moderna, Spikevax)
Single-dose adenovirus vector-based Ad26.COV.S (Janssen [Johnson & Johnson]) can be given in some situations
Two-dose adjuvanted, protein subunit–based NVXCoV2373 (Novavax)
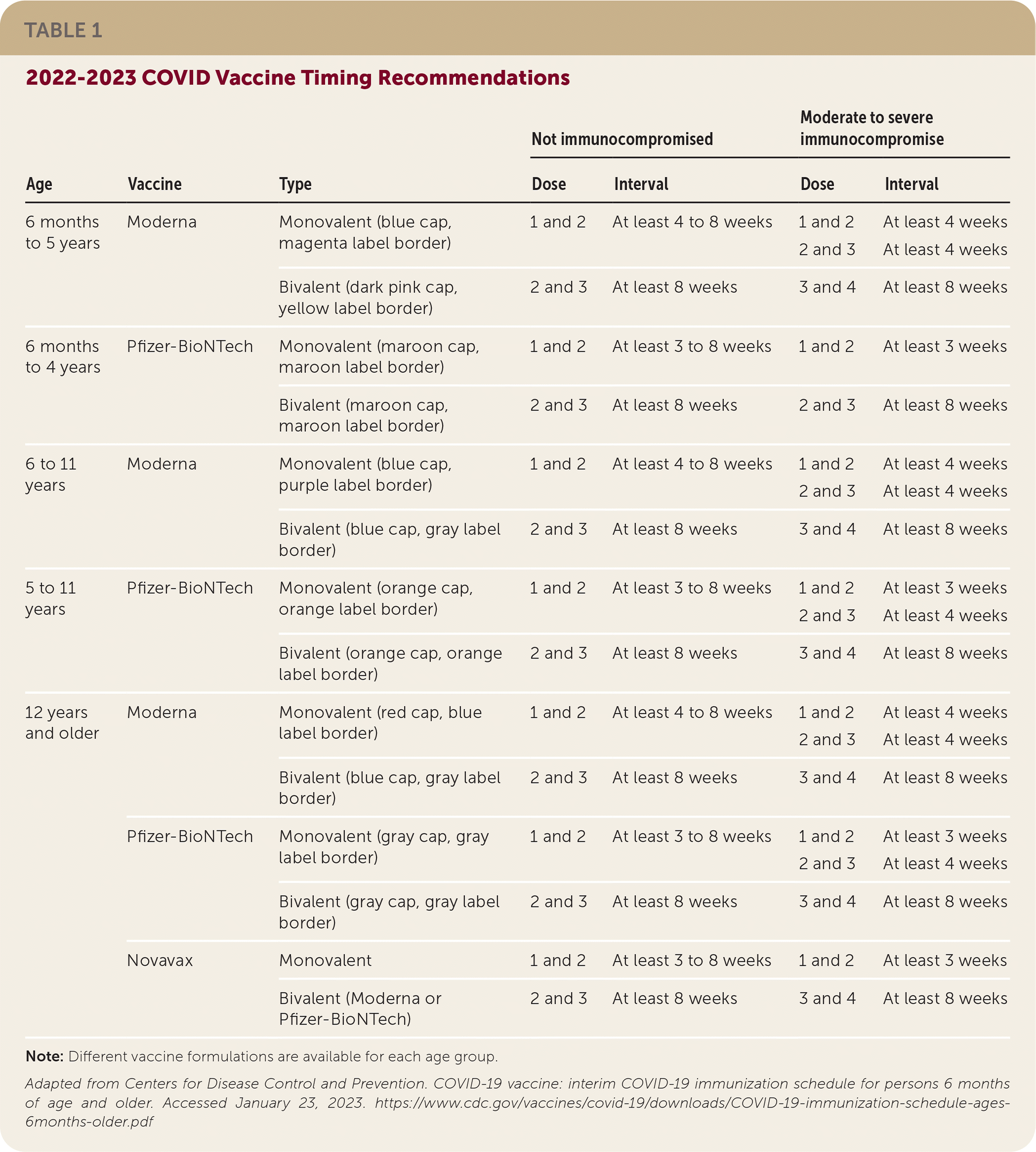
| Age | Vaccine | Type | Not immunocompromised | Moderate to severe immunocompromise | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose | Interval | Dose | Interval | |||
| 6 months to 5 years | Moderna | Monovalent (blue cap, magenta label border) | 1 and 2 | At least 4 to 8 weeks | 1 and 2 2 and 3 | At least 4 weeks At least 4 weeks |
| Bivalent (dark pink cap, yellow label border) | 2 and 3 | At least 8 weeks | 3 and 4 | At least 8 weeks | ||
| 6 months to 4 years | Pfizer- BioNTech | Monovalent (maroon cap, maroon label border) | 1 and 2 | At least 3 to 8 weeks | 1 and 2 | At least 3 weeks |
| Bivalent (maroon cap, maroon label border) | 2 and 3 | At least 8 weeks | 2 and 3 | At least 8 weeks | ||
| 6 to 11 years | Moderna | Monovalent (blue cap, purple label border) | 1 and 2 | At least 4 to 8 weeks | 1 and 2 2 and 3 | At least 4 weeks At least 4 weeks |
| Bivalent (blue cap, gray label border) | 2 and 3 | At least 8 weeks | 3 and 4 | At least 8 weeks | ||
| 5 to 11 years | Pfizer- BioNTech | Monovalent (orange cap, orange label border) | 1 and 2 | At least 3 to 8 weeks | 1 and 2 2 and 3 | At least 3 weeks At least 4 weeks |
| Bivalent (orange cap, orange label border) | 2 and 3 | At least 8 weeks | 3 and 4 | At least 8 weeks | ||
| 12 years and older | Moderna | Monovalent (red cap, blue label border) | 1 and 2 | At least 4 to 8 weeks | 1 and 2 2 and 3 | At least 4 weeks At least 4 weeks |
| Bivalent (blue cap, gray label border) | 2 and 3 | At least 8 weeks | 3 and 4 | At least 8 weeks | ||
| Pfizer-BioNTech | Monovalent (gray cap, gray label border) | 1 and 2 | At least 3 to 8 weeks | 1 and 2 2 and 3 | At least 3 weeks At least 4 weeks | |
| Bivalent (gray cap, gray label border) | 2 and 3 | At least 8 weeks | 3 and 4 | At least 8 weeks | ||
| Novavax | Monovalent | 1 and 2 | At least 3 to 8 weeks | 1 and 2 | At least 3 weeks | |
| Bivalent (Moderna or Pfizer-BioNTech) | 2 and 3 | At least 8 weeks | 3 and 4 | At least 8 weeks | ||
