Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(1):34-41
Related editorial: Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma.
Patient information: See related handout on lymphoma, written by the authors of this article.
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Lymphoma is a group of malignant neoplasms of lymphocytes with more than 90 subtypes. It is traditionally classified broadly as non-Hodgkin or Hodgkin lymphoma. Approximately 82,000 new U.S. patients are diagnosed with lymphoma annually. Any tobacco use and obesity are major modifiable risk factors, with genetic, infectious, and inflammatory etiologies also contributing. Lymphoma typically presents as painless adenopathy, with systemic symptoms of fever, unexplained weight loss, and night sweats occurring in more advanced stages of the disease. An open lymph node biopsy is preferred for diagnosis. The Lugano classification system incorporates symptoms and the extent of the disease as shown on positron emission tomography/computed tomography to stage lymphoma, which is then used to determine treatment. Chemotherapy treatment plans differ between the main subtypes of lymphoma. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is treated with CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) with or without rituximab (R-CHOP), bendamustine, and lenalidomide. Hodgkin lymphoma is treated with combined chemotherapy with ABVD (doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine), Stanford V (a chemotherapy regimen consisting of mechlorethamine, doxorubicin, vinblastine, vincristine, bleomycin, etoposide, and prednisone), or BEACOPP (bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone) with radiotherapy. Subsequent chemotherapy toxicities include neuropathy, cardiotoxicity, and secondary cancers such as lung and breast, and should be considered in the shared decision-making process to select a treatment regimen. Once remission is achieved, patients need routine surveillance to monitor for complications and relapse, in addition to age-appropriate screenings recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Patients should receive a 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine followed by a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine at least eight weeks later with additional age-appropriate vaccinations because lymphoma is an immunosuppressive condition. Household contacts should also be current with their immunizations.
Lymphoma represents a heterogeneous group of malignant neoplasms of lymphocytes, which can involve lymphatic tissue, bone marrow, or extranodal sites. The World Health Organization’s classification system identifies more than 90 different subtypes (Table 1).1,2 The initial stratification is derived from B-cell, T-cell, or natural killer cell origin. Further classification of distinct lymphoma subtypes is beyond the scope of this article; however, they are ultimately each defined by morphology, immunopheno-type, genetic, molecular, and clinical features.1,3 This article will focus on the types of lymphoma traditionally classified as non-Hodgkin or Hodgkin.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Open lymph node biopsy should be used to definitively diagnose lymphoma.14,15 | C | Expert opinion and clinical review articles |
