
Am Fam Physician. 2023;108(5):527-529
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Key Points for Practice
• Limited evidence suggests that tricyclic antidepressants and antispasmodic medications improve IBS symptoms, including pain.
• For IBS-C, linaclotide appears to be the most effective medication, with a common adverse effect of diarrhea.
• For IBS-D, rifaximin improves discomfort and bloating and has some benefit with repeat administration for recurrent symptoms.
From the AFP Editors
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) affects at least one in every 25 adults worldwide and is more common in women and younger adults. IBS is associated with a decreased quality of life, increased psychological comorbidity, high economic costs, and more than double the rate of work absenteeism. The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) performed systematic reviews to create guidelines on how to manage IBS with pharmacotherapy.
Global Symptoms
People with IBS are more likely to have difficulty concentrating, feel self-conscious, avoid sex, and not feel able to reach their potential. Several medications have been proposed to treat the global symptoms and abdominal pain of IBS overall. These medications should be considered when alarm symptoms are not present.
ANTIDEPRESSANT MEDICATIONS
Tricyclic antidepressants have been used to treat IBS because of the effects on the peripheral and central nervous system that can affect motility, secretion, and sensation. Studies of tricyclic antidepressants demonstrate reduction of global symptoms and pain, although the evidence is low quality. Broad study shows more than twice the withdrawal for adverse effects with tricyclic antidepressants as with placebo.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors do not improve global symptoms or abdominal pain. Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors have not been studied in IBS.
ANTISPASMODIC MEDICATIONS
The AGA suggests that antispasmodics be considered for patients who have IBS accompanied by constipation or diarrhea. A Cochrane review found low-quality evidence that antispasmodics improve global symptom relief and very low-quality evidence that they reduce abdominal pain.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Constipation
In more than one-third of cases, IBS presents with constipation (IBS-C). Rome IV criteria are used to diagnose IBS-C after verifying the absence of alarm symptoms (Table 1). For IBS-C, the AGA defined successful treatment using the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) definition, which is at least a 30% reduction in average daily worst abdominal pain and an increase of at least one complete spontaneous bowel movement per week over baseline for at least six of 12 weeks. The effective treatments produce this level of response in about 33% of patients, in contrast with a 24% average response to placebo.

| Family history of inflammatory bowel disease, colon cancer, or celiac disease |
| Iron deficiency anemia |
| New symptom onset after 50 years of age |
| Nocturnal diarrhea |
| Rectal bleeding not attributable to hemorrhoids or anal fissures |
| Unintentional weight loss |
LINACLOTIDE
Linaclotide (Linzess), a guanylate cyclase C receptor agonist, causes fluid and electrolyte secretion into the intestinal lumen and reduces visceral hypersensitivity. It has the strongest evidence of benefit in patients with IBS-C. Linaclotide reduces abdominal pain and increases bowel movements, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of 7 (95% CI, 6 to 9). Diarrhea is the most common adverse effect, occurring in 16% of patients treated with linaclotide compared with 2% treated with placebo and leading to discontinuation in 3% of patients. Although head-to-head evidence is lacking, linaclotide was the most effective option in a recent network meta-analysis.
OTHER EFFECTIVE MEDICATIONS
Plecanatide (Trulance), another guanylate cyclase C receptor agonist, works similarly to linaclotide but seems to be slightly less effective, with an NNT of 10 (95% CI, 8 to 15). Diarrhea is the most common adverse effect, involving 4% of patients and leading to discontinuation in 1% of patients.
Tenapanor (Ibsrela), a small-molecule inhibitor of the gastrointestinal sodium/hydrogen exchanger expressed in the small intestine and colon, has a different mechanism of action than linaclotide and plecanatide. Based on lower-certainty evidence, the guidelines suggest considering tenapanor based on an NNT of 8 (95% CI, 7 to 15). Diarrhea is the most common adverse effect, occurring in 15% of patients and leading to discontinuation in 7% of patients. Studies have shown benefit from tenapanor for up to 26 weeks.
