
Am Fam Physician. 2023;107(5):490-498
Related Letter to the Editor: Guidelines for Performing Disability Evaluations
Related FPM article: FMLA Does Not Need to Be a Four-Letter Word
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Disability is a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits at least one major life activity. Family physicians are often asked to assess patients with disabling conditions that can impact insurance benefits, employment, and ability to access needed accommodations. Disability evaluations are needed for short-term work restrictions following a simple injury or illness and for more complex cases involving Social Security Disability Insurance, Supplemental Security Income, Family and Medical Leave Act, workers' compensation, and personal/private disability insurance claims. Using a stepwise approach built on awareness of the biologic, psychological, and social elements of disability assessment may facilitate this evaluation. Step 1 establishes the role of the physician in the disability evaluation process and the context of the request. In Step 2, the physician assesses impairments and establishes a diagnosis based on findings from an examination and validated diagnostic tools. In Step 3, the physician identifies specific participation restrictions by assessing the patient's ability to perform specific movements or activities and reviewing the employment environment and tasks. Steps 4 and 5 ensure proper documentation, billing, and coding. In complex cases, consultants such as psychiatrists and physical therapists may assist by providing insight into a patient's mental and physical impairments, activity limitations, and response to treatment.
Disability is a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits at least one major life activity. More than 1 billion people, about 15% of the global population, live with some form of disability.1 In the United States, 1 in 4 noninstitutionalized adults reports having at least one disability.2 Disabling conditions can limit a person's ability to work, participate fully in social roles, maintain a household, and pursue hobbies. Disability can lead to substantial personal, physical, social, emotional, and economic hardships for the patient, caregiver, and family.3–5
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| When possible, validated clinical tools (Table 3) should be used to estimate outcomes related to return to work.27,29–41 | C | Low-quality studies that reported reliability and validity rather than health outcomes |
| Physicians should not rely on Waddell signs to differentiate organic causes of pain from malingering (i.e., nonorganic causes).47,48 | B | Systematic review of low-quality studies showing that Waddell signs correlate with poor surgical outcomes but do not discriminate the source of pain |
| The consultative examination report should enable an independent reviewer to understand the patient's impairment and ability to perform basic work-related functions. Conclusions should be consistent with the objective findings on the examination and the patient's history, symptoms, laboratory test results, and response to treatment.21 | C | Expert opinion in the absence of clinical trials |
The number of people with a disability is increasing because the population is aging and noncommunicable diseases are becoming more prevalent.6 In addition, the full effect of post–COVID-19 condition (long COVID) remains uncertain and may increase rates of disability.7 Women are somewhat more likely to have a disability than men, in part because of their longer life expectancy.8 The highest prevalence of disability is reported in non-Hispanic Black and Native American/Alaska Native populations.2 These rates may be influenced by perception of disability by culture; stigma of self-report; and racial or ethnic disparities related to smoking, income, and education.9 Arthritis, back or spinal problems, and heart conditions are the most common causes of self-reported disability.10
Disability is more than impairment. Disability is categorized by three dimensions: impairment, activity limitation, and participation restriction. An impairment is a problem in structure or function, such as loss of range of motion in the wrist or hemiplegia. An activity limitation is difficulty in executing a task or action, such as the inability to hold a hammer or get out of bed. A participation restriction is a life situation in which the person can no longer fully participate, such as the inability to carry out work duties or live independently.13,14
Skillful assessment of a patient's disability is critical because of the impact on insurance benefits, employment, and ability to access needed accommodations. The definition and classification of disability can differ among medical personnel, insurers, legal statutes, and employers.
What Are the Most Common Disability Evaluations?