| Positron emission tomography/computed tomography should be used to determine the staging of the lymphoma.19 | C | Expert opinion and clinical review article |
| Patients with lymphoma should have intensive follow-up surveillance for the first two years following remission.40 | C | Expert opinion and clinical review article |
| A 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (Prevnar 13), followed by a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (Pneumovax 23) at least eight weeks later and then again at least five years later, should be administered following lymphoma treatment.44,45 | C | Expert opinion and guidelines |
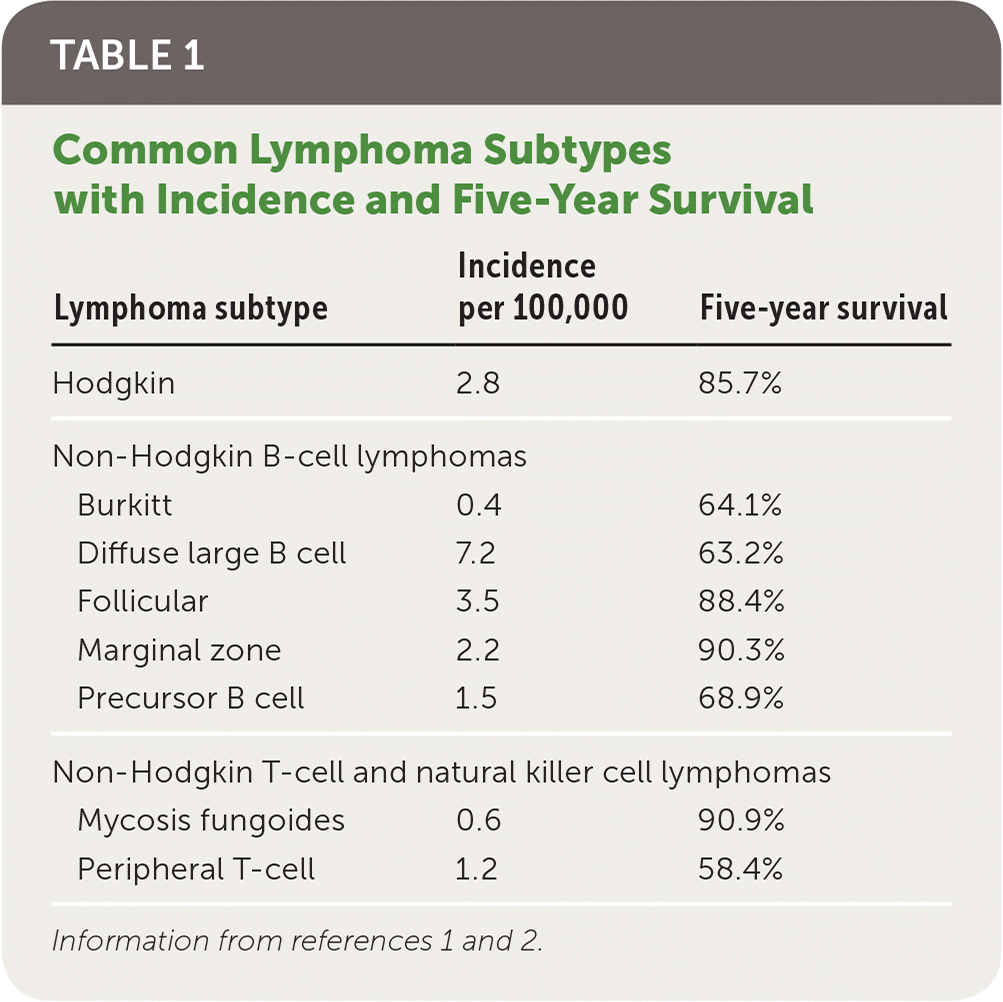
| Lymphoma subtype | Incidence per 100,000 | Five-year survival |
|---|---|---|
| Hodgkin | 2.8 | 85.7% |
| Non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas | ||
| Burkitt | 0.4 | 64.1% |
| Diffuse large B cell | 7.2 | 63.2% |
| Follicular | 3.5 | 88.4% |
| Marginal zone | 2.2 | 90.3% |
| Precursor B cell | 1.5 | 68.9% |
| Non-Hodgkin T-cell and natural killer cell lymphomas | ||
| Mycosis fungoides | 0.6 | 90.9% |
| Peripheral T-cell | 1.2 | 58.4% |
Epidemiology
More than 82,000 new patients are projected to be diagnosed with lymphoma in 2019, representing 4.7% of all new cancer cases in the United States. The current five-year survival rate for non-Hodgkin lymphoma is 72.0%, and for Hodgkin lymphoma it is 86.6%. Almost 21,000 people are projected to die from lymphoma in 2019, representing 3.5% of all cancer deaths. Incidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma is higher in men and whites, and it increases with age. The median age of patients at diagnosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma is 67 years, and the median age at death is 76. Hodgkin lymphoma is most commonly diagnosed at 20 to 34 years of age; however, the median age at death is 68 because of the higher survival rate among younger patients.2,4
Risk Factors
Genetic, infectious, and inflammatory etiologies increase the risk of lymphoma. First-degree relatives of patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma have a respective 1.7-fold and 3.1-fold increased risk of developing lymphoma. A family history of a specific subtype of lymphoma is associated with developing that same subtype.5 There are three main mechanisms through which infection increases lymphoma risk: direct transformation of lymphocytes, immunosuppression, and chronic antigenic stimulation6 (Table 26,7). Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, dermatomyositis, and celiac disease are inflammatory conditions that increase the risk of lymphoma through disease-specific causes and the chronic use of immunosuppressive medications.8