Tegaserod is a partial 5-HT4 receptor agonist that acts as a prokinetic medication that increases motility and fluid within the gastrointestinal tract. Initially introduced in 2002, tegaserod was withdrawn because of an increased risk of cardiovascular events with a number needed to harm of 1,000. After observational studies showed no association, tegaserod was remarketed for women younger than 65 years with no history of myocardial infarction, stroke, transient ischemic attack, or angina. It produces a response in about one-third of patients with an NNT of 10 (95% CI, 7 to 19) compared with placebo. Diarrhea is the most common adverse effect and leads to discontinuation in 2% of patients.
QUESTIONABLY EFFECTIVE MEDICATIONS
Lubiprostone (Amitiza), a type 2 chloride channel activator, mildly improves global symptoms and abdominal pain in a way that may not be clinically relevant. Adverse effects are similar to placebo.
Polyethylene glycol is an osmotic laxative that increases the number of spontaneous bowel movements but may not affect abdominal pain or other symptoms, based on a single lower-quality trial.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome With Diarrhea
Up to 40% of cases of IBS present with diarrhea (IBS-D). After the absence of alarm symptoms has been confirmed (Table 1), the Rome IV criteria are used to diagnose IBS-D. The AGA focused on the responder end points defined by the FDA as at least a 30% reduction in average daily worst abdominal pain and at least a 50% reduction in the number of days per week with the loosest stool (type 6 or 7 on the Bristol Stool Form Scale).
RIFAXIMIN
Rifaximin (Xifaxan) is a nonabsorbable antibiotic that reduces global discomfort, bloating, and abdominal pain. The same three times daily dosing for 14 days is for acute and recurrent symptoms. Adverse effects are not significantly different than with placebo.
OTHER EFFECTIVE MEDICATIONS
Eluxadoline (Viberzi), a minimally absorbed mixed opioid receptor agonist and antagonist, will decrease symptoms to a greater extent than placebo in some patients (NNT = 10; 95% CI, 8 to 15). However, it causes constipation, nausea, and abdominal pain in up to 8% of patients, and 8% of patients will discontinue eluxadoline because of adverse effects. It should not be used in patients without a gallbladder or those who drink more than three alcoholic beverages per day because of the rare possibility of pancreatitis and sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.
Alosetron is a selective 5-HT3 receptor agonist that affects the enteric nervous system centrally and peripherally. It improves global symptoms, pain, urgency, and quality of life. Due to the risk of ischemic colitis, use is limited to women with severe IBS-D, and it is prescribed as part of a risk management program.
