
Am Fam Physician. 2023;108(5):501-505
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Animal bites are a significant burden to health care systems worldwide. In the United States, dog bites account for an average of 337,000 emergency visits and generate medical costs of up to $2 billion per year. Most animal bites in adults and children are from a dog, and most bite patients are children who have been bitten by animals known to them. Dog bites may cause crush and soft-tissue avulsion, whereas cat bites usually cause deeper puncture-type wounds. Children most often present with dog bites on the head and neck, and adolescents and adults usually present with dog bites on the extremities and hands. Bite wounds should be examined, cleaned, and irrigated with warm water or normal saline solution, and any foreign bodies and devitalized tissue should be removed. Neurovascular function (e.g., pulses, sensation) and range and movement of adjacent joints should be examined and documented. Antibiotic prophylaxis, with amoxicillin/clavulanate as the first-line choice, should be considered for all bites, particularly for those at increased risk of infection. Imaging and laboratory studies are usually not required unless there is suspicion of a retained foreign body, damage to underlying structures, infection, or extensive injury. Primary closure of bite wounds may be performed if there is low risk of infection. The need for tetanus vaccination and rabies postexposure prophylaxis should be evaluated for each patient; bites that do not break the skin generally do not require rabies postexposure prophylaxis.
Dog and cat bites are a common presentation in primary care clinics and emergency departments worldwide. This article summarizes the best available evidence for the evaluation and management of dog and cat bites.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Patients at increased risk of infection from dog and cat bites should receive antibiotic prophylaxis.10,17–19 | C | Expert opinion and consensus guidelines |
| The need for tetanus vaccination and rabies postexposure prophylaxis should be assessed in each patient presenting with a dog or cat bite.10–12 | C | Risk of rabies exposure varies worldwide and by region; clinicians should consult local guidelines |
| Primary closure may be performed at the time of injury for dog bite wounds at low risk of infection; wounds that are at risk of infection should be allowed to heal by secondary intention.10,21 | B | Meta-analysis and a Cochrane review with inconsistent conclusions |
| Injuries to underlying structures (e.g., tendons, joints, bone) and those that could lead to scarring warrant referral for possible surgical exploration and repair.11,12,15,27 | C | Expert opinion |
Epidemiology
In the United States, dog bites account for an average of 337,000 emergency visits per year.1 The burden on the health care system is higher in developing regions. For example, in Latin America, approximately 1 million people seek care annually for possible exposure to rabies from dog bites. This means that with a population of about 540 million people, 1 in 500 of the region's inhabitants were bitten by a dog and sought care to prevent rabies in one year.2 Most animal bites in adults and children are from a dog.1
Estimates suggest that 20% of patients with an animal bite in the United States seek care in health units.3 Approximately 800,000 cases of dog bites require some type of medical attention and generate $2 billion in medical costs per year.4–6
Dog and cat bites are most common in male, school-aged children. Most bites involving infants and preschoolers occur in their homes with a dog the child is familiar with, whereas adolescents are more often bitten by unfamiliar dogs.4,5,7
There is significant regional variation in hospitalization rates for dog bites. In England, the highest hospitalization rates occur in underprivileged areas (27 per 100,000 people).8 Children are more likely than adults to receive medical care for these injuries.9 Children younger than nine years are disproportionately affected by dog bites (17.6 per 100,000 children) and account for two-thirds of hospital admissions among those younger than 18 years.8
Diagnosis
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Dog and cat bites may present in different patterns.10 Children most often present with dog bites on the head and neck, and adolescents and adults usually present with dog bites on the extremities and hands.11
Cat bites usually cause puncture-type wounds that can penetrate deeply and conta minate joint capsules or periosteum with oral flora.