| Mechanism | Infection | Lymphoma type |
|---|---|---|
| Direct lymphocyte transformation | Epstein-Barr virus | Burkitt, non-Hodgkin, Hodgkin |
| Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 | T-cell leukemia | |
| Immunosuppression | HIV | Hodgkin, non-Hodgkin |
| Chronic antigenic stimulation | Helicobacter pylori Chlamydia psittaci Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter coli Borrelia burgdorferi | Non-Hodgkin (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) |
| Hepatitis C | Splenic marginal zone |
Clinical Presentation
Lymphoma commonly presents as painless adenopathy. Adenopathy can wax and wane over years in indolent presentations or involve rapidly progressive adenopathy in more aggressive subtypes. Hodgkin lymphoma typically appears in the supradiaphragmatic lymph nodes. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can originate anywhere in the body, with specific subtypes originating in the gastrointestinal tract, skin, or central nervous system. Systemic symptoms of fever, unexplained weight loss, and night sweats occur in a subset of patients with more advanced disease. Lymphoma spreads to extranodal sites by direct invasion or by hematogenous spread to the spleen, liver, lungs, or bone marrow.14,15 High-grade lymphomas can present as oncologic emergencies because of the structural compression from the enlarging tumor, including superior vena cava syndrome, malignant epidural spinal cord compression, or malignant pericardial effusion.16 Paraneoplastic syndromes are rare with lymphoma, occurring as paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration in Hodgkin lymphoma and as dermatomyositis and polymyositis in Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas.17
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of lymphoma is made using an open lymph node biopsy, based off morphology, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry.3 Although fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy are often part of the initial evaluation of any adenopathy, neither will provide adequate tissue for the diagnosis of lymphoma because of the need to verify Hodgkin lymphoma via the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells.15,18
Staging
The Ann Arbor staging system was initially developed in 1971 for Hodgkin lymphoma, and was later adapted for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The Lugano classification system further modified staging by incorporating positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET-CT) results to determine the staging of the lymphoma (Table 319). PET-CT is used for fluorodeoxyglucose-avid lymphoma subtypes, with symptoms alone being used for staging the remaining subtypes. The new staging system incorporates two symptom-based classifications: A (absence of symptoms) and B (presence of fever, weight loss, and night sweats) for Hodgkin lymphoma. A bone marrow biopsy is now recommended only for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with a negative PET-CT result.19