Loperamide, a synthetic peripheral opioid receptor agonist, inhibits peristalsis and secretions while prolonging intestinal transit time. Very low-quality evidence suggests that loperamide improves global symptoms, reduces abdominal pain, and improves stool consistency in IBS-D.
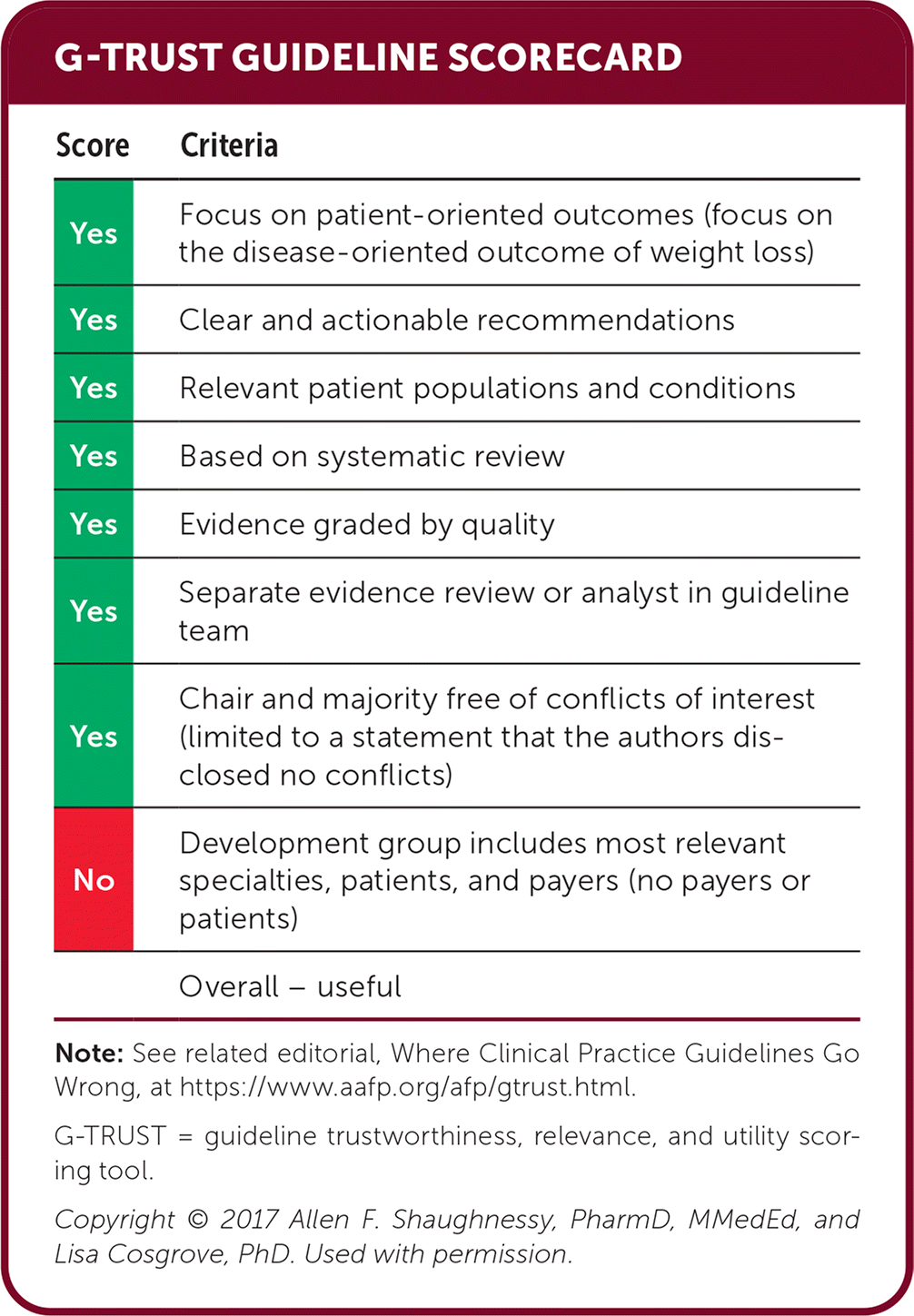
| Score | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Yes | Focus on patient-oriented outcomes (focus on the disease-oriented outcome of weight loss) |
| Yes | Clear and actionable recommendations |
| Yes | Relevant patient populations and conditions |
| Yes | Based on systematic review |
| Yes | Evidence graded by quality |
| Yes | Separate evidence review or analyst in guideline team |
| Yes | Chair and majority free of conflicts of interest (limited to a statement that the authors disclosed no conflicts) |
| No | Development group includes most relevant specialties, patients, and payers (no payers or patients) |
| Overall – useful |
The views expressed are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, U.S. Navy, U.S. Department of Defense, or U.S. government.
Editor's Note: This guideline reviews patient-oriented evidence for IBS medications. Some, such as tegaserod and alosetron, were removed and reintroduced with caveats, and others, such as eluxadoline, have severe risks for patients with alcohol use or a history of cholecystectomy that may limit use. For medications more familiar in primary care, limited evidence supports use of tricyclic antidepressants and loperamide, yet polyethylene glycol is not effective for pain associated with IBS-C. The effectiveness end point chosen for this guideline includes only a 30% improvement in pain, demonstrating the significant limitations of all these medications. The guideline is further limited in that it does not review behavioral treatments or dietary recommendations, nor does it compare them to medications.—Michael J. Arnold, MD, Assistant Medical Editor
The numbers needed to treat and related CIs reported in this Practice Guideline were calculated by the author based on raw data provided in the original guideline.
Guideline source: American Gastroenterological Association
Published sources: Chang L, Sultan S, Lembo A, et al. AGA clinical practice guideline on the pharmacological management of irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(1):118–136, and Lembo A, Sultan S, Chang L, et al. AGA clinical practice guideline on the pharmacological management of irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(1):137–151.