For the primary vaccination series, an eight-week gap is recommended between first and second doses of Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, or Novavax vaccines for anyone between six months and 64 years of age. This longer time frame between the first and second primary doses may increase protection and further reduce the risk of myocarditis and pericarditis.
Bivalent mRNA vaccines contain components of the original SARS-CoV-2 strain and the Omicron strain. All people six months to four years of age who completed the Moderna primary series and all people five years or older should receive a single bivalent vaccine booster dose at least two months after completion of the primary vaccination series with the monovalent vaccine. People 12 years and older who completed the Novavax vaccine series should receive a bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna booster. The additional bivalent vaccination is recommended because COVID-19 vaccines are less effective when the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2 predominates. For adults 65 years and older, bivalent vaccines reduce hospitalizations by 73% compared with monovalent vaccines.
INFLUENZA VACCINATION
Annual influenza vaccination continues to be recommended for all people six months or older without contraindications. About 93% of the projected vaccine supply produced for the 2022–2023 flu season will be thimerosal-free or thimerosal-reduced (i.e., preservative-free).
All flu vaccines for the 2022–2023 season are quadrivalent, including hemagglutinin from one influenza A(H1N1) pdm09 virus, one influenza A(H3N2) virus, one influenza B/Victoria lineage virus, and one influenza B/Yamagata lineage virus. Trivalent influenza vaccines are no longer available.
For people younger than 65 years, all vaccines are equally safe and effective. Fluzone high-dose quadrivalent, Flublok quadrivalent recombinant, and Fluad quadrivalent adjuvanted flu vaccines are preferred for people 65 years or older.
Because of the continuing circulation of SARS-CoV-2 during the 2022–2023 influenza season, influenza vaccination is recommended because it reduces symptoms that might be confused with those of COVID-19, outpatient visits, hospitalizations, and intensive care unit admissions and mitigates stress on the health care system.