| Stage* | Description of disease from positron emission tomography/computed tomography results |
|---|---|
| I | Single nodal group or single extralymphatic lesion |
| II† | Multiple nodal groups on same side of diaphragm or with limited contiguous extralymphatic involvement |
| III | Multiple nodal groups on both sides of the diaphragm; may involve the spleen |
| IV | Noncontiguous extralymphatic involvement |
Prognosis
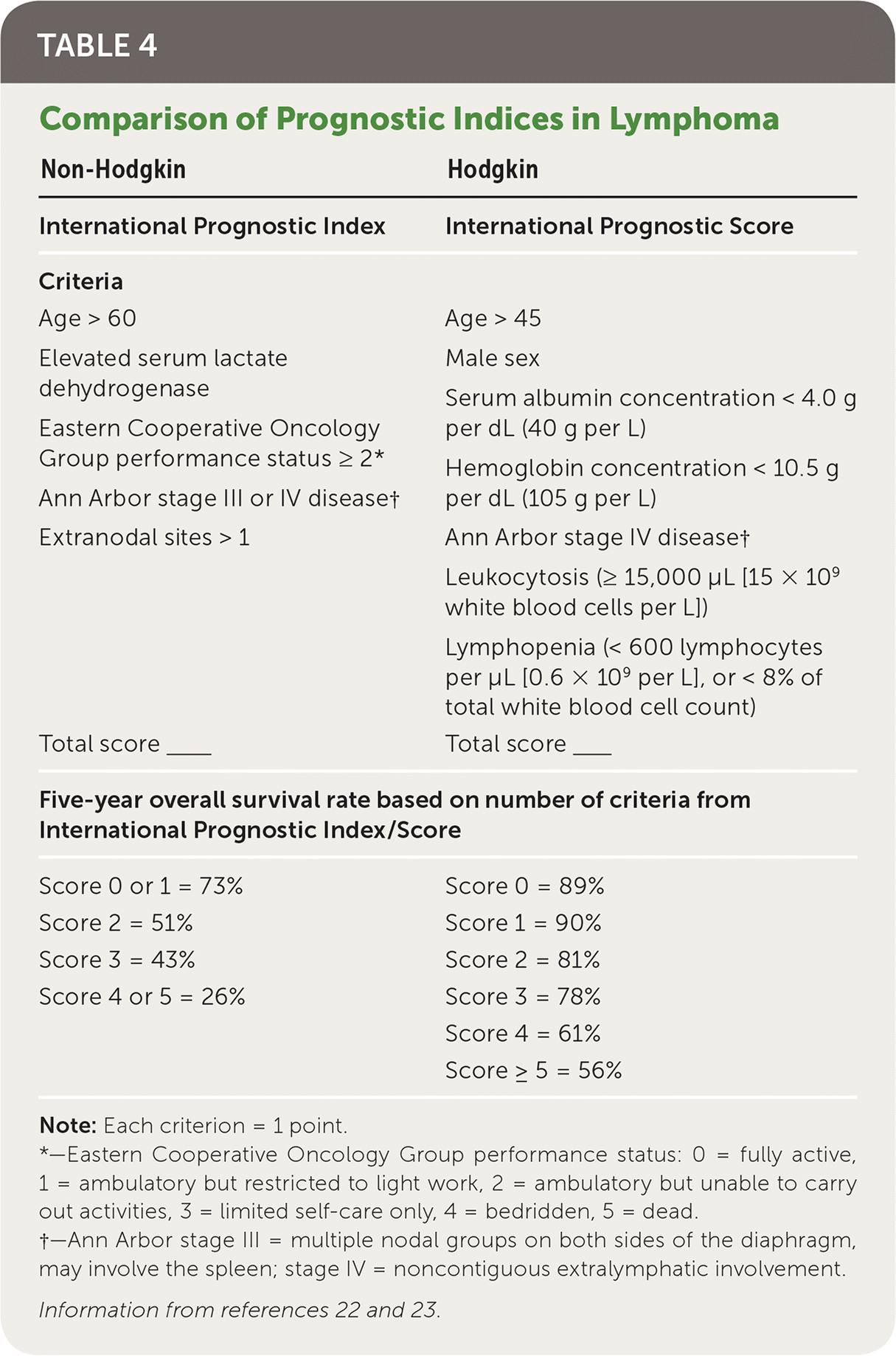
| Non-Hodgkin | Hodgkin |
|---|---|
| International Prognostic Index | International Prognostic Score |
| Criteria | Criteria |
| Age > 60 | Age > 45 |
| Elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase | Male sex |
| Eastern Cooperative Oncology | Serum albumin concentration < 4.0 g per dL (40 g per L) |
| Group performance status ≥ 2* | Hemoglobin concentration < 10.5 g per dL (105 g per L) |
| Ann Arbor stage III or IV disease† | |
| Extranodal sites > 1 | Ann Arbor stage IV disease† Leukocytosis (≥ 15,000 μL [15 × 109 white blood cells per L]) Lymphopenia (< 600 lymphocytes per μL [0.6 × 109 per L], or < 8% of total white blood cell count) |
| Total score____ | Total score____ |
| Five-year overall survival rate based on number of criteria from International Prognostic Index/Score | |
| Score 0 or 1 = 73% | Score 0 = 89% |
| Score 2 = 51% | Score 1 = 90% |
| Score 3 = 43% | Score 2 = 81% |
| Score 4 or 5 = 26% | Score 3 = 78% |
| Score 4 = 61% | |
| Score ≥ 5 = 56% | |
Treatment
Treatment of lymphoma consists of chemotherapy alone or in combination with radiotherapy.24 Radiotherapy alone is not recommended.25 Toxicity from radiotherapy can lead to serious long-term complications such as secondary cancers in the irradiated area, including breast or lung cancers.25 Additionally, patients receiving chemotherapy can subsequently develop breast or lung cancers, melanoma, or acute myeloid leukemia.26,27 Patients who are older than 60 years at diagnosis have worse outcomes, regardless of the staging. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) recommends avoiding certain chemotherapeutic agents in patients older than 60 years. The physician should focus on shared decision-making when discussing treatment options with all patients, but particularly for those older than 60 years, including whether the patient should pursue treatment.25
