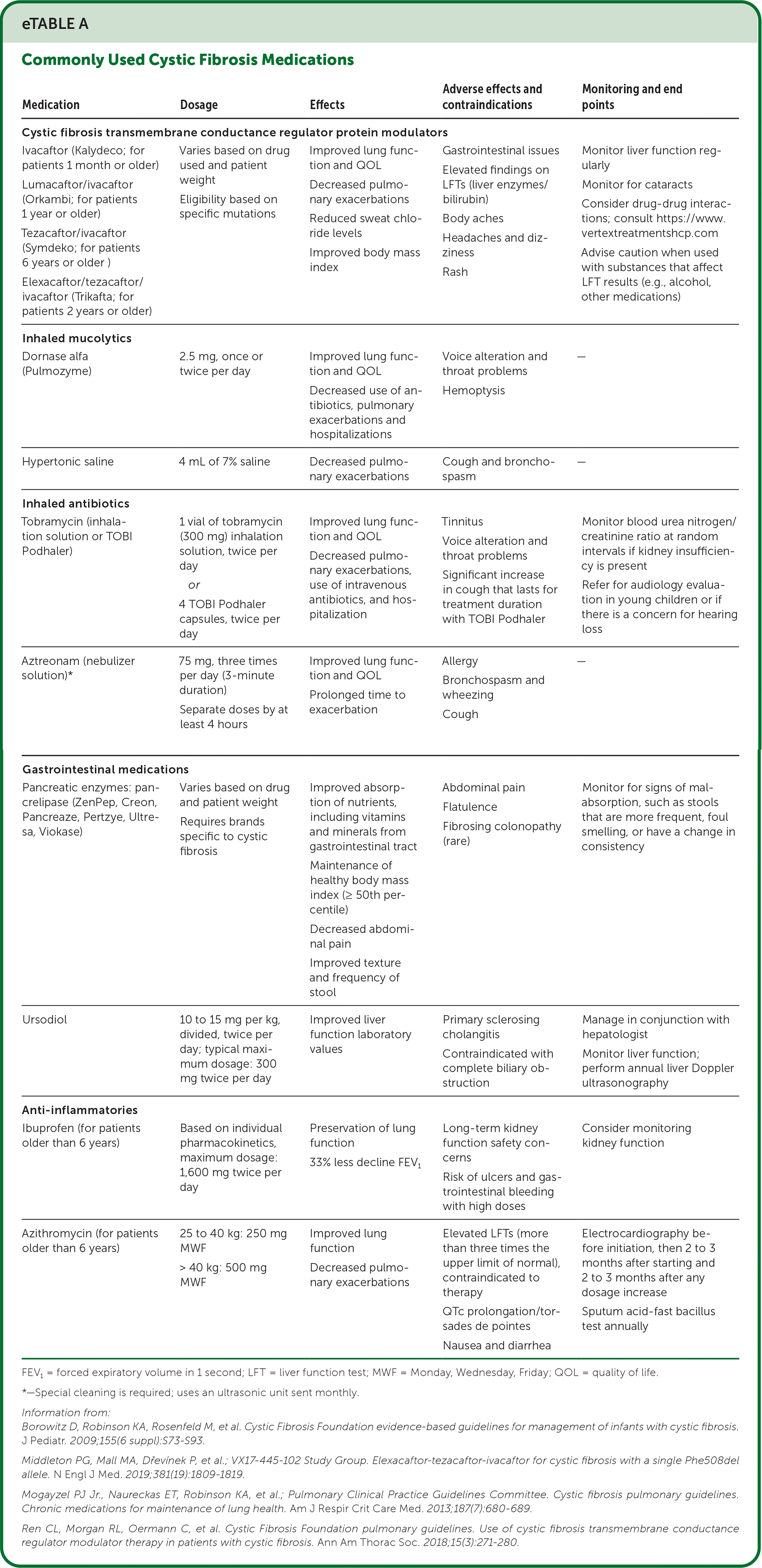
| Medication | Dosage | Effects | Adverse effects and contraindications | Monitoring and end points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein modulators | ||||
| Ivacaftor (Kalydeco; for patients 1 month or older) Lumacaftor/ivacaftor (Orkambi; for patients 1 year or older) Tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Symdeko; for patients 6 years or older) Elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trikafta; for patients 2 years or older) | Varies based on drug used and patient weight Eligibility based on specific mutations | Improved lung function and QOL Decreased pulmonary exacerbations Reduced sweat chloride levels Improved body mass index | Gastrointestinal issues Elevated findings on LFTs (liver enzymes/bilirubin) Body aches Headaches and dizziness Rash | Monitor liver function regularly Monitor for cataracts Consider drug-drug interactions; consult https://www.vertextreatmentshcp.com Advise caution when used with substances that affect LFT results (e.g., alcohol, other medications) |
| Inhaled mucolytics | ||||
| Dornase alfa (Pulmozyme) | 2.5 mg, once or twice per day | Improved lung function and QOL Decreased use of antibiotics, pulmonary exacerbations and hospitalizations | Voice alteration and throat problems Hemoptysis | — |
| Hypertonic saline | 4 mL of 7% saline | Decreased pulmonary exacerbations | Cough and bronchospasm | — |
| Inhaled antibiotics | ||||
| Tobramycin (inhalation solution or TOBI Podhaler) | 1 vial of tobramycin (300 mg) inhalation solution, twice per day or 4 TOBI Podhaler capsules, twice per day | Improved lung function and QOL Decreased pulmonary exacerbations, use of intravenous antibiotics, and hospitalization | Tinnitus Voice alteration and throat problems Significant increase in cough that lasts for treatment duration with TOBI Podhaler | Monitor blood urea nitrogen/creatinine ratio at random intervals if kidney insufficiency is present Refer for audiology evaluation in young children or if there is a concern for hearing loss |
