
Am Fam Physician. 2025;111(1):77-78
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
A 71-year-old woman presented for routine follow-up after a skin lesion was noted on her right cheek; it had appeared 6 months prior. The patient said it began as acne, bled when scratched, and then crusted. After healing, the lesion persisted and was nonpruritic. The patient had no personal or family history of skin cancer. She had a history of colon cancer in her late 30s that was treated with chemotherapy and radiation.
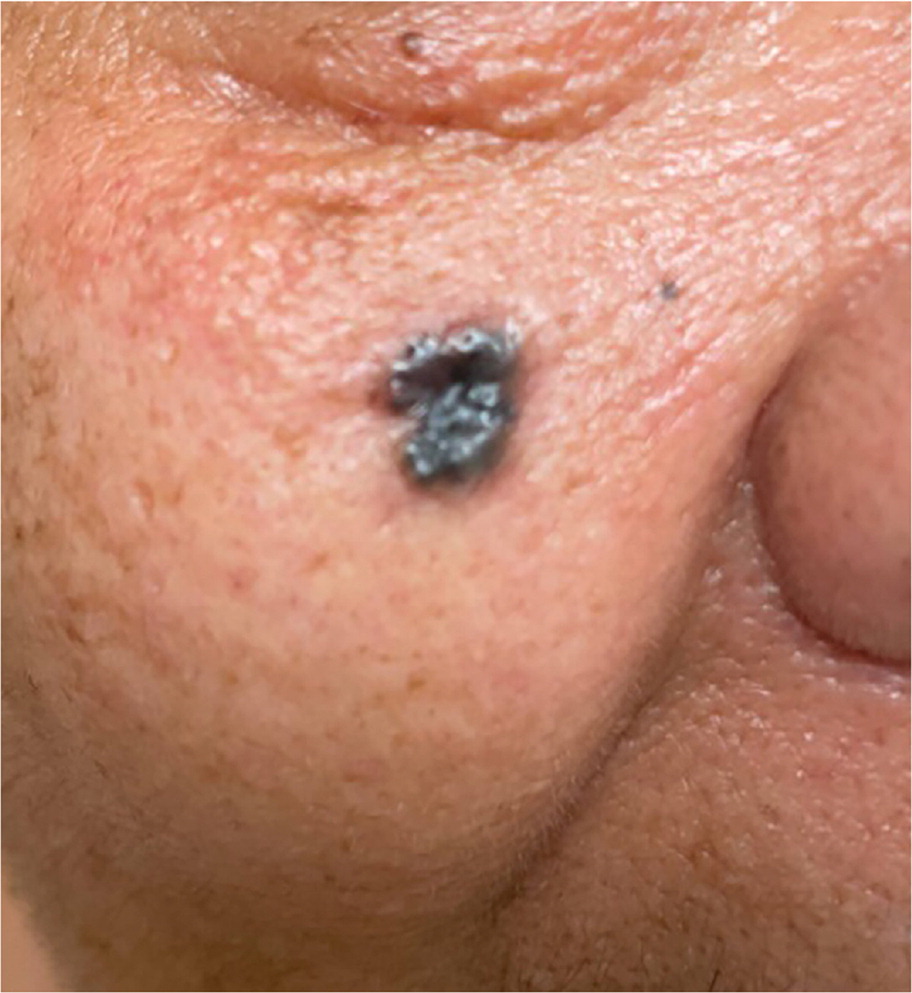
Physical examination revealed a uniformly brown papule with rolled borders on her right cheek measuring 7 × 6 mm (Figure 1). A biopsy was performed.
QUESTION
Based on the patient's history and physical examination, which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Basal cell carcinoma.
B. Lentigo.
C. Melanoma.
D. Nevus.
E. Squamous cell carcinoma.
DISCUSSION
The answer is A: basal cell carcinoma, which is the most common type of skin cancer and originates in the basal cell layer of the skin.1 It is more common in patients with lighter skin tones and is usually found on sun-exposed areas such as the face and neck. In patients with darker skin tones, basal cell carcinoma often presents as pearly black lesions. In patients with lighter skin tones, it typically presents as pearly papules with central ulceration and telangiectasias.2
Subscribe
From $180- Immediate, unlimited access to all AFP content
- More than 125 CME credits/year
- AAFP app access
- Print delivery available
Issue Access
$59.95- Immediate, unlimited access to this issue's content
- CME credits
- AAFP app access
- Print delivery available