Disability evaluations are most commonly performed for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), Supplemental Security Income (SSI), Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) eligibility, workers' compensation, and personal/private disability insurance claims. These programs routinely require millions of evaluations per year.15 Although all types of disability evaluations decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic, they are now rebounding.16
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
The SSDI and SSI programs are managed by the U.S. Social Security Administration and are offered to individuals who have a disability and meet the medical criteria for each program.17 The FMLA mandates all employers with 50 or more employees to provide up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave within a 52-week period to eligible employees.18 Workers' compensation programs are regulated by individual states and provide benefits to employees with work-related injuries and diseases (e.g., preexisting conditions such as asthma and osteoarthritis that may be clearly aggravated by the work environment or duties).19,20 Personal disability insurance can be purchased by the employer or employee. In contrast to workers' compensation benefits, patients may be eligible for income benefits from personal disability insurance for injuries and illnesses that did not occur at work. Table 1 compares disability benefits programs.15–20
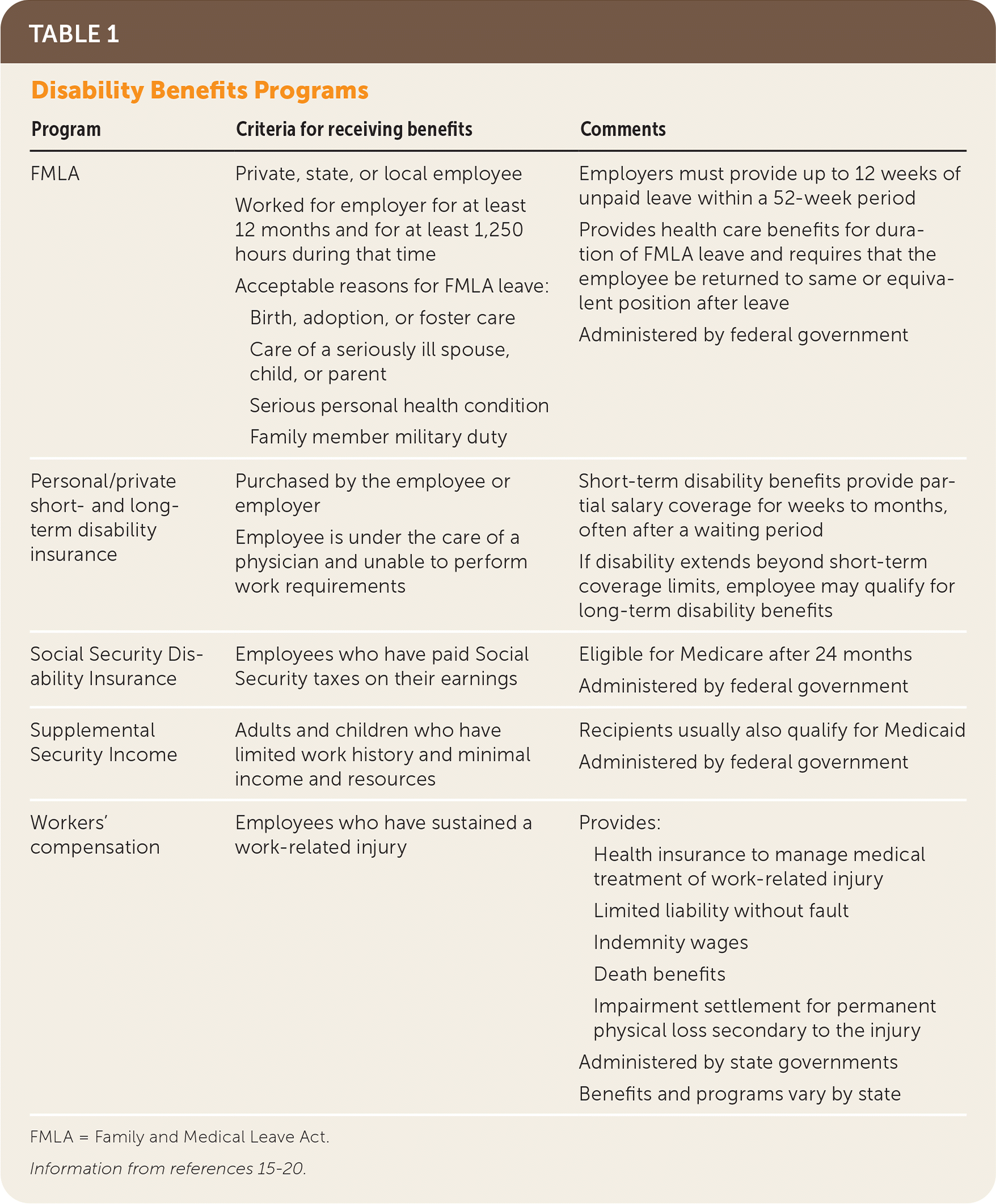
| Program | Criteria for receiving benefits | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| FMLA | Private, state, or local employee Worked for employer for at least 12 months and for at least 1,250 hours during that time Acceptable reasons for FMLA leave: Birth, adoption, or foster care Care of a seriously ill spouse, child, or parent Serious personal health condition Family member military duty | Employers must provide up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave within a 52-week period Provides health care benefits for duration of FMLA leave and requires that the employee be returned to same or equivalent position after leave Administered by federal government |
| Personal/private short- and long-term disability insurance | Purchased by the employee or employer Employee is under the care of a physician and unable to perform work requirements | Short-term disability benefits provide partial salary coverage for weeks to months, often after a waiting period If disability extends beyond short-term coverage limits, employee may qualify for long-term disability benefits |
| Social Security Disability Insurance | Employees who have paid Social Security taxes on their earnings | Eligible for Medicare after 24 months Administered by federal government |
| Supplemental Security Income | Adults and children who have limited work history and minimal income and resources | Recipients usually also qualify for Medicaid Administered by federal government |
| Workers' compensation | Employees who have sustained a work-related injury | Provides: Health insurance to manage medical treatment of work-related injury Limited liability without fault Indemnity wages Death benefits Impairment settlement for permanent physical loss secondary to the injury Administered by state governments Benefits and programs vary by state |
What Certifications Are Required to Perform Disability Evaluations?