The standard treatment for Hodgkin lymphoma is ABVD (doxorubicin [Adriamycin], bleomycin, vinblastine [Velban], and dacarbazine), but other regimens such as the Stanford V (doxorubicin, vinblastine, mechlorethamine, etoposide [Toposar], vincristine, bleomycin, and prednisone) and escalated-BEACOPP (bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine [Matulane], and prednisone) can be used.24–28 Treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma varies depending on the histology, but often uses treatments such as CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) with or without rituximab (Rituxan; R-CHOP), a monoclonal antibody specific for CD20-positive B lymphocytes.29 Other medications such as bendamustine (Bendeka), an alkylating agent, and lenalidomide (Revlimid) are also used in many non-Hodgkin lymphoma treatments.30,31 Common complications of these therapies are listed in Table 5.25–27,29–36

| Therapy | Regimen | Short-term complications | Long-term complications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hodgkin lymphoma | |||
| ABVD | Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) | Nausea/vomiting Alopecia Neutropenia Neuropathy Bleomycin-induced pulmonary toxicity | Cardiotoxicity (heart failure) Neuropathy Pulmonary fibrosis Increased risk of myocardial infarction |
| Bleomycin | |||
| Vinblastine (Velban) | |||
| Dacarbazine | |||
| Stanford V | Doxorubicin | Nausea/vomiting Fatigue Pulmonary toxicity Neuropathy | Neuropathy Pulmonary fibrosis Cardiotoxicity Rarely solid secondary malignancies of breast, lung, and skin |
| Vinblastine | |||
| Mechlorethamine | |||
| Etoposide (Toposar) | |||
| Vincristine | |||
| Bleomycin | |||
| Prednisone | |||
| Escalated-BEACOPP | Bleomycin | Anemia Leukopenia Thrombocytopenia Nausea/vomiting Infection Disulfiram reaction between ethanol and procarbazine | Acute myeloid leukemia Sterility/infertility |
| Etoposide | |||
| Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) | |||
| Cyclophosphamide | |||
| Vincristine (Oncovin) | |||
| Procarbazine (Matulane) | |||
| Prednisone | |||
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma | |||
| CHOP | Cyclophosphamide | Heart failure Constipation Hyperglycemia Neuropathy | Cardiomyopathy Myelosuppression Neuropathy |
| Doxorubicin | |||
| (Hydroxydaunorubicin) | |||
| Vincristine (Oncovin) | |||
| Prednisone | |||
| R-CHOP | Rituximab (Rituxan) + CHOP | Reactivate hepatitis B infection | Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy |
A Cochrane review that examined seven trials consisting of more than 2,500 adult patients with early Hodgkin lymphoma concluded that the use of combined therapy could increase progression-free survival with little difference between the overall survival rates.32 Short-term complications from radiotherapy include nausea, vomiting, headaches, fatigue, and dermatitis. Radiotherapy can also lead to long-term complications, including cardiac and pulmonary toxicity, hypothyroidism, or breast or lung cancers.24–32 Radiotherapy can be avoided in patients with stage IA or IIA lymphoma without bulky disease25 (Table 319).