Dog bites may cause crush wounds, extensive lacerations, and soft-tissue avulsion that can result in tissue devitalization.10,12
Neurovascular function (e.g., pulses, sensation) and range and movement of adjacent joints should be examined and documented because bites can cause tendon tears or disruption, particularly in the hands.12
Dog and cat bites may leave teeth fragments in the wound; therefore, careful examination of the area for foreign objects should be performed.13
DIAGNOSTIC TESTING
Ancillary studies are not routinely necessary. In cases of delayed presentation (more than eight to 12 hours since the bite occurred) or if there is suspicion of a wound infection, cellulitis, abscess, or sepsis, a wound culture and blood cultures should be obtained. The wound culture sample should be collected before irrigating the wound, and samples should be studied for aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms.14
In deep wounds or extensive wounds to the limbs caused by medium- or large-breed dogs, plain radiography should be performed to rule out fractures or foreign bodies that may have gone unnoticed during the wound exploration.14
Plain radiography and computed tomography of the skull and facial bones should be performed for injuries located on the face if the physical examination shows a deformity. It is not uncommon to find associated fractures in these types of injuries.15
Treatment
MEDICAL
Bite wounds should be examined, cleaned, and irrigated with warm water or normal saline solution.10–12
Any foreign body (e.g., teeth fragments) and devitalized tissue should be removed.1,13
Routine antibiotic prophylaxis for dog and cat bites is controversial.12,16 For bites that have not broken the skin or drawn blood, antibiotic prophylaxis is not warranted.10
Dog and cat bites at risk of infection (Table 11,10–12,16,17) should receive antibiotic prophylaxis.10,17–19
When treatment with antibiotic prophylaxis is indicated, it should cover the most common pathogens found in animal bites, including Staphylococcus, Pasteurella, Streptococcus, Capnocytophaga, Moraxella, Corynebacterium, Neisseria, and anaerobic bacteria.11,20 Table 2 outlines antibiotic prophylaxis dosing regimens and alternatives for dog and cat bites.11,12,17,21
The need for tetanus vaccination and rabies postexposure prophylaxis should be assessed in each patient presenting with a dog or cat bite. Bites that do not break the skin generally do not require rabies postexposure prophylaxis.10–12 Table 3 shows specific guidelines on rabies postexposure prophylaxis for bites that break the skin or expose mucous membranes to the animal's saliva.11,22–24 Table 4 lists guidelines for tetanus prophylaxis.10,11,13,25

| Bite location |
| Face |
| Feet |
| Genitalia |
| Hand |
| Near a prosthetic joint |
| Underlying structures (e.g., joints, bone, vascular, tendons) penetrated |
Other factors |
| Cat bites that penetrate the skin |
| Crush injuries |
| Delayed presentation (8 to 12 hours or more after bite) |
| Heavy contamination or foreign body (e.g., dirt, teeth) in wound |
| Immunosuppression |
| Preexisting or resulting edema of the affected area |
| Puncture wounds |
| Vascular or lymphatic compromise possible |

| Adults |
| First line: amoxicillin/clavulanate, 875 mg/125 mg every 12 hours |
| Alternative: clindamycin, 300 mg three times per day plus ciprofloxacin, 500 mg twice per day |
Children |
| First line: amoxicillin/clavulanate, 45 mg per kg per day divided every 12 hours |
| Alternative: clindamycin, 10 to 25 mg per kg per day divided every six to eight hours, plus trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, 8 to 10 mg per kg per day of the trimethoprim component divided every 12 hours |
Pregnant patients who are allergic to penicillin |
| First line: clindamycin, 300 mg three times per day, plus trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole,* 160 mg of the trimethoprim component every 12 hours |
| Alternative: azithromycin, 250 to 500 mg per day† |
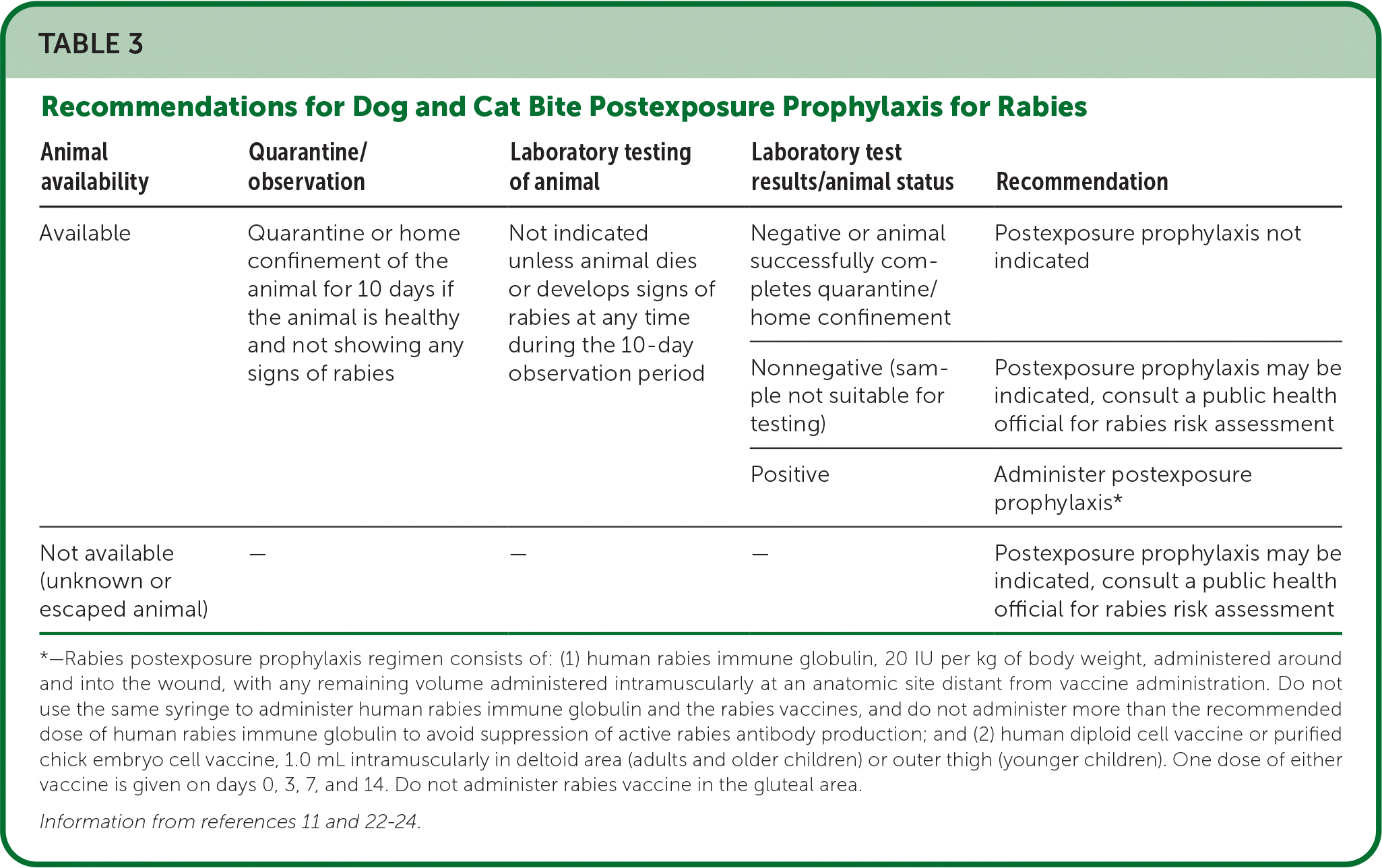
