
Am Fam Physician. 2023;107(2):202-203
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Key Points for Practice
• In patients with suspected acute left-sided colonic diverticulitis, abdominal contrast CT has high sensitivity and specificity and is recommended if there is diagnostic uncertainty.
• Uncomplicated diverticulitis in patients with no risk factors for complicated diverticulitis can be managed in the outpatient setting with medical supervision if they can drink fluids, have social support, and wish to avoid admission.
• In patients with uncomplicated diverticulitis and no risk factors for complicated diverticulitis, antibiotic treatment does not affect quality of life or reduce related complications or need for surgery, although it may slightly decrease the likelihood of ongoing diverticulitis.
From the AFP Editors
Acute colonic diverticulitis is the inflammation of abnormal colonic outpouchings and is most common in the left colon in Western countries. An estimated one out of 10 cases of diverticulosis develops into acute diverticulitis and one in eight cases develops into acute diverticulitis complicated by abscess, phlegmon, fistula, obstruction, bleeding, or perforation. There are approximately 200,000 hospitalizations per year for acute diverticulitis in the United States. The American College of Physicians (ACP) performed a systematic review to determine the most effective diagnosis and management options for acute left-sided colonic diverticulitis.
Diagnostic Imaging
Abdominal computed tomography (CT) with oral, intravenous, or rectal contrast is the most effective imaging modality (94% sensitivity and 99% specificity) for suspected diverticulitis. There may be a benefit to CT evaluation over clinical diagnosis alone to improve management, and abdominal CT is recommended if there is diagnostic uncertainty for suspected acute left-sided colonic diverticulitis. CT imaging is particularly useful if there are risk factors for progression to complicated diverticulitis, which is defined as signs of perforation, bleeding, obstruction, or abscess. When CT is not available, abdominal ultrasonography may be considered. Studies suggest that diverticulitis that is missed on CT rarely causes clinical harm.
Harms associated with CT include incidental findings, radiation exposure, and adverse effects of contrast. Up to 9% of adults who undergo CT for suspected diverticulitis have incidental findings requiring further workup. The clinical effect of these harms is unclear.
Need for Hospitalization
For patients with uncomplicated diverticulitis who can drink fluids, want to avoid admission, and have social support, there is no evidence that hospitalization improves the outcomes of future elective surgery or risk of recurrence. The impact of hospitalization on treatment failure, quality of life, and mortality is unknown. Most patients with uncomplicated disease may be managed in an outpatient setting. Outpatient management has not been evaluated for patients with complicated diverticulitis or who have risk factors for complicated diverticulitis (Table 1).

| Computed tomography findings of pericolic extraluminal air, fluid collection, or longer inflamed colon segment |
| C-reactive protein level greater than 14 mg per dL (140 mg per L) |
| Immunosuppression |
| Recent or current antibiotic use |
| Signs of sepsis or systemic inflammatory response syndrome |
| Symptoms for more than five days |
| Systemic or unstable comorbidity |
| Vomiting |
Antibiotics
For patients with uncomplicated diverticulitis, the ACP recommends a trial of supportive care that includes bowel rest and hydration. In these patients, complication rates, quality of life, need for surgery, length of hospital stay, and long-term recurrence are similar whether antibiotics are given or not. Antibiotics may slightly decrease the likelihood of ongoing diverticulitis or short-term recurrence.
Patients with complicated diverticulitis or risk factors for complicated diverticulitis should receive antibiotics. The best antibiotic regimen for diverticulitis is unknown.
Uncertainties
Most studies were performed in the emergency department and not in a primary care setting. No studies compare the additional value of CT in refining a clinical diagnosis of diverticulitis. The accuracy of CT to diagnose colorectal cancer in patients suspected to have diverticulitis is not known.
The harms of antibiotic therapy, including nosocomial infection, Clostridioides difficile infection, and antibiotic resistance, were not reported in the available studies.
In complicated diverticulitis, the benefit of percutaneous drainage is uncertain. The few observational studies had uncertain outcomes and did not report procedural adverse events.
