
Am Fam Physician. 2024;110(2):online
As published by the USPSTF.
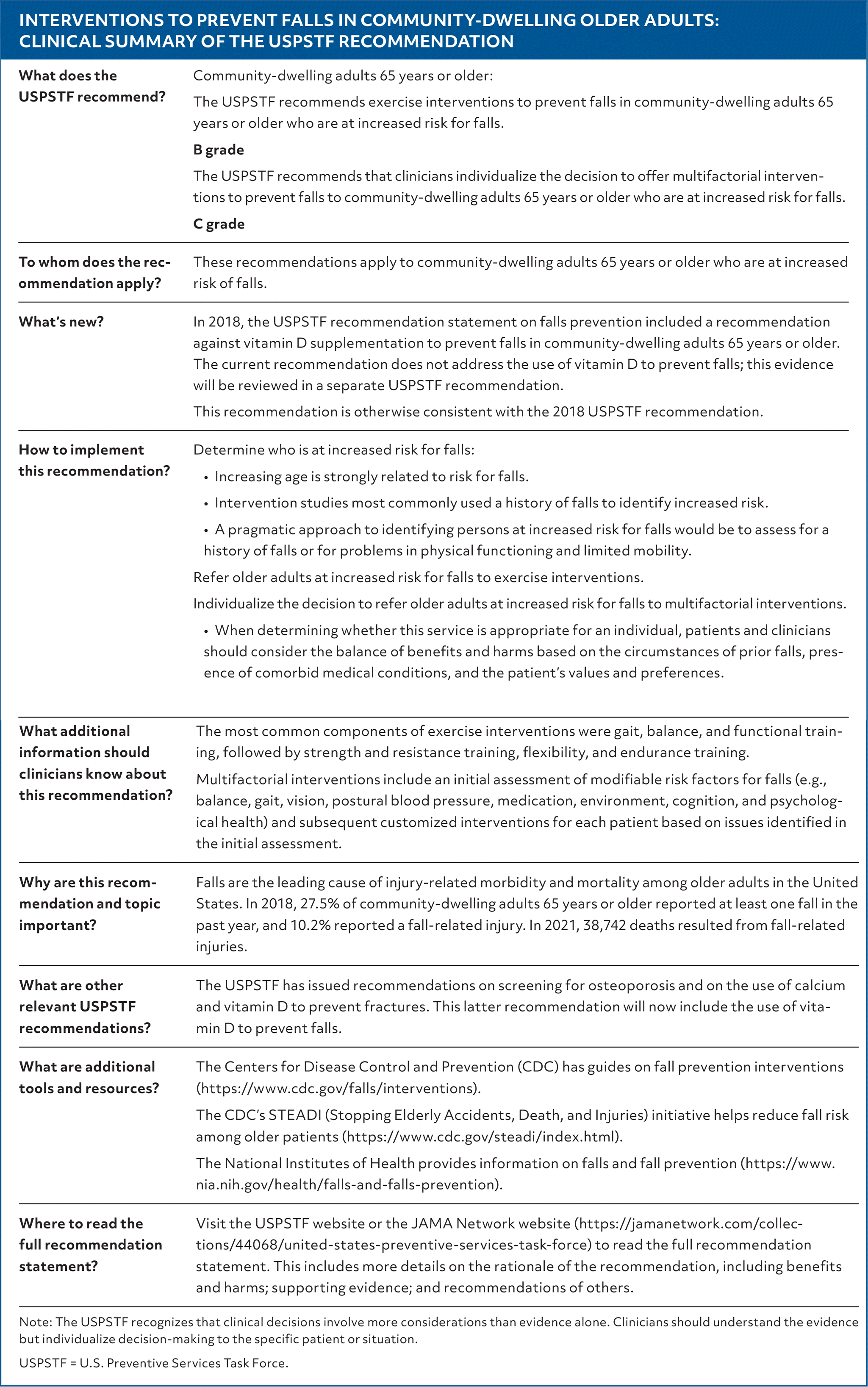
| What does the USPSTF recommend? | Community-dwelling adults 65 years or older: The USPSTF recommends exercise interventions to prevent falls in community-dwelling adults 65 years or older who are at increased risk for falls. B grade The USPSTF recommends that clinicians individualize the decision to offer multifactorial interventions to prevent falls to community-dwelling adults 65 years or older who are at increased risk for falls. C grade |
| To whom does the recommendation apply? | These recommendations apply to community-dwelling adults 65 years or older who are at increased risk of falls. |
| What’s new? | In 2018, the USPSTF recommendation statement on falls prevention included a recommendation against vitamin D supplementation to prevent falls in community-dwelling adults 65 years or older. The current recommendation does not address the use of vitamin D to prevent falls; this evidence will be reviewed in a separate USPSTF recommendation. This recommendation is otherwise consistent with the 2018 USPSTF recommendation. |
| How to implement this recommendation? | Determine who is at increased risk for falls:
Refer older adults at increased risk for falls to exercise interventions. Individualize the decision to refer older adults at increased risk for falls to multifactorial interventions.
|
| What additional information should clinicians know about this recommendation? | The most common components of exercise interventions were gait, balance, and functional training, followed by strength and resistance training, flexibility, and endurance training. Multifactorial interventions include an initial assessment of modifiable risk factors for falls (e.g., balance, gait, vision, postural blood pressure, medication, environment, cognition, and psychological health) and subsequent customized interventions for each patient based on issues identified in the initial assessment. |
| Why are this recommendation and topic important? | Falls are the leading cause of injury-related morbidity and mortality among older adults in the United States. In 2018, 27.5% of community-dwelling adults 65 years or older reported at least one fall in the past year, and 10.2% reported a fall-related injury. In 2021, 38,742 deaths resulted from fall-related injuries. |
| What are other relevant USPSTF recommendations? | The USPSTF has issued recommendations on screening for osteoporosis and on the use of calcium and vitamin D to prevent fractures. This latter recommendation will now include the use of vitamin D to prevent falls. |
| What are additional tools and resources? | The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has guides on fall prevention interventions (https://www.cdc.gov/falls/interventions). The CDC’s STEADI (Stopping Elderly Accidents, Death, and Injuries) initiative helps reduce fall risk among older patients (https://www.cdc.gov/steadi/index.html). The National Institutes of Health provides information on falls and fall prevention (https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/falls-and-falls-prevention). |
| Where to read the full recommendation statement? | Visit the USPSTF website or the JAMA Network website (https://jamanetwork.com/collections/44068/united-states-preventive-services-task-force) to read the full recommendation statement. This includes more details on the rationale of the recommendation, including benefits and harms; supporting evidence; and recommendations of others. |
The full recommendation statement is available at https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/falls-prevention-community-dwelling-older-adults-interventions. The USPSTF recommendations are independent of the U.S. government. They do not represent the views of the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, or the U.S. Public Health Service.