| Aztreonam (nebulizer solution)* | 75 mg, three times per day (3-minute duration) Separate doses by at least 4 hours | Improved lung function and QOL Prolonged time to exacerbation | Allergy Bronchospasm and wheezing Cough | — |
| Gastrointestinal medications | ||||
| Pancreatic enzymes: pancrelipase (ZenPep, Creon, Pancreaze, Pertzye, Ultresa, Viokase) | Varies based on drug and patient weight Requires brands specific to cystic fibrosis | Improved absorption of nutrients, including vitamins and minerals from gastrointestinal tract Maintenance of healthy body mass index (≥ 50th percentile) Decreased abdominal pain Improved texture and frequency of stool | Abdominal pain Flatulence Fibrosing colonopathy (rare) | Monitor for signs of malabsorption, such as stools that are more frequent, foul smelling, or have a change in consistency |
| Ursodiol | 10 to 15 mg per kg, divided, twice per day; typical maximum dosage: 300 mg twice per day | Improved liver function laboratory values | Primary sclerosing cholangitis Contraindicated with complete biliary obstruction | Manage in conjunction with hepatologist Monitor liver function; perform annual liver Doppler ultrasonography |
| Anti-inflammatories | ||||
| Ibuprofen (for patients older than 6 years) | Based on individual pharmacokinetics, maximum dosage: 1,600 mg twice per day | Preservation of lung function 33% less decline FEV1 | Long-term kidney function safety concerns Risk of ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding with high doses | Consider monitoring kidney function |
| Azithromycin (for patients older than 6 years) | 25 to 40 kg: 250 mg MWF > 40 kg: 500 mg MWF | Improved lung function Decreased pulmonary exacerbations | Elevated LFTs (more than three times the upper limit of normal), contraindicated to therapy QTc prolongation/torsades de pointes Nausea and diarrhea | Electrocardiography before initiation, then 2 to 3 months after starting and 2 to 3 months after any dosage increase Sputum acid-fast bacillus test annually |