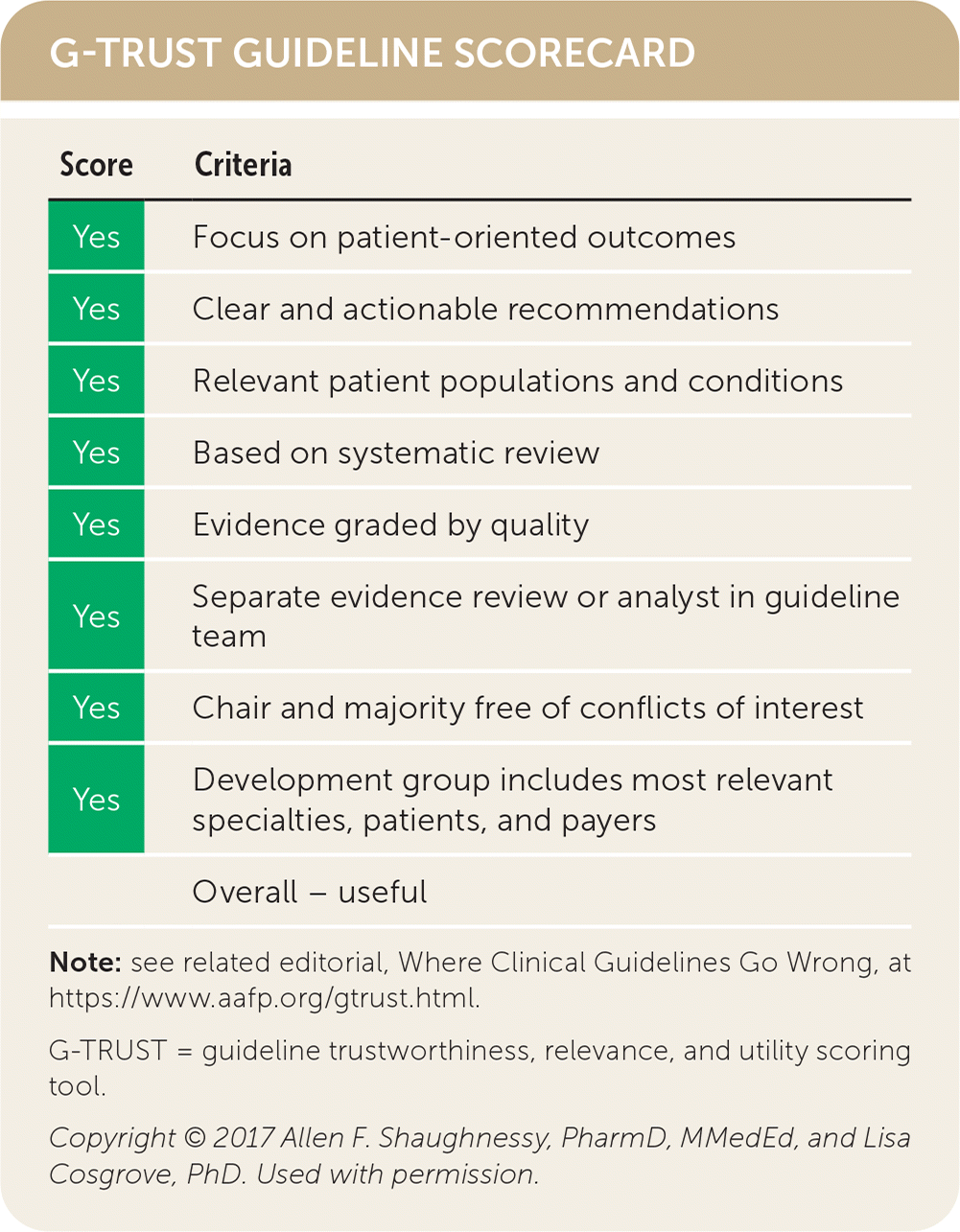
| Score | Criteria |
|---|---|
| Yes | Focus on patient-oriented outcomes |
| Yes | Clear and actionable recommendations |
| Yes | Relevant patient populations and conditions |
| Yes | Based on systematic review |
| Yes | Evidence graded by quality |
| Yes | Separate evidence review or analyst in guideline team |
| Yes | Chair and majority free of conflicts of interest |
| Yes | Development group includes most relevant specialties, patients, and payers |
| Overall – useful |
Guideline source: American College of Physicians
Published source: Ann Intern Med. March 2022;175(3):399–415
Available at: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/m21-2710
The views expressed are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the U.S. Department of the Navy, U.S. Department of the Air Force, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, U.S. Department of Defense, or the U.S. government.
Editor's Note: Although the evidence is somewhat limited, it is important to know that uncomplicated diverticulitis without risk factors is simple to treat. Imaging is not required if the clinical diagnosis is certain. Outpatient treatment without antibiotics has similar outcomes as admission or prescribing antibiotics.—Michael J. Arnold, MD, Contributing Editor