Medical licensure is sufficient for most disability evaluations such as FMLA, personal short-term disability claims, and workers' compensation. SSDI and SSI evaluations may require further training.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
SSDI and SSI evaluations require an understanding of their unique disability determination processes, Listing of Impairments, and billing and documentation requirements.21 The evaluation for SSDI and SSI claims can be performed by the treating physician or another clinician, such as an optometrist or psychologist. If the treating physician is not comfortable with the SSDI or SSI process, an independent examiner can also perform the consultative examination. Physicians interested in being certified as independent examiners can get more information from their state Disability Bureau or Disability Determination Service. Table 2 lists resources for disability evaluations, including education and optional certifications related to consultative examinations.
| Evaluation | Resources |
|---|---|
| Developmental disability | Bélanger SA, Caron J. Evaluation of the child with global developmental delay and intellectual disability. Paediatr Child Health. 2018;23(6):403–419. Hyman SL, Levy SE, Myers SM; Council on Children With Disabilities, Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics. Identification, evaluation, and management of children with autism spectrum disorder. Pediatrics. 2020;145(1):e20193447. |
| Independent medical examiner certification for Social Security benefits and automobile casualty, personal injury, or other legal settings | American Board of Independent Medical Examiners https://www.abime.org/ https://www.abime.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/CIME.pdf American Medical Association AMA Guides to the Evaluation of Permanent Impairment, 6th ed. CME sponsored by the American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine or International Academy of Independent Medical Evaluators https://acoem.org/Learning https://iaime.org |
| Psychiatric disability, dementia, neuropsychiatric evaluation | Consultation with psychiatrists, psychologists Allen ND, Couser GP, Bostwick JM. Disability evaluation and treatment for patients with psychiatric disorders. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(8):1766–1774. Falk N, Cole A, Meredith TJ. Evaluation of suspected dementia. Am Fam Physician. 2018;97(6):398–405. Schroeder RW, Martin PK, Walling A. Neuropsychological evaluations in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(2):101–108. |
| Temporary disability, return to work, workers' compensation, Family Medical Leave Act | Kantner AC. FMLA does not need to be a four-letter word. Fam Pract Manag. 2021;28(4):12–16. Nordling P, Priebe G, Björkelund C, et al. Assessing work capacity - reviewing the what and how of physicians' clinical practice. BMC Fam Pract. 2020;21(1):72. |
| U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs | Code of Federal Regulations: schedule for rating disabilities https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-38/chapter-I/part-4 Veterans compensation and pension examination https://www.benefits.va.gov/COMPENSATION/claimexam.asp Veterans disability and compensation https://www.va.gov/disability |
| U.S. Social Security Administration | Disability evaluation under social security https://www.ssa.gov/disability/professionals/bluebook |
What Is the Best Approach to the Disability Evaluation?