| Animal availability | Quarantine/observation | Laboratory testing of animal | Laboratory test results/animal status | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available | Quarantine or home confinement of the animal for 10 days if the animal is healthy and not showing any signs of rabies | Not indicated unless animal dies or develops signs of rabies at any time during the 10-day observation period | Negative or animal successfully completes quarantine/home confinement | Postexposure prophylaxis not indicated |
| Nonnegative (sample not suitable for testing) | Postexposure prophylaxis may be indicated, consult a public health official for rabies risk assessment | |||
| Positive | Administer postexposure prophylaxis* | |||
| Not available (unknown or escaped animal) | — | — | — | Postexposure prophylaxis may be indicated, consult a public health official for rabies risk assessment |

| History of tetanus immunization | Clean, minor wounds | All other wounds (e.g., contaminated with dirt, foreign bodies, or saliva; crush injuries; puncture wounds; tearing; avulsions) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaccine | Immune globulin | Vaccine | Immune globulin | |
| Unknown or less than three doses | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Three or more doses | No, unless it has been more than 10 years since last dose | No | No, unless is has been five years or longer since last dose | No |
SURGICAL
For dog bites at low risk of infection and in areas of cosmetic concern, primary closure is an acceptable option.21,26 Bites at increased risk of infection, including any cat bite that penetrates the skin, should be allowed to heal by secondary intention.10,21,26
A Cochrane review identified two trials that compared primary closure with healing by secondary intention, and one that compared primary closure with closure delayed by 48 hours. The small size and limited quality of the studies precluded any conclusions regarding the optimal strategy.21
Suspicion of injuries to underlying structures (e.g., tendons, joints, bone) and injuries that are extensive or in cosmetically or functionally important areas (e.g., face, scalp, neck, hands) and could lead to scarring warrant referral for possible surgical exploration and repair.11,12,15,27
Prognosis
In most cases, dog bite injuries are not serious. However, worldwide, approximately 50% of bites leave permanent scars, 10% require sutures, 5% to 21% require attention by a specialist,4 and 1% to 5% require hospitalization.28
Psychological sequelae of dog bite attacks have been described in children and adults (ranging from fear and avoidance of dogs to posttraumatic stress disorder). Therefore, patients and their caregivers should be counseled about normal reactions to trauma (e.g., nightmares, avoidance) and encouraged to seek care if these symptoms persist.1
Prevention
Dog-control, not just breed-specific, legislation for all dogs, including leash laws, stray dog control, and infringements can reduce dog bite rates.29
Adult-directed, but not child-directed, educational strategies may be effective in reducing dog bite rates.29,30 Table 5 lists tips to prevent dog and cat bites.1,11,30 The American Veterinary Medical Association also provides dog bite prevention information at https://www.avma.org/resources-tools/pet-owners/dog-bite-prevention.

| Do not leave children alone or unsupervised with pets. |
| Socialize dogs with children and other people as puppies. |
| Ensure pets get regular veterinary care and are up to date on vaccinations. |
| Train dogs to help reduce the likelihood that they will bite out of fear. |
| Do not approach a strange or unknown dog without the dog owner's permission. |
| Use environmental barriers in and around the home (e.g., baby gates, property fences to prevent dogs from escaping or wandering unsupervised, keeping the dog in a separate room if it is hurt or anxious) to help reduce the likelihood of a dog attack. |
This article updates previous articles on this topic by Ellis and Ellis11 and Presutti.31
Data Sources: Searches were performed in Essential Evidence Plus, the Cochrane database, Google Scholar, and PubMed using the Clinical Queries function for the term dog and cat bites. Search dates: December 2022, and January and July 2023.