Interim Reassessment
PET-CT scans, and subsequent Deauville scoring (Table 621), should be used to assess the response to chemotherapy in non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma.25,30,31,33 A score of 3 or less is considered complete remission in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and should conclude the current treatment course. A score of 4 or 5 is an indicator to consider escalating therapy.25 Patients with Hodgkin lymphoma with a Deauville score of 1 or 2 have been shown to have similar progression and mortality outcomes between radiotherapy and no further treatment.32 Patients who receive a score of 3 or 4 should receive additional chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy, and a score of 5 indicates the need for a biopsy (excisional or core needle) in addition to chemotherapy and radiotherapy.25 A positive biopsy should be considered refractory disease.25

| PET-CT finding | Score |
|---|---|
| No FDG uptake related to lymphoma | 1 |
| FDG uptake at lymphoma site is ≤ mediastinum FDG uptake | 2 |
| FDG uptake at lymphoma site is > mediastinum FDG uptake but < liver FDG uptake | 3 |
| FDG uptake at lymphoma site is > liver FDG uptake at any site | 4 |
| FDG uptake at lymphoma site is substantially > liver FDG uptake or new FDG uptake sites found | 5 |
Relapse
Relapse rates for non-Hodgkin lymphoma are variable and based on the specific subtype. The most common subtype, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, has a 40% lifetime relapse rate.37 Lifetime relapse in Hodgkin lymphoma occurs in 10% to 15% of patients with early stage disease and 40% of patients with advanced stage disease.38
Surveillance
Patients who have achieved remission need routine surveillance to monitor for complications and relapse, as well as age-appropriate screenings recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force.39 Complications of lymphoma treatment include secondary malignancies (e.g., breast, lung, skin, colon), cardiac disease, infertility, and endocrine, neurologic, and psychiatric dysfunctions. Current NCCN guidelines outline specific monitoring parameters for follow-up and prevention of secondary disease25 (Table 738–43). The extent and frequency of follow-up specifically depend on the histologic subtype of lymphoma. Patients should follow up with an oncologist every three to six months for the first two years, every six to 12 months until year 3, then annually thereafter. After five years of being cancer free, the patient can be transitioned to a primary care physician.40

| Cancer screening | Laboratory screening | Cardiac screening | Counseling | Immunizations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast: annual screening mammography starting at age 40; history of chest or axilla radiation: start eight to 10 years after treatment or at age 40, whichever comes first; consider annual breast magnetic resonance imaging if chest radiation was received between ages 10 and 30; consider referral to breast subspecialist to discuss possible chemoprevention | Complete blood count, fasting blood glucose, and comprehensive metabolic panel annually | Annual blood pressure screening, lifestyle modification, and treatment of obesity, hypertension, and tobacco use | Annual depression screening | Age-appropriate immunizations per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention schedule, including annual influenza vaccine; resume live vaccines at least three months after completion of chemotherapy |
| Routine surveillance tests for cervical, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancers per the USPSTF guidelines | Lipid profile per the USPSTF guidelines | Consider stress test and/or echocardiography at 10-year intervals (frequency of testing based on findings and other associated risk factors) | Neurocognitive impairment screening for any patient who is high risk (e.g., history of brain radiation or intrathecal treatment) | PCV13 (Prevnar 13), followed by PPSV23 (Pneumovax 23) at least eight weeks later and again at least five years later |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone annually if neck irradiation | Carotid ultrasonography every 10 years if neck irradiation | Infertility: consider reproductive endocrinologist referral | Haemophilus influenzae type b: three doses following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
If a patient is asymptomatic, routine surveillance imaging does not improve outcomes or provide a clinical benefit.40,41 Surveillance imaging should be used in patients who have reported symptoms or who are at high risk of relapse in a place that would not be easily examined, and who would be candidates for treatment. However, NCCN imaging guidelines for lymphoma surveillance state that it is acceptable to perform chest radiography or CT of the chest every six to 12 months for the first two years and then yearly for the next three to five years posttreatment.41 Surveillance imaging with PET-CT scans following complete remission is not recommended.40,41 Disease marker research is ongoing, examining minimal residual disease measurements, a polymerase chain reaction–based method that looks at identifying tumor-specific DNA sequences.41
Immunizations
All patients with lymphoma should receive pneumococcal vaccination initially with a 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (Prevnar 13), followed at least eight weeks later by a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23; Pneumovax 23) and then another PPSV23 at least five years later.44 Patients receiving anti–B-cell antibodies should not receive annual influenza vaccination, and administration of live vaccines is contraindicated during chemotherapy. Routine vaccinations recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) should resume, including any recommended inactivated or live vaccines three months after chemotherapy or six months after anti–B-cell antibody therapy.43,45 Patients receiving a hematopoietic stem cell transplant should receive a series of three doses of Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine starting six to 12 months after a successful transplant. Household contacts should receive appropriate CDC-recommended immunizations.43
Data Sources: A PubMed search was completed using combinations of the key terms lymphoma, non-Hodgkin, Hodgkin, presentation, diagnosis, staging, treatment, and follow up. The search included meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, and reviews. Search dates: April 18, May 17, and May 31, 2018, and August 30, 2019. We also searched the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality evidence reports, UpToDate, the Cochrane database, Essential Evidence Plus, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, and the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. Search dates: April 18, 2018, and August 30, 2019.
Research reported in this article was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under award number 5U54GM104942-03. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.