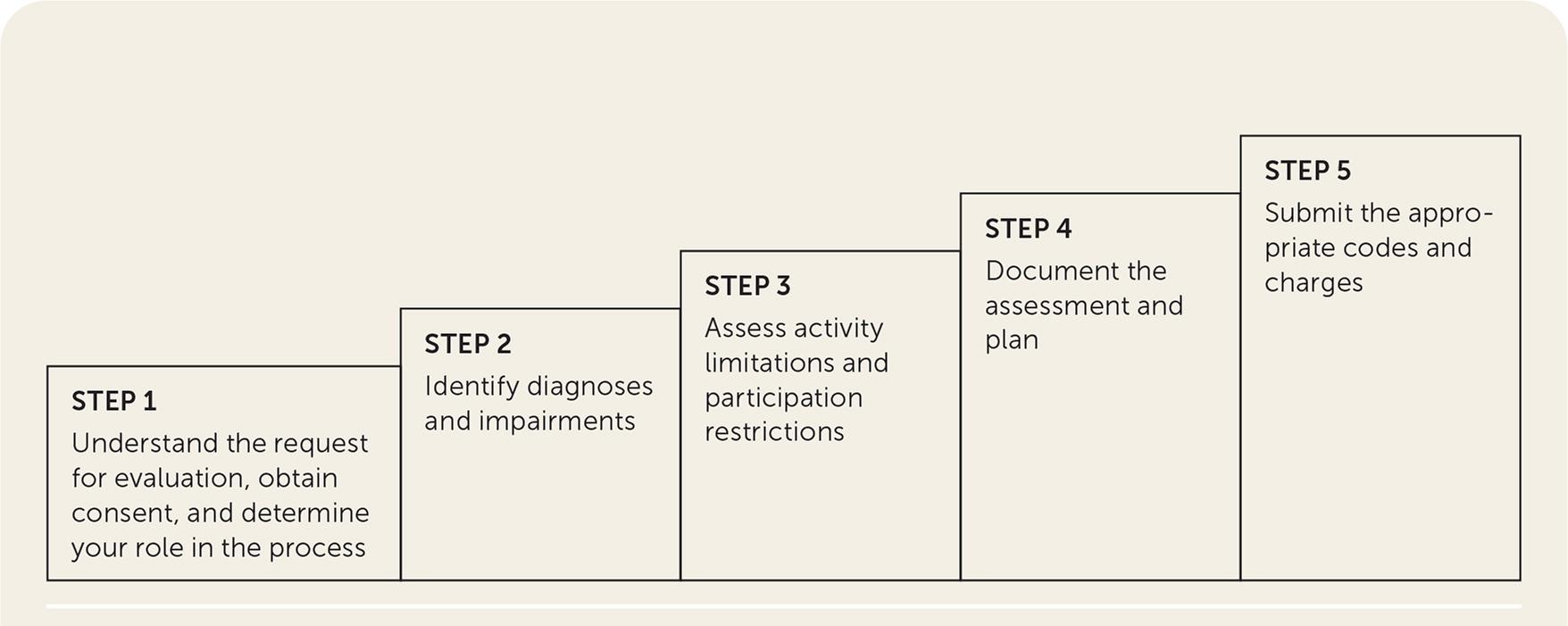
A stepwise approach is recommended to ensure a thorough evaluation that addresses the questions asked by the referring party and does not limit disability benefits for the patient (Figure 1). The World Health Organization's International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health model uses a comprehensive checklist that includes qualifiers regarding the nature of impairments and changes to body functions and structures, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. 22 These three dimensions of disability are further characterized by environmental and social barriers and supports. 14
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
The following approach incorporates the biologic, psychological, and social elements from the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health model in addition to common, practical requirements of disability evaluation in the United States.
Step 1. Understand the Request for Evaluation, Obtain Consent, and Determine Your Role. Evaluation for impairment and disability may be requested in the contexts of legal proceedings or employment, insurance claims, and entitlement programs. The physician should identify the third party making the request, understand the issues to be addressed, and determine the physician's role in the process. Roles can include treating physician, new consultant, or independent medical examiner.18,22 For example, an FMLA evaluation requires an assessment of the patient's temporary inability to perform job duties due to illness or need for time away from work to care for an ill family member. An evaluation to activate a health care power of attorney may require two clinicians and involve a detailed assessment of capacity, including memory and decision-making. When evaluating a patient's impairment under a specific benefits system, the physician must use the appropriate guidelines for that system. Some evaluations, such as those for SSDI, may require specialized training or certification.