Flu vaccines can be administered with other vaccines, including those for COVID-19, if they are administered in separate body sites. Guidance on the influenza vaccine recommendations is available at https://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/acip/summary/summary-recommendations.htm.
Changes to the Child/Adolescent Immunization Schedule
COVID-19 VACCINATION
For children six months to four years of age, the bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine can be given after two previous monovalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines to complete their primary series, but not if a third vaccine has been received. The bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech booster vaccine is recommended at least eight weeks after completing the primary Pfizer-BioNTech series or last booster in children five years and older. Children six years and older can get a bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna booster at least eight weeks after second dose or last booster.
For the Moderna vaccine series, all children six months or older can receive a single bivalent Moderna booster vaccine at least eight weeks after completing the primary series. Children five years or older can receive the bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine or the bivalent Moderna vaccine as their booster dose.
For the Novavax vaccine series, the bivalent Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna booster is recommended for children 12 years and older at least eight weeks after completing the primary series.
Changes to Adult Immunization Schedule
PNEUMOCOCCAL VACCINATION
In 2021, recommendations for pneumococcal vaccination changed, and these have been further clarified. Either the 15- or 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV15, PCV20) is recommended for adults 65 years or older to prevent pneumococcal disease. A single dose is sufficient; but if PCV15 is given, it should be followed by a dose of the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23).
For adults younger than 65 years with certain risk factors (Table 22), either PCV15 and then PPSV23 after eight weeks, or a single PCV20 are recommended. [corrected] Patients with an immunocompromising condition, cochlear implant, or cerebrospinal leak who receive a pneumococcal vaccination every five years can continue to receive PPSV23 every five years or substitute PCV20.

| Alcoholism |
| Cerebral spinal fluid leak |
| Chronic heart disease |
| Chronic kidney disease or nephrotic syndrome |
| Chronic liver disease |
| Chronic lung disease |
| Cigarette smoking |
| Cochlear implant |
| Congenital or acquired asplenia |
| Diabetes mellitus |
| Generalized malignancy |
| HIV |
| Hodgkin disease |
| Immunodeficiency or iatrogenic immunosuppression |
| Leukemia, lymphoma, or multiple myeloma |
| Sickle cell disease or other hemoglobinopathies |
| Solid organ transplant recipient |
Adults who have received an older pneumococcal vaccination should receive an updated vaccine. Those who previously received the PPSV23 vaccine should receive either the PCV15 or PCV20 at least one year later without another PPSV23 dose. Those who received the PCV13 should receive PCV15 or PCV20 and PPSV23 at least one year later. Those who received the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and the PPSV23 can opt to receive a PCV20 at least five years after their most recent vaccine dose if they choose.
MPOX VACCINATION
Following the U.S. outbreak in May 2022, ACIP issued interim recommendations on two vaccines that may be used for mpox vaccination.
The Jynneos vaccine is approved for prevention of smallpox and mpox and is primarily delivered subcutaneously as a 0.5-mL dose. To maximize limited supplies, Jynneos can also be delivered intradermally as a 0.1-mL dose based on an emergency use authorization.
The ACAM2000 smallpox vaccine has been approved as an alternative to Jynneos under an Expanded Access Investigational New Drug protocol. ACAM2000 has more adverse effects than Jynneos and many contraindications.
Preexposure prophylaxis can be offered to people at high risk of mpox, with early data demonstrating that Jynneos vaccination reduces mpox incidence by a factor of 14. Postexposure prophylaxis with Jynneos can prevent mpox symptoms.
| • The COVID-19 primary vaccination series is recommended for everyone six months and older. |
| • Bivalent COVID-19 vaccine boosters are recommended for everyone six months to four years of age who completed the Moderna primary series and everyone five years and older to improve protection from the Omicron variant. |
| • The pneumococcal vaccines PCV15 and PCV20 are recommended for adults 65 years and older; those who received older vaccines should be given an updated version. |
| • For pre- and postexposure prophylaxis against mpox, Jynneos is recommended as a standard 0.5-mL subcutaneous injection or a 0.1-mL intradermal injection. |
| From the AFP Editors |
Editor's Note: Dr. Rockwell serves as liaison to ACIP for the AAFP.