Patient consent should be obtained before releasing information to any involved third party, and fees for the evaluation service should be agreed on in advance. If there is uncertainty about whether a third party has a right to view the disability report, obtaining advice from legal counsel should be considered to ensure compliance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) regulations.23
Step 2. Identify Diagnoses and Impairments. After identifying a diagnosis, the physician should determine the extent of mental and physical impairments. Some diagnoses, such as a femur fracture, have clear objective findings to guide a treatment plan, whereas other diagnoses, such as depression, require more clinical judgment based on the patient's self-reported symptoms.
Patient-reported outcome tools provide a standardized assessment of a patient's function or perception of their health, quality of life, mental well-being, or health care experience.24 Patient-reported outcomes and other validated measures for evaluating disability (Table 325–41) can be selected based on the diagnosis and contribute to a multidimensional assessment of disability by complementing standard clinical decision-making and fostering communication.24,42 More research is needed to establish the best way to incorporate patient-reported outcomes in the assessment and treatment of disabling conditions.24,27,41,43,44
| Tool | Comments |
|---|---|
| Psychosocial impact | |
| Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire25 | Assesses fear-avoidance beliefs about physical activity that contribute to back pain and disability https://www.sralab.org/rehabilitation-measures/fear-avoidance-beliefs-questionnaire |
| Patient Health Questionnaire-9 26 | Used to diagnose depression and grade severity of symptoms https://www.mdcalc.com/calc/1725/phq9-patient-health-questionnaire9 |
| Patient-reported outcome measures | |
| Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand27 | Measures severity of symptoms and ability to complete tasks using the upper extremities https://dash.iwh.on.ca/about-dash |
| Health and Work Questionnaire28 | Assesses workplace productivity in relation to worker health https://tobaccocontrol.bmj.com/content/suppl/2001/09/13/10.3.233.DC1/halpern.pdf |
| Medical Outcomes Study 36-item short-form survey29 | Measures quality of life https://www.rand.org/health-care/surveys_tools/mos/36-item-short-form/survey-instrument.html |
| Neck Disability Index30 | Measures how neck pain affects ADL https://www.smcnd.org/assets/docs/pt/neck_disability_index.pdf |
| Örebro Musculoskeletal Pain Questionnaire31,32 | Predicts long-term disability and work absenteeism in adults with acute and chronic musculoskeletal pain following injury https://aci.health.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0004/212908/Orebro_musculoskeletal_pain_questionnaire_Final.pdf |
| Oswestry Disability Index33,34 | Measures permanent functional disability in ADL due to low back pain https://www.aaos.org/globalassets/quality-and-practice-resources/patient-reported-outcome-measures/spine/oswestry-2.pdf |
| Pain Disability Index35 | Measures disruptions to ADL due to chronic pain https://www.med.umich.edu/1info/FHP/practiceguides/pain/detpdi.pdf |
| Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System36 | Evaluates and monitors physical, mental, and social health https://www.healthmeasures.net/index.php |
| Patient-Specific Functional Scale37 | Quantifies activity limitations and measures functional outcomes for patients with orthopedic conditions https://www.sralab.org/sites/default/files/2017-06/Patient-specific.pdf |
| Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire38 | Measures disability related to low back pain https://www.rmdq.org |
| Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia39 | Evaluates fear of movement or physical activity and fear-related avoidance in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain https://novopsych.com.au/assessments/health/tampa-scale-of-kinesiophobia-tsk |
| Work Ability Index40 | Assesses work ability https://workbox.chrodis.eu/repository/pdf/WAI_Work-Ability-Index.pdf |
| Activity limitations, participation restrictions | |
| Functional capacity evaluation41 | Evaluates functional capacity in relation to job demands https://www.physio-pedia.com/Functional_Capacity_Evaluation |
Step 3. Assess Activity Limitations and Participation Restrictions. The patient's work environment and tasks need to be considered to fully evaluate the level of disability. Employers can provide job descriptions to help the physician understand the patient's job requirements. The collected information related to the medical diagnoses and impairments are used to determine the impact on the patient's ability to perform specific movements or activities, considering both mental and physical functional abilities. For example, two patients with the same knee activity limitation may have different participation restrictions because one works at a computer, whereas the other regularly lifts 50 lb.
Participation restrictions should be consistent and credible. For example, a patient cannot reasonably have a restriction to sit for no more than 10 minutes but not have driving restrictions.
Cases in which there are limited objective measures of impairment or the patient is involved in litigation or has a prolonged period of healing may prompt concern about malingering.45 Malingering is “the intentional production of false or grossly exaggerated physical or psychological symptoms motivated by external incentives.” 46 No clinical tools, including the Waddell signs suggested for low back pain, are reliable or valid for the identification of malingering.45,47,48 A thorough, objective, and systematic evaluation identifying behaviors consistent with patient report is the most effective way to support the diagnosis and the assessment of activity and participation.
Step 4. Document the Assessment and Plan. Accurate and timely documentation is a critical component of the disability evaluation. If possible, the assessment and plan should be documented using fillable forms or phrases built into the electronic health record (EHR). Some EHRs allow the physician to track restrictions over time and monitor patients' progress toward goals. Clinical decision tools may also be embedded in the EHR software.49 Third parties often provide paper forms that should be scanned into the EHR for future reference and reevaluations. Completing these forms with clarity and sufficient detail will reduce follow-up requests and avoid a delay in patients receiving benefits.50
When evaluations result in work restrictions, follow-up visits should be scheduled to reassess impairments and ensure that the patient is safe to return to restricted or full job duties.
The consultative examination report should enable an independent reviewer to understand the patient's impairment and ability to perform basic work-related functions. Conclusions in the report should be consistent with the objective findings on examination and the patient's history, symptoms, laboratory test results, and response to treatment. Reports should not include the physician's opinion about the veracity of the patient's claim of disability.21
Depending on the third party requesting the disability evaluation, there may be a request for assessment of the permanency of disability, causality, or apportionment. Decisions about permanency should be delayed until the patient has fully participated in a rehabilitation program. Causality in the context of disability means that the patient's job duties or environment caused the disabling condition. Apportionment is an estimate of how much of a permanent disability was caused by a patient's work duties vs. causes unrelated to work. Causality and apportionment have specific legal implications that are described in the AMA Guides to the Evaluation of Permanent Impairment, 6th ed.51 Determining causality and apportionment can be simple (e.g., acute on-the-job trauma) or challenging because of multifactorial origins (e.g., poor endurance due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease that could be the result of both tobacco use and occupational toxin exposure).44,52
Step 5. Submit the Appropriate Codes and Charges. A patient who comes to a health facility for services unrelated to occupational medicine may have a personal or employer-provided health insurance on file. A patient's personal health insurance carrier should not be billed for third-party assessments and care, such as workers' compensation claims. However, when services related to a workers' compensation claim and treatment of other medical conditions are provided during the same visit, separately documented encounters will be needed to bill appropriately.53 Time-based coding can be used to capture time spent evaluating disability, filling out forms, and communicating with other care team members as long as these services are completed on the day the patient is seen.54
How Can Other Medical Professionals Assist in a Disability Evaluation?
The disability evaluation often requires a team approach. Other clinicians such as psychiatrists, psychologists, physical therapists, and occupational therapists have expertise in evaluating complex cases and implementing rehabilitation programs.
EVIDENCE SUMMARY
For complex mental health concerns, psychiatrists or psychologists may have more expertise or time available to implement tools to measure the psychosocial construct of impairments and activity limitations. Physical and occupational therapists can play a similar role with complex physical concerns, providing insight into the patient's impairments, activity limitations, and response to treatment. For example, physical and occupational therapists can perform patient-report outcome assessments such as the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand tool or the Functional Capacity Evaluation, which may take several hours to administer.27,43 Access to these consultations may be affected by limits in insurance coverage.
This article updates previous articles on this topic by Maness and Khan44; Taiwo and Cantley52; and Barron.55
Data Sources: The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.S. Department of Labor, and World Health Organization were searched using the key words disability evaluation, disability prevalence, and patient reported outcomes. Original research and clinical practice guidelines were identified using PubMed when searching for validated tools for impairment and disability evaluation. Race, gender, and ethnicity were specifically searched when attempting to assess the scope of disability throughout the world and in the United States. Search dates: June 1, 2022, through March 10, 2023